Carcino: The Root of Cancer in Medical and Everyday Language
Delve into the impactful root "carcino," originating from Greek, meaning "cancer." Found in terms like "carcinogen" and "carcinoma," this root sheds light on the complexities of cancer research and its implications in health and science.
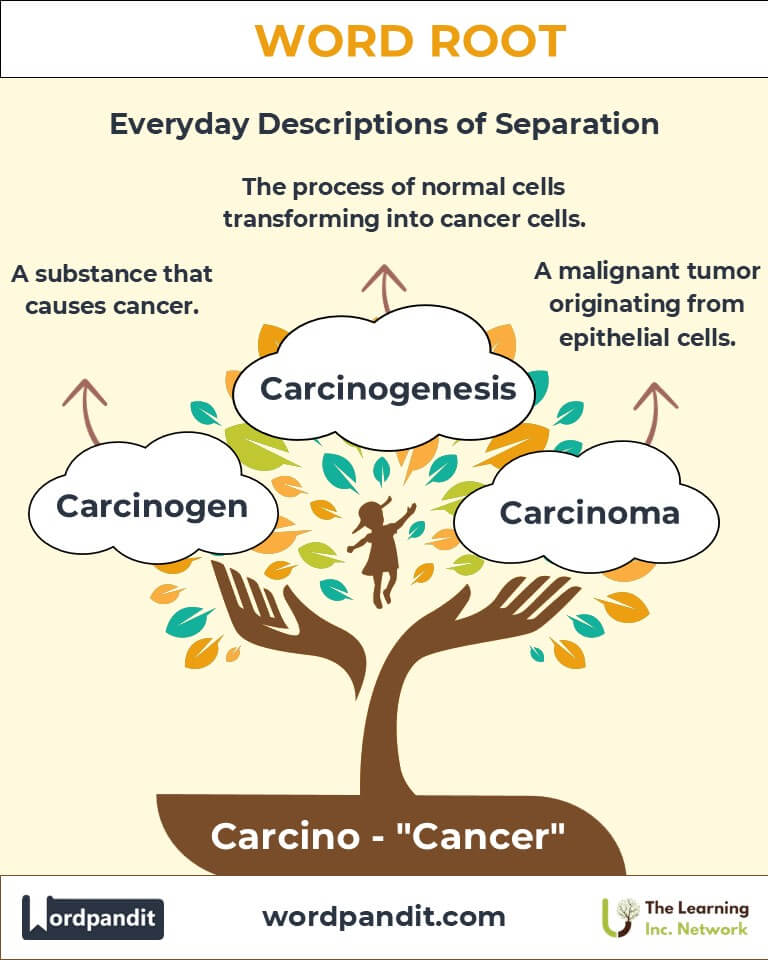
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Carcino"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Carcino
- Common Carcino-Related Terms
- Carcino Through Time
- Carcino in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Carcino in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Carcino Root
- The Carcino Family Tree
- FAQs About the Carcino Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Carcino Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Carcino
1. Introduction: The Essence of "Carcino"
The word root "carcino" (pronounced kar-see-noh) has a profound presence in the medical field. Derived from the Greek word karkinos, meaning "crab," it reflects the crab-like spread of cancerous cells. This root is fundamental in words that describe cancers, toxins, and related medical phenomena. Its relevance spans not only the technical language of oncology but also public health discourse, underscoring the importance of awareness and prevention.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The term "carcino" originates from the Greek karkinos, meaning crab, a metaphor for the way cancerous growths cling to tissues. Hippocrates, the father of medicine, used "karkinos" to describe tumors, noting their spreading limbs resembled a crab’s pincers. Over centuries, the term evolved, entering Latin as "cancer" and eventually blending into English medical terminology. The enduring use of "carcino" reflects its pivotal role in cancer studies and healthcare advancements.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Carcino
To remember "carcino," envision a crab with its pincers spreading outward, mirroring the invasive nature of cancer cells.
Mnemonic Device: "Carcino clings like a crab—cells spreading with stealth."
4. Common Carcino-Related Terms
- Carcinogen (kar-sin-uh-jen): A substance that causes cancer.
Example: "Tobacco smoke contains carcinogens linked to lung cancer." - Carcinoma (kar-sin-oh-muh): A malignant tumor originating from epithelial cells.
