Anthropy: The Root of Humanity and Understanding
Byline:
Explore the profound depth of the word root "Anthropy," derived from the Greek "anthrōpos," meaning "human." This root shapes the language of human studies, empathy, and societal constructs, influencing fields as diverse as anthropology, philosophy, and humanitarian efforts.
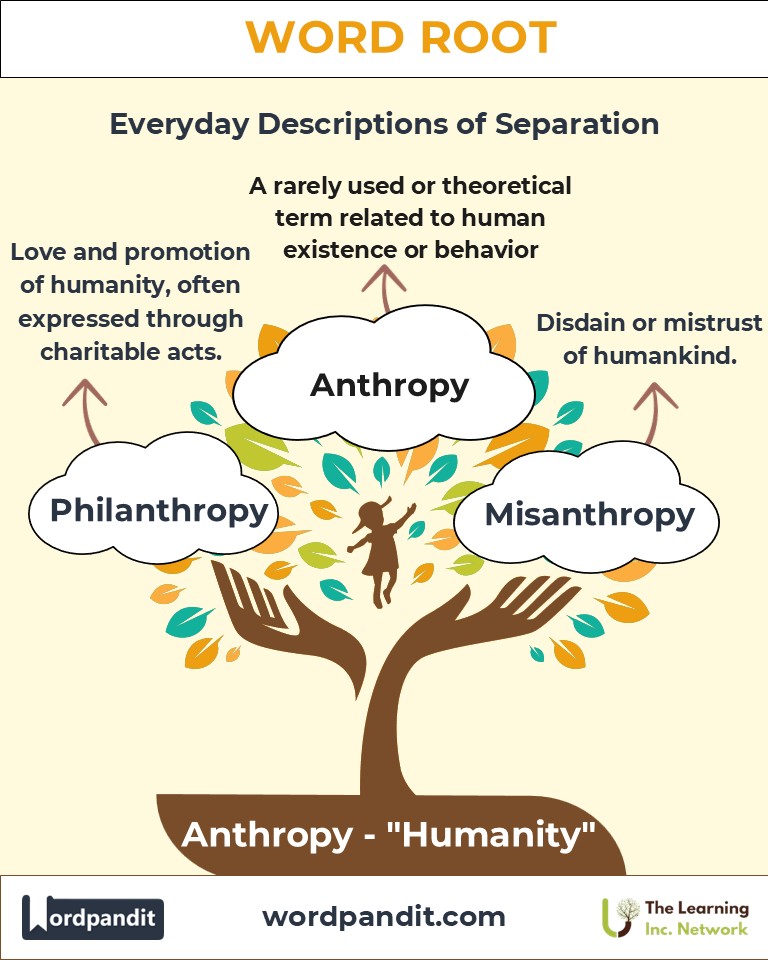
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Anthropy
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Anthropy
- Common Anthropy-Related Terms
- Anthropy Through Time
- Anthropy in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Anthropy in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Anthropy Root
- The Anthropy Family Tree
- FAQs about the Anthropy Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Anthropy Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Anthropy
1. Introduction: The Essence of Anthropy
The root "Anthropy," pronounced an-thruh-pee, emerges from the Greek "anthrōpos," meaning "human being" or "mankind." This linguistic cornerstone underscores the intrinsic nature of humanity in vocabulary and thought. From terms like "philanthropy" (love of humanity) to "anthropology" (study of humans), Anthropy resonates across disciplines, emphasizing our collective pursuit of understanding and improving human life.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "Anthropy" traces its origins to the Ancient Greek word ἄνθρωπος (anthrōpos), combining "anēr" (man) and "ōps" (face or appearance). Initially used to describe humanity’s distinguishing characteristics, it evolved to encompass broader themes of empathy, knowledge, and coexistence. As Greek philosophy thrived, terms derived from "Anthropy" permeated scientific and moral discourse, influencing modern languages.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Anthropy
Picture a globe surrounded by people holding hands, symbolizing humanity's unity and shared identity.
Mnemonic Device: “Anthropy brings humanity together—understanding, studying, and loving mankind.”
4. Common Anthropy-Related Terms
- Philanthropy (fi-lan-thruh-pee): Love and promotion of humanity, often expressed through charitable acts.
Example: "The billionaire's philanthropy provided clean water to thousands." - Anthropology (an-thruh-pol-uh-jee): The study of human societies, cultures, and evolution.
