Bronch: Breathing Life into Medical Terminology
Byline: Delve into the linguistic essence of "bronch," derived from the Greek root "brónchos," meaning "windpipe." This vital root underpins medical terms related to the respiratory system, such as "bronchial" and "bronchitis," shedding light on the airways that sustain life.
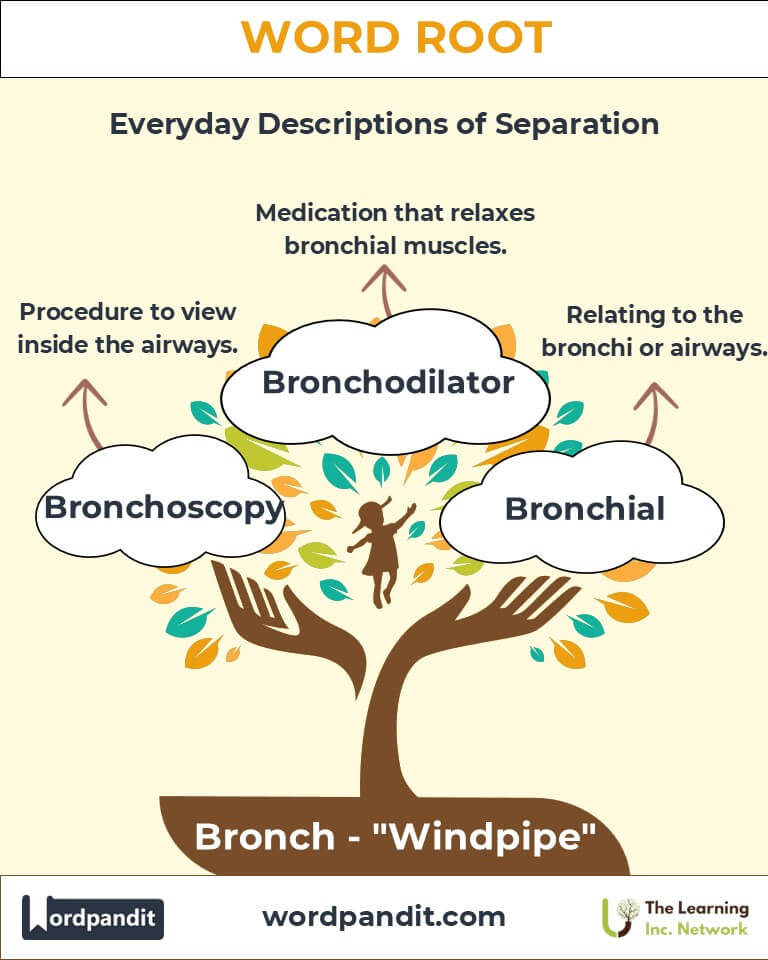
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Breath of "Bronch"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Bronch"
- Common "Bronch"-Related Terms
- "Bronch" Through Time
- "Bronch" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Bronch" in Action
- Cultural Significance of "Bronch"
- The "Bronch" Family Tree
- FAQs about the Bronch Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Bronch Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Bronch"
Introduction: The Breath of "Bronch"
Picture the intricate network of airways that deliver oxygen to your lungs, keeping you alive with every breath. The root "bronch" (pronounced "bronk") stems from the Greek word "brónchos," meaning "windpipe." This essential root forms the foundation of numerous medical terms that describe the respiratory system's functions and conditions, highlighting its significance in health and medicine.
Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "bronch" originates from ancient Greek, where "brónchos" referred to the trachea or windpipe. The term was adopted into Latin as "bronchus," eventually finding its way into English medical terminology. Its evolution reflects humanity’s growing understanding of the respiratory system, from basic descriptions of air passages to detailed studies of bronchial diseases and treatments.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Bronch"
Imagine a tree with its branches resembling the bronchial tubes that spread throughout the lungs. Just as the tree's branches deliver nutrients, the bronchial tubes distribute air.
Mnemonic Device:
“Think of bronchial tubes as the ‘branches’ of the respiratory tree, spreading air to nourish the lungs.”
Common "Bronch"-Related Terms
- Bronchial (bron-kee-uhl): Relating to the bronchi or airways in the lungs.
Example: "The doctor detected bronchial inflammation during the examination." - Bronchitis (bron-kai-tis): Inflammation of the bronchial tubes, often causing coughing and difficulty breathing.
Example: "Cold weather often triggers bronchitis in sensitive individuals." - Bronchoscopy (bron-koh-skuh-pee): A diagnostic procedure to view the inside of the airways using a bronchoscope.
Example: "The specialist performed a bronchoscopy to investigate the persistent cough." - Bronchospasm (bron-koh-spaz-uhm): Sudden constriction of the muscles in the walls of the bronchi.