Example: "The patient was diagnosed with a carcinoma in the breast tissue." - Carcinogenic (kar-sin-oh-jen-ik): Having the potential to cause cancer.
Example: "Asbestos fibers are carcinogenic and harmful to lung health." - Carcinogenesis (kar-sin-oh-jen-uh-sis): The process by which normal cells transform into cancer cells.
Example: "Studying carcinogenesis helps researchers identify potential therapies." - Carcinosarcoma (kar-sin-oh-sahr-koh-muh): A rare cancer combining carcinoma and sarcoma elements.
Example: "Carcinosarcomas often require aggressive treatment."
5. Carcino Through Time
Hippocratic Roots: The first use of "karkinos" described both malignant and benign tumors, indicating early attempts to classify diseases.
Modern Oncology: The term "carcinogen" emerged in the 20th century as scientists identified substances that trigger cancer, marking progress in prevention efforts.
6. Carcino in Specialized Fields
- Oncology: Carcinoma forms the backbone of cancer classification, shaping treatment protocols.
- Environmental Science: Carcinogens like industrial chemicals are studied for their ecological and health impacts.
- Pharmacology: Anti-carcinogenic compounds are explored to prevent carcinogenesis in high-risk individuals.
7. Illustrative Story: Carcino in Action
Dr. Aria Patel, an oncologist, had spent years studying carcinogenesis in smokers. Her breakthrough came when she discovered a molecule that neutralized specific carcinogens in tobacco. This discovery led to a preventive treatment, significantly reducing lung cancer cases among at-risk populations. Dr. Patel’s work exemplified the fight against cancer, rooted in understanding the behavior of carcinogens and carcinomas.
8. Cultural Significance of the Carcino Root
The root "carcino" resonates deeply in cultural narratives surrounding health and resilience. Cancer awareness campaigns emphasize early detection and the dangers of carcinogens, fostering global solidarity in combating this disease. Additionally, ancient myths likening cancer to a crab underscore the timeless struggle between health and disease.

9. The Carcino Family Tree
- Onco- (tumor): Oncologist, Oncology
- Neo- (new): Neoplasm (a new, abnormal growth of tissue)
- Toxo- (poison): Toxin, Toxicology
FAQs About the "Carcino" Root
Q: What does "carcino" mean?
A: The root "carcino" means "cancer" and is derived from the Greek word karkinos, meaning crab. This metaphor reflects the invasive, spreading nature of cancer cells.
Q: How is a carcinogen different from a mutagen?
A: A carcinogen is any substance that causes cancer, while a mutagen refers specifically to agents that cause genetic mutations. Many carcinogens are mutagens, but not all mutagens directly lead to cancer.
Q: What is a carcinoma, and how does it differ from sarcoma?
A: A carcinoma is a malignant tumor originating in epithelial cells, while a sarcoma arises in connective or supportive tissues like bone, muscle, or fat.
Q: Are all carcinogens synthetic?
A: No, carcinogens can be natural or synthetic. Natural examples include UV radiation and certain molds like aflatoxins, while synthetic examples include tobacco smoke and industrial chemicals.
Q: What does carcinogenesis refer to?
A: Carcinogenesis is the process through which normal cells transform into cancerous cells, involving genetic mutations, abnormal cell growth, and the ability to invade nearby tissues.
Q: Can a substance be carcinogenic and beneficial?
A: Yes, some substances can be carcinogenic in high doses but beneficial when used therapeutically. For example, radiation therapy uses ionizing radiation to treat cancer despite its potential to cause cancer at high exposure levels.
Q: How do carcinogens cause cancer?
A: Carcinogens damage DNA or disrupt cellular processes, leading to mutations that accumulate over time. These mutations may result in uncontrolled cell growth and tumor formation.
Test Your Knowledge: "Carcino" Mastery Quiz
1. What does "carcino" mean?
2. What is a carcinogen?
3. What is carcinoma?
4. Which field studies carcinogenesis?
5. What does carcinogenic mean?

12. Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Carcino
The root "carcino" serves as a vital reminder of humanity’s ongoing battle against cancer. Through understanding its origins and applications, we enhance our ability to prevent and treat one of the world’s most significant health challenges. By embracing advancements in science and medicine, the legacy of "carcino" propels us toward a future of hope and healing.













