Brit: Exploring British Identity and Heritage
Discover the cultural richness and linguistic versatility of the root "Brit," derived from Britain’s name. From historical terms like "Briton" to modern expressions of British pride, this root encapsulates the essence of an island that has shaped global history and identity.
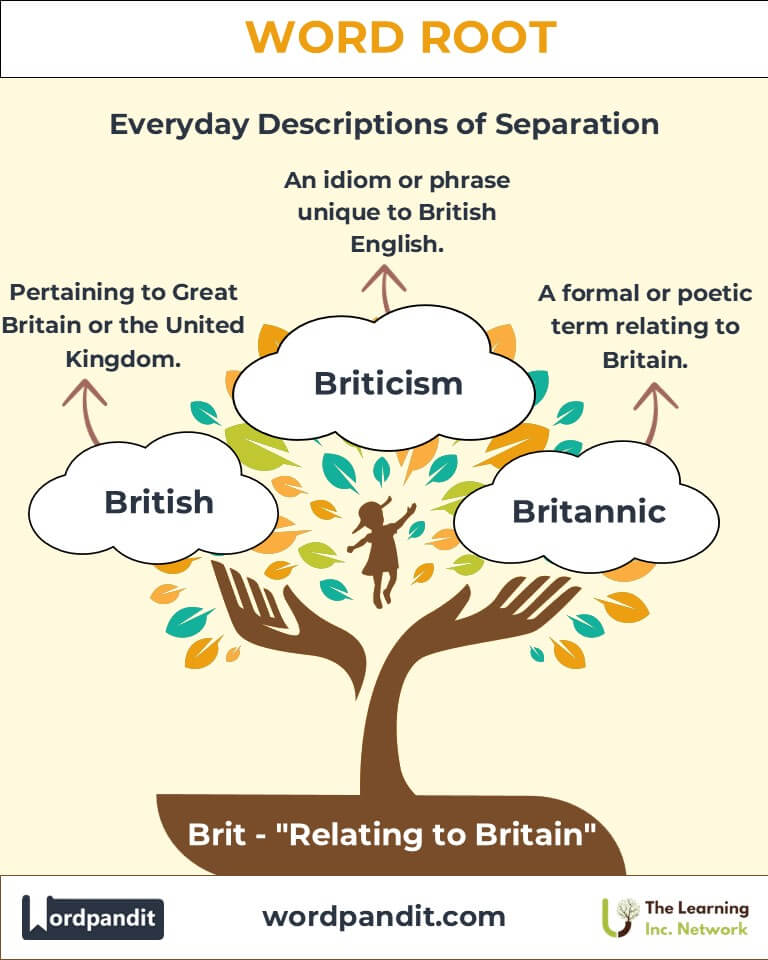
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Foundation of Brit-
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Brit-
- Common Brit-Related Terms
- Brit- Through Time
- Brit- in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Brit- in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Brit- Root
- The Brit- Family Tree
- FAQs About the Brit- Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Brit- Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Brit-
Introduction: The Foundation of Brit-
Have you ever pondered how the name of an island became a symbol of culture, history, and influence? The root Brit- reflects the legacy of Britain, its people, and its unique identity. Found in words that resonate with pride, culture, and tradition, this root links us to an enduring narrative of exploration, innovation, and resilience.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root Brit- originates from the Latin word Britannia, a term used by the Romans to describe the island of Britain. Before this, ancient Greek texts referred to the land as Prettanike or Brettaniai, describing a cluster of islands inhabited by Celtic tribes known as Britons. Over centuries, Britannia came to signify not just the island but the culture and identity of its people.
Key Historical Moments:
- Roman Era: Britannia was personified as a goddess on coins and monuments, symbolizing strength and unity.
- Middle Ages: Terms like Briton distinguished the Celtic inhabitants from Anglo-Saxon settlers.
- Modern Era: The rise of the British Empire cemented Brit- as a global symbol of governance, culture, and exploration.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Brit-
Picture the Union Jack fluttering above iconic landmarks like Stonehenge, Big Ben, and the White Cliffs of Dover. Add a teapot and a red double-decker bus for good measure, and you’ll never forget the cultural depth of the root Brit-.
Mnemonic Device: “Brit-: A timeless root celebrating Britain’s pride and people.”
Common Brit-Related Terms
- British (BRIT-ish): Relating to Great Britain or the United Kingdom.
Example: “The British Isles are known for their lush landscapes and rich history.” - Briton (BRIT-uhn): A native of Great Britain, particularly of Celtic descent.
