Antho: The Root of Blossoming Beauty in Language and Science
Discover the elegant significance of the word root "antho," derived from the Greek word "anthos," meaning "flower." From poetic expressions like "anthology" to scientific terms like "anthocyanin," this root connects the natural beauty of flowers to language, literature, and science.
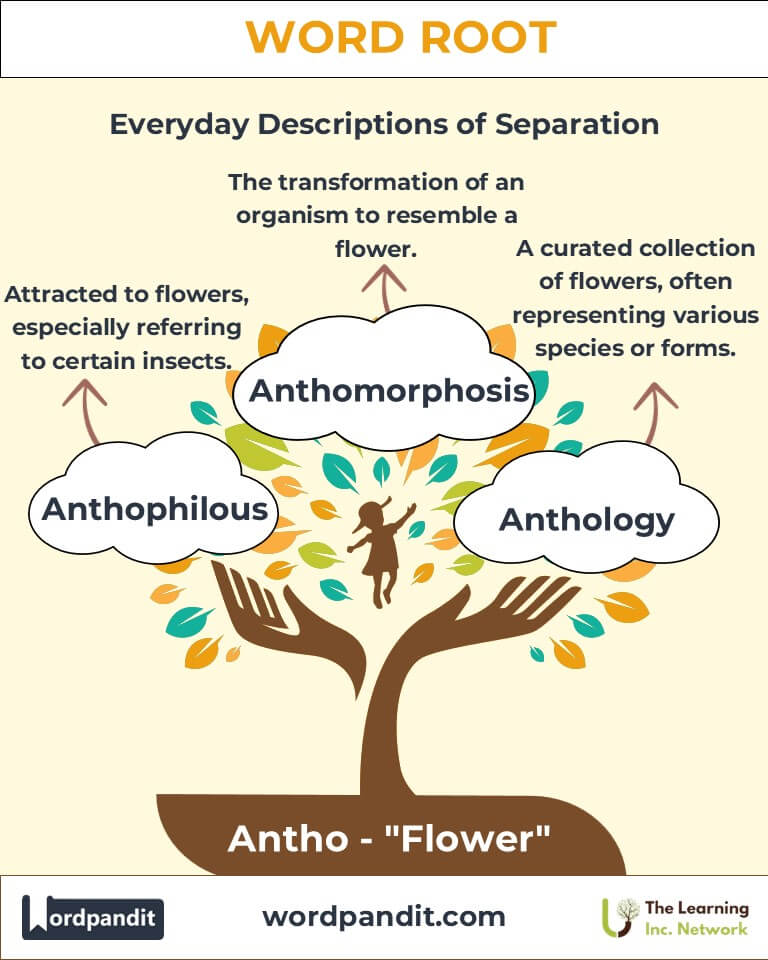
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Antho
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Antho
- Common Antho-Related Terms
- Antho Through Time
- Antho in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Antho in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Antho Root
- The Antho Family Tree
- FAQs about the Antho Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Antho Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Antho
Introduction: The Essence of Antho
Picture a vibrant meadow in full bloom, where every petal tells a story. The word root "antho" (pronounced "an-tho") embodies this vivid imagery. Derived from the Greek word "anthos," meaning "flower," this root finds its way into terms that celebrate beauty, diversity, and expression. Whether in the arts, biology, or chemistry, "antho" serves as a metaphorical bridge to the world of blossoms.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "antho" traces back to ancient Greece, where "anthos" symbolized not only literal flowers but also the flourishing of ideas and creativity. Classical texts used "anthos" to describe poetic collections, while later scientific advancements adopted the root to describe compounds, pigments, and processes related to flowers. Over time, "antho" has remained synonymous with beauty and growth in both language and science.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Antho
Imagine a flowering tree with every branch representing a word tied to the root "antho." Each bloom unfolds a new meaning, illustrating how "antho" enriches language and science alike.
Mnemonic Device: "Antho blooms into words like a flower spreading its beauty far and wide."
Common Antho-Related Terms
- Anthology (an-thol-uh-jee)
- Definition: A collection of literary or artistic works.
- Example: "The anthology of poems included works by both classical and contemporary poets."
- Anthocyanin (an-tho-sigh-uh-nin)
- Definition: A pigment responsible for the red, purple, and blue hues in flowers and plants.
- Example: "Anthocyanins in blueberries are known for their antioxidant properties."
- Anthophilous (an-tho-fi-lus)
- Definition: Attracted to or feeding on flowers.