Example: "Asthma attacks often involve severe bronchospasms." - Bronchodilator (bron-koh-dy-lay-ter): A medication that relaxes the bronchial muscles to improve airflow.
Example: "He used a bronchodilator to relieve his wheezing."
"Bronch" Through Time
- Ancient Descriptions: Early Greek physicians like Hippocrates used "brónchos" to refer to the windpipe, a critical component of breathing.
- Modern Medicine: Over time, the understanding of bronchial structures has advanced, leading to terms like "bronchoscopy" for innovative diagnostic techniques.
"Bronch" in Specialized Fields
- Medicine:
- Bronchiectasis: Chronic dilation of the bronchi, leading to respiratory complications.
Importance: Essential for diagnosing long-term lung conditions.
- Bronchiectasis: Chronic dilation of the bronchi, leading to respiratory complications.
- Pharmacology:
- Bronchodilators: Medications critical for treating asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Pulmonology:
- Bronchoscopy: Key in diagnosing airway abnormalities.
Illustrative Story: "Bronch" in Action
Sophia, a dedicated pulmonologist, encountered a patient struggling with severe asthma. Using a bronchoscope, she identified inflamed bronchial passages. After prescribing a combination of bronchodilators and anti-inflammatory medications, the patient’s breathing improved dramatically. Sophia’s expertise in "bronch"-related terms exemplified their life-saving importance in modern medicine.
Cultural Significance of "Bronch"
The root "bronch" extends beyond medicine, symbolizing the fragility and resilience of human life. The metaphor of bronchial tubes as "life's branches" is often used in art and literature to illustrate the interconnection between breath and vitality.
The "Bronch" Family Tree
- Trachea (Latin: "rough artery"): The main airway, branching into the bronchi.
- Pulmo (Latin: "lung"): Related to pulmonary or lung functions.
- Pneumo (Greek: "air, lung"): Found in terms like "pneumonia" (lung inflammation).
FAQs About the Bronch Word Root
Q: What does "bronch" mean?
A: The root "bronch" comes from the Greek word "brónchos," meaning "windpipe." It refers specifically to the passages that carry air from the trachea into the lungs. These airways, called bronchi, are essential for breathing and oxygen exchange.
Q: How does "bronchitis" differ from "asthma"?
A: Bronchitis is the inflammation of the bronchial tubes, often caused by infection or irritation, leading to symptoms like coughing, mucus production, and shortness of breath. Asthma, on the other hand, is a chronic condition where the airways narrow and become inflamed due to triggers like allergens or exercise, resulting in wheezing, tightness in the chest, and difficulty breathing.
Q: What is a bronchoscope, and how is it used?
A: A bronchoscope is a medical instrument used to visually inspect the bronchi and airways. It is a flexible or rigid tube equipped with a camera and light, allowing doctors to diagnose conditions like tumors, blockages, or infections and sometimes even perform treatments or biopsies during the procedure.
Q: What are bronchodilators, and how do they work?
A: Bronchodilators are medications that relax the muscles surrounding the bronchial tubes, making the airways wider and allowing for easier breathing. They are commonly used to treat asthma, COPD, and other respiratory conditions by relieving symptoms like wheezing and shortness of breath.
Q: Can bronchitis become a long-term condition?
A: Yes, bronchitis can be chronic. Chronic bronchitis is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) characterized by persistent inflammation and irritation of the bronchial tubes, typically caused by smoking or long-term exposure to pollutants. This condition often leads to ongoing coughing and mucus production.
Q: What’s the difference between "bronchial" and "pulmonary"?
A: While both terms relate to the respiratory system, "bronchial" refers specifically to the bronchial tubes and airways that branch off the trachea, whereas "pulmonary" pertains to the lungs as a whole, including structures like alveoli where gas exchange occurs.
Q: What causes bronchospasms, and how are they treated?
A: Bronchospasms are sudden contractions of the muscles in the bronchial walls, causing airway narrowing and difficulty breathing. Common triggers include allergens, exercise, cold air, and respiratory infections. Treatment often involves quick-relief bronchodilators (like albuterol) and preventive measures to avoid known triggers.
Test Your Knowledge: Bronch Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "bronch" mean?
2. Which condition involves inflammation of the bronchi?
3. What is a bronchodilator used for?
4. What is the purpose of a bronchoscopy?
5. Which term describes a sudden narrowing of the bronchi?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Bronch"
The root "bronch" reminds us of the vital role airways play in sustaining life. From ancient descriptions to cutting-edge medical innovations, this linguistic cornerstone continues to underpin our understanding of respiratory health. As new treatments emerge, the legacy of "bronch" endures, inspiring ongoing advancements in medicine and care.