Example: “The ancient Britons constructed hill forts across the countryside.” - Britannia (brih-TAN-yuh): The Latin name for Britain; also, a symbol of British unity and strength.
Example: “Britannia is depicted as a warrior queen on coins and statues.” - Briticism (BRIT-uh-siz-uhm): An idiom or phrase unique to British English.
Example: “Calling a truck a ‘lorry’ is a classic Briticism.” - Britannic (brih-TAN-ik): Relating to Britain in a formal or poetic sense.
Example: “The Britannic spirit of resilience was evident during the Blitz.”
Brit- Through Time
- Bretwalda (BRET-wal-duh): An Old English term for an overlord of several Anglo-Saxon kingdoms.
Historical Context: Reflects early political unity in Britain. - Britoness (BRIT-uh-ness): An archaic term for a British woman.
Relevance: Though outdated, it offers a glimpse into linguistic evolution.
Brit- in Specialized Fields
- Linguistics:
- Briticism: Reveals unique aspects of British English, aiding in the study of regional language variations.
- History:
- Briton and Bretwalda: Crucial terms for understanding the early sociopolitical landscape of Britain.
- Cultural Studies:
- Britannia: A symbol of national pride frequently appearing in art and literature.
Illustrative Story: Brit- in Action
Lily, a history student, visited the British Museum, marveling at artifacts from ancient Britons to the Industrial Revolution. A tour guide explained the significance of Britannia as a national icon, linking the past to present-day British identity. Inspired, Lily wrote a paper exploring how Brit- words encapsulate Britain’s cultural journey.
Cultural Significance of the Brit- Root
The Brit- root reflects Britain’s global influence. From the artistic representation of Britannia to idiomatic expressions like Briticism, the root is woven into the cultural fabric of the English-speaking world. Its resonance is evident in literature, music, and the global legacy of British traditions.

The Brit- Family Tree
- Anglo- (England, English):
- Anglophile: Someone who admires England.
- Anglophone: An English-speaking person.
- Celt- (Celtic):
- Celtic: Relating to the Celts, ancient inhabitants of Britain.
- Celtdom: The Celtic world or culture.
- Scot- (Scotland):
- Scotophobia: Fear of Scottish people or culture.
- Scotsman: A male native of Scotland.
FAQs About the Brit- Word Root
Q: What does Brit- mean?
A: The root Brit- refers to Britain, its people, culture, and heritage. It derives from the Latin Britannia, the Roman name for the island, which symbolized its distinct identity. Words like "Briton" and "British" trace their origins to this root, highlighting its linguistic and cultural influence.
Q: What is Britannia?
A: Britannia was the Latin name given to Britain by the Romans and is often personified as a powerful, armored woman holding a shield and trident. Over centuries, Britannia became a symbol of unity, strength, and resilience, frequently depicted in British coins, art, and national iconography.
Q: What are Briticisms?
A: Briticisms are words, idioms, or phrases distinctive to British English, such as "lorry" for "truck" or "flat" for "apartment." These terms reflect the unique linguistic identity of British English compared to other varieties, like American English.
Q: What is a Bretwalda?
A: A Bretwalda was an overlord or high king in early Anglo-Saxon England, presiding over multiple smaller kingdoms. This term, derived from Old English, highlights the historical attempts to unify Britain politically during the early medieval period.
Q: What is Britannic used for?
A: Britannic is a formal or poetic term relating to Britain or its people. For example, the RMS Britannic, a British ocean liner, reflected national pride in its naming. The term emphasizes Britain's heritage and achievements.
Q: How does Briton differ from British?
A: Briton typically refers to the original Celtic inhabitants of Britain or a poetic description of a British person. Meanwhile, British is a broader, modern term encompassing the people, culture, or nationality of Great Britain.
Q: Why is Britannia a female figure?
A: The Romans often personified lands and concepts as goddesses. Britannia’s depiction as a warrior queen symbolizes Britain’s strength, maritime power, and unity, mirroring similar personifications like France's Marianne or the United States' Columbia.
Test Your Knowledge: Brit- Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root Brit- refer to?
2. What does Briticism mean?
3. What is Britannia?
4. What is the meaning of Bretwalda?
5. What is the origin of the Brit- root?
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Brit-
The Brit- root represents more than a geographical entity; it captures a legacy of cultural pride, innovation, and resilience. By understanding Brit-, we uncover a linguistic connection to Britain’s rich history and its global influence. As the world evolves, so too does the story of this enduring root—continuing to inspire and unite.