- Example: "Bees and butterflies are anthophilous creatures vital for pollination."
- Anthozoan (an-tho-zoh-an)
- Definition: Marine invertebrates like corals and sea anemones, named for their flower-like appearance.
- Example: "The reef was teeming with anthozoans, creating a colorful underwater garden."
- Anthesis (an-thee-sis)
- Definition: The period during which a flower is fully open and functional.
- Example: "The anthesis of cherry blossoms marks the arrival of spring."
Antho Through Time
- Anthology: Originally coined to mean a collection of "flowering" ideas, it has expanded from poetry to include collections in music, essays, and art.
- Anthocyanin: Initially studied for its role in plant coloration, it now holds significance in nutrition and health research.
These shifts demonstrate how "antho" adapts to cultural and scientific developments, preserving its symbolic connection to beauty and growth.
Antho in Specialized Fields
- Botany: Anthophilous: Essential for understanding plant-pollinator relationships.
- Marine Biology: Anthozoans: Key to coral reef ecosystems and biodiversity studies.
- Biochemistry: Anthocyanins: Studied for their antioxidant properties, influencing health and food sciences.
- Literature: Anthologies: A way to preserve and celebrate cultural heritage.
Illustrative Story: Antho in Action
Lila, a budding biologist, marveled at the vibrant colors of wildflowers on a field trip. Her professor explained how anthocyanins determine flower hues, which in turn attract pollinators like bees. This sparked Lila’s curiosity, leading her to compile an "Anthology of Pollinators," combining poetry, photography, and scientific insights—a tribute to the interconnected beauty of nature.
Cultural Significance of the Antho Root
The "antho" root blooms in cultural traditions, from floral motifs in art and design to anthologies preserving literary treasures. Festivals like Japan’s Hanami, celebrating cherry blossoms, underscore the universal reverence for flowers as symbols of life’s fleeting beauty.

The Antho Family Tree
- Flor- (Latin: Flower)
- Floral: Relating to flowers.
- Florist: A person who arranges and sells flowers.
- Bloss- (Old English: Bloom)
- Blossom: A flower or bloom, often symbolic of youth.
- Botan- (Greek: Plant)
- Botany: The scientific study of plants.
FAQs About " Antho "
Q: What does "antho" mean?
A: "Antho" means "flower" and originates from the Greek word "anthos." This root is used to form words that describe the beauty, structure, or symbolism of flowers in language and science.
Q: How is "antho" used in science?
A: In science, "antho" appears in terms like "anthocyanin" (pigments in flowers) and "anthophilous" (flower-loving organisms). These words highlight how "antho" connects biology and chemistry to plant life and ecological interactions.
Q: What is the origin of the word "anthology"?
A: The term "anthology" originates from Greek, where it literally meant a "bouquet of flowers." Over time, the meaning evolved to refer to collections of poems, stories, or songs, as if gathering "blossoms" of creativity into one place.
Q: Are anthozoans actual flowers?
A: No, anthozoans are marine invertebrates like corals and sea anemones. They are named for their resemblance to flowers, but they are part of the animal kingdom and play a key role in forming coral reefs.
Q: What does "anthesis" refer to in botany?
A: "Anthesis" refers to the phase when a flower is fully open and functional, marking the stage of its life cycle when pollination typically occurs. It’s a critical moment for a plant's reproduction process.
Q: How are anthocyanins important to human health?
A: Anthocyanins, pigments found in flowers and fruits, are studied for their antioxidant properties. They contribute to the vibrant colors of berries and other plants and may play a role in preventing chronic diseases by neutralizing harmful free radicals in the body.
Q: Why is "antho" significant in cultural traditions?
A: "Antho" reflects humanity's fascination with flowers, evident in art, literature, and rituals. Traditions like Hanami in Japan, which celebrates cherry blossoms, illustrate how flowers symbolize beauty, life’s transience, and renewal in cultures worldwide.
Test Your Knowledge: " Antho " Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "antho" mean?
2. Which term refers to pigments in flowers?
3. What does "anthology" originally mean?
4. Which creatures are anthozoans?
5. What is "anthesis" in the life cycle of a flower?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Antho
From ancient poetry to cutting-edge biochemistry, the root "antho" continues to blossom across disciplines. Its enduring appeal reminds us of nature’s beauty and its profound influence on human creativity and discovery. As we deepen our appreciation for "antho," we honor the vibrant legacy of flowers in our language and lives.