Example: "Anthropology revealed new insights into ancient civilizations." - Misanthropy (mis-an-thruh-pee): Disdain or mistrust of humankind.
Example: "His misanthropy grew after witnessing widespread corruption." - Anthropocentric (an-thruh-poh-sen-trik): Viewing humans as the central or most significant species.
Example: "The anthropocentric perspective often neglects ecological balance." - Anthropoid (an-thruh-poyd): Resembling humans, often used to describe primates.
Example: "Chimpanzees, as anthropoids, share many traits with humans."
5. Anthropy Through Time
- Anthropomorphism: Historically, humans assigned human traits to gods and animals. Over time, it became central to storytelling and psychology.
Example: The anthropomorphism of deities in ancient myths created relatable narratives. - Anthropic Principle: Introduced in the 20th century, it suggests the universe’s laws are finely tuned for human existence, blending science with philosophy.
6. Anthropy in Specialized Fields
- Sociology: Anthropocentric perspectives raise questions about ethical environmental policies.
- Astronomy: The Anthropic Principle links humanity's place in the universe with observable phenomena.
- Medicine: Anthropometry measures human body variations for health and ergonomics.
- Psychology: Misanthropy examines distrust in humanity to promote social reintegration.
7. Illustrative Story: Anthropy in Action
In a bustling city, a philanthropist named Maya sought to address homelessness. Partnering with anthropologists, she studied cultural and systemic causes of poverty. By integrating insights into her foundation, Maya transformed lives and inspired a shift toward empathy and understanding. Her story showcased Anthropy’s power to unite compassion with knowledge for lasting impact.
8. Cultural Significance of the Anthropy Root
The root "Anthropy" reflects humanity’s quest for identity and connection. Literature, art, and philosophy teem with themes of "Anthropy," from Renaissance humanism to modern humanitarian movements. These expressions underscore its enduring relevance in defining and celebrating our shared existence.

9. The Anthropy Family Tree
- Andro-: Meaning "man." Example: Androgyny.
- Human-: Latin for human. Example: Humanity.
- Phil-: Meaning "love." Example: Philanthropy.
- Mis-: Meaning "hate." Example: Misanthropy.
10. FAQs About the Anthropy Word Root
Q: What does "Anthropy" mean, and where does it come from?
A: "Anthropy" comes from the Greek word anthrōpos, meaning "human being" or "mankind." It is a linguistic foundation for terms describing human traits, behaviors, and relationships with the world.
Q: How do "Philanthropy" and "Misanthropy" differ?
A: Philanthropy stems from phil- (love) and anthrōpos (human), meaning "love of humanity," often expressed through charitable acts. Misanthropy, in contrast, combines mis- (hate) and anthrōpos and signifies distrust or dislike of humans.
Q: What is the Anthropocentric perspective?
A: Anthropocentrism is the belief that humans are the central or most significant entities in the universe. While it highlights humanity's role, critics argue it neglects the value of other species and ecosystems.
Q: What does "Anthropology" study, and why is it important?
A: Anthropology is the scientific study of human beings, their cultures, societies, and evolutionary history. It fosters cross-cultural understanding and helps address global challenges such as inequality and climate change.
Q: What is "Anthropomorphism," and where is it used?
A: Anthropomorphism is the attribution of human traits, emotions, or intentions to non-human entities, like animals, gods, or objects. It is common in literature, art, and religion.
Q: What are "Anthropoids," and how are they related to humans?
A: Anthropoids are primates resembling humans, such as gorillas, chimpanzees, and monkeys. The term reflects shared evolutionary traits, offering clues about human origins and behavior.
Q: How does "Anthropy" connect to environmental concerns?
A: Concepts like anthropocentrism highlight the human-centered worldview, which has often led to environmental exploitation. Recognizing this perspective is crucial for promoting sustainability.
11. Test Your Knowledge: Anthropy Word Root Quiz
1. What does the root "Anthropy" signify?
2. Which term describes love for humanity?
3. What does "Anthropomorphism" mean?
4. What does Anthropology study?
5. What is Misanthropy?
12. Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Anthropy
The root "Anthropy" encapsulates humanity’s profound exploration of itself, bridging empathy, knowledge, and societal progress. Its enduring relevance shapes disciplines from anthropology to humanitarianism. Let Anthropy guide your journey in celebrating the intricate tapestry of humanity.














