Anemo: The Root of Wind in Language and Science
Explore the fascinating word root "anemo," derived from the Greek word anemos, meaning "wind." This root serves as the basis for terms used in meteorology, botany, and more. From devices that measure wind speed to the wonders of wind-pollination, "anemo" highlights the intricate connection between language and natural phenomena.
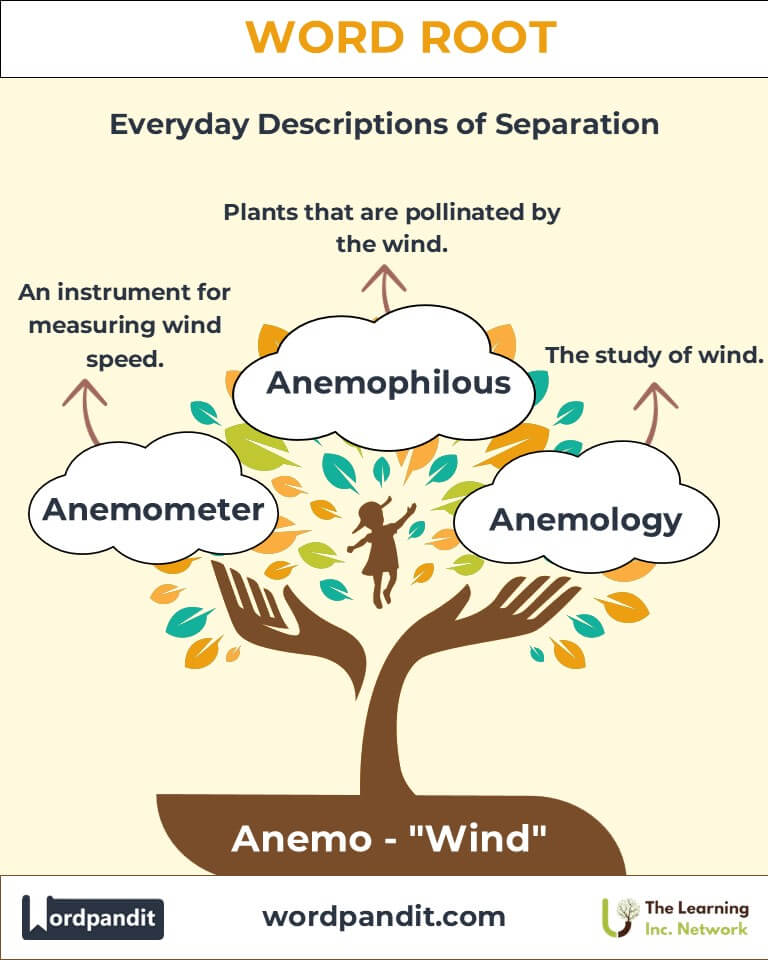
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Power of "Anemo"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Remembering "Anemo"
- Common "Anemo"-Related Terms
- "Anemo" Through Time
- "Anemo" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Anemo" in Action
- Cultural Significance of "Anemo"
- The "Anemo" Family Tree
- FAQs about the "Anemo" Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Anemo" Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Anemo"
Introduction: The Power of "Anemo"
Imagine the force of the wind—gentle breezes, fierce gales, and everything in between. This elemental power is encapsulated in the root "anemo," pronounced uh-NEE-mo. Originating from Greek, anemos has influenced a variety of terms that connect us to the natural world. From scientific instruments like the anemometer to ecological concepts like anemophily, "anemo" continues to play a vital role in both language and science.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The word root "anemo" comes from the Greek anemos, which simply means "wind." This term was central to ancient Greek culture, where the wind was often personified in mythology, such as Boreas (the North Wind) and Zephyrus (the West Wind). As science evolved, "anemo" became integrated into specialized terminology, particularly in meteorology and botany.
Mnemonic: Remembering "Anemo"
Picture a weather vane spinning wildly atop a rooftop during a windy day. To solidify the association, think:
Mnemonic Device: “Anemo animates the air, measuring and moving with the wind.”
Common "Anemo"-Related Terms
- Anemometer (uh-NEE-muh-ter)
- Definition: A device used to measure wind speed.
- Example: "The meteorologist used the anemometer to track wind gusts before the storm."
- Anemophily (uh-NEE-muh-fil-ee)
- Definition: The process of wind-pollination, common in certain plants like grasses.
- Example: "Anemophily ensures the wide dispersal of pollen in open fields."
- Anemology (uh-NEE-muh-loh-jee)
- Definition: The study of wind patterns and their effects on the environment.
- Example: "Advances in anemology have improved weather prediction models."
- Anemotropism (uh-NEE-muh-troh-piz-um)
- Definition: A plant's growth response to wind direction.
- Example: "Trees on windy coasts often display anemotropism, leaning away from strong gales."
- Anemoclastic (uh-NEE-muh-klas-tik)
- Definition: Referring to rocks or sediment shaped by wind erosion.
- Example: "The desert landscape was marked by anemoclastic formations."
"Anemo" Through Time
- Ancient Greece: Winds were considered divine forces, influencing navigation and agriculture.
- Renaissance Science: The invention of the anemometer by Italian scientist Leon Battista Alberti in the 15th century revolutionized wind measurement.
- Modern Meteorology: Terms like "anemology" and "anemograph" have become essential in weather forecasting.
"Anemo" in Specialized Fields
- Meteorology:
- Anemometer: Measures wind speed for weather predictions and climate studies.
- Anemograph: Records wind direction and speed over time.
- Botany:
- Anemophily: Crucial for plants like corn and wheat, which rely on the wind for pollination.
- Geology:
- Anemoclastic: Describes landforms shaped by wind, emphasizing the erosive power of air currents.
Illustrative Story: "Anemo" in Action
Maya, a young meteorologist, was tasked with tracking the movements of a severe storm. Armed with an anemometer, she recorded wind speeds exceeding 100 mph. Meanwhile, in a nearby field, an ecologist observed how the wind-pollinated grasses thrived despite the gusts. Both professionals marveled at the unseen force shaping their worlds—a true testament to the power of "anemo."
Cultural Significance of "Anemo"
The wind has always held a mystical allure, inspiring myths and idioms across cultures. In Greek mythology, the Anemoi (wind gods) were believed to govern the seasons. Even today, phrases like "winds of change" reflect wind's symbolic representation of transformation and power.

The "Anemo" Family Tree
- Aero (air)
- Aerodynamics: The study of how air moves around objects.
- Vent (wind)
- Ventilation: The movement of air to maintain airflow in spaces.
- Pneuma (breath, air)
- Pneumatics: The use of pressurized air to perform mechanical work.
FAQs About " Anemo "
Q: What does the root "anemo" mean?
A: The root "anemo" originates from the Greek word anemos, meaning "wind." It appears in terms related to air movement and its effects, particularly in scientific disciplines like meteorology and botany.
Q: What is an anemometer, and how does it work?
A: An anemometer is an instrument used to measure wind speed and sometimes its direction. It often has rotating cups or vanes that spin faster as wind speeds increase, allowing for precise measurements. It’s crucial for weather forecasting and studying wind energy.
Q: What is anemophily, and why is it important?
A: Anemophily refers to wind-pollination, where plants rely on the wind to carry pollen. This is a key adaptation in plants like grasses, pines, and some crops, ensuring pollination without animal pollinators. It highlights nature's efficiency in diverse ecosystems.
Q: How is "anemo" used in meteorology?
A: Meteorology, the study of atmospheric phenomena, frequently uses "anemo"-based terms. Instruments like anemometers measure wind speed, while anemology is the study of wind patterns, which helps predict weather and climate events.
Q: What are anemoclastic rocks, and how are they formed?
A: Anemoclastic rocks are formed through wind erosion and weathering. Strong winds carry sand and debris, which erode rock surfaces over time, sculpting unique formations found in deserts and windy coastal areas.
Q: What role does "anemo" play in botany?
A: In botany, "anemo" is central to terms like anemophily (wind-pollination) and anemotropism (a plant's growth response to wind). These concepts show how plants adapt to their environments, ensuring survival and reproduction.
Q: Are there any cultural or mythological associations with "anemo"?
A: Yes, in Greek mythology, the Anemoi were wind gods representing cardinal directions (e.g., Boreas for the North Wind). Their actions were believed to influence weather and seasons, reflecting humanity’s early fascination with wind.
Test Your Knowledge: " Anemo " Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "anemo" mean?
2. What does an anemometer measure?
3. What is anemophily?
4. Which term refers to rocks or landforms shaped by wind?
5. What is anemology?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Anemo"
The root "anemo" captures the essence of wind's omnipresence and its profound impact on science, culture, and daily life. As a foundation for meteorological tools and ecological concepts, "anemo" reminds us of the invisible yet vital forces shaping our world. Embrace the "winds of knowledge" and explore the marvels of "anemo" in action!














