Cardi: The Heart of Language and Life
Byline: Discover the pulsating essence of the root "Cardi," derived from the Greek word "kardia," meaning "heart." From "cardiac" to "cardiovascular," this vital root beats its way into medical terminology and everyday language, symbolizing the core of human life and emotion.
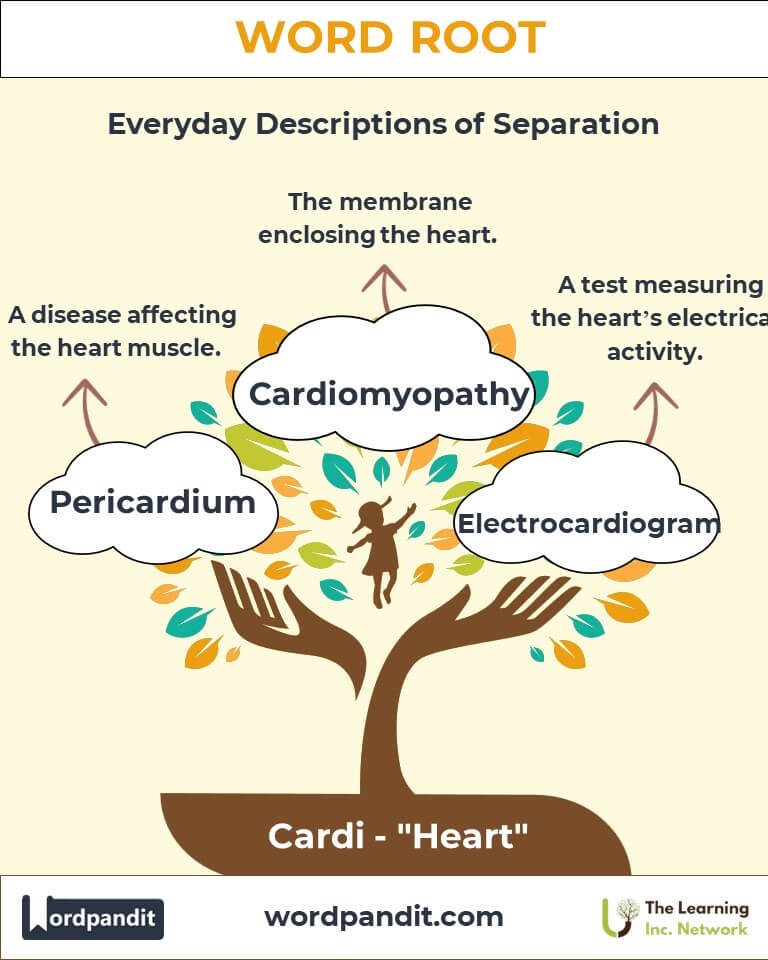
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Heartbeat of "Cardi"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Cardi"
- Common "Cardi"-Related Terms
- "Cardi" Through Time
- "Cardi" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Cardi" in Action
- Cultural Significance of "Cardi"
- The "Cardi" Family Tree
- FAQs about the "Cardi" Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Cardi" Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Cardi"
Introduction: The Heartbeat of "Cardi"
The root "Cardi" is a linguistic lifeline connecting language to the biological and emotional core of existence. Derived from the Greek word kardia (heart), this root forms the foundation of numerous terms that describe the heart's functions, diseases, and symbolic meanings. Whether in medicine, literature, or metaphors, "Cardi" signifies vitality and centrality.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "Cardi" originates from the Greek kardia (heart), evolving into Latin cardiacus. Early usage described physical heart conditions but later expanded to include symbolic representations of courage and love. By the 19th century, as medical science advanced, "Cardi" became a cornerstone of cardiology—a field dedicated to studying the heart.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Cardi"
Picture a heart glowing in the center of a human silhouette, radiating life. This imagery ties the root "Cardi" to its literal and metaphorical meanings.
Mnemonic Device: "Cardi keeps the beat, linking health and heat to life's heartbeat."
Common "Cardi"-Related Terms
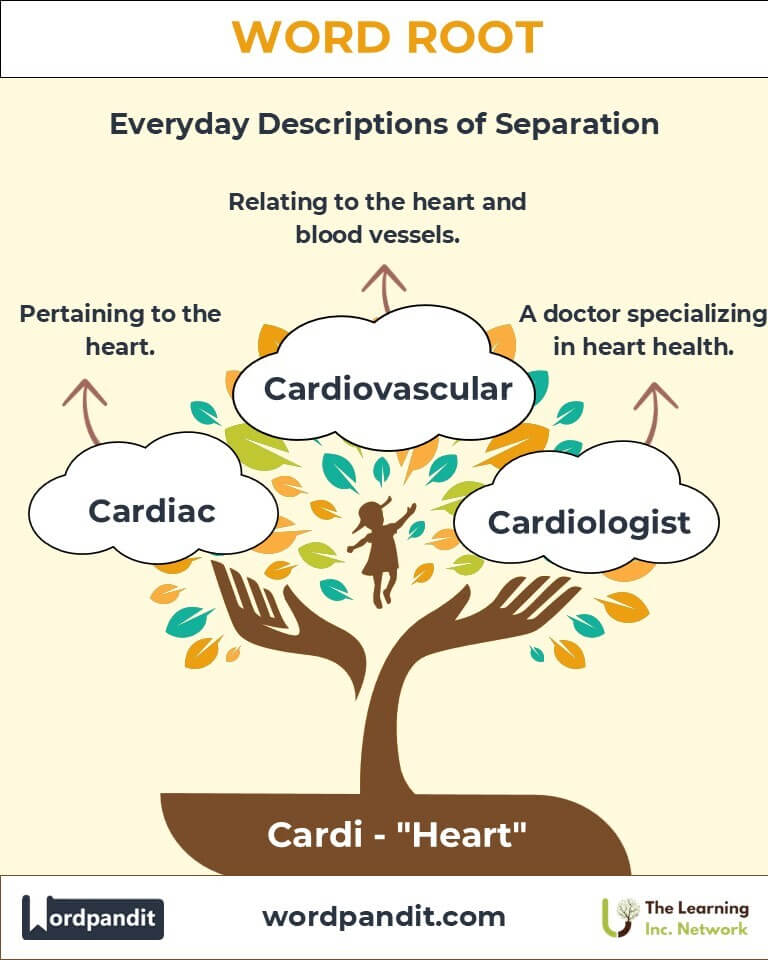
- Cardiac (kar-dee-ak): Pertaining to the heart.
Example: "The cardiac monitor tracked her heartbeat during surgery." - Cardiovascular (kar-dee-oh-vas-kyoo-lar): Relating to the heart and blood vessels.
Example: "Cardiovascular exercises improve heart health." - Cardiologist (kar-dee-ol-uh-jist): A doctor specializing in heart health.
Example: "The cardiologist recommended lifestyle changes to manage hypertension." - Cardiomyopathy (kar-dee-oh-my-op-uh-thee): A disease affecting the heart muscle.
Example: "Cardiomyopathy can lead to heart failure if untreated." - Pericardium (per-i-kar-dee-um): The membrane enclosing the heart.
Example: "Inflammation of the pericardium can cause sharp chest pain."
"Cardi" Through Time
-
Cardia (Ancient): Originally used to denote the heart's physical and emotional center in ancient Greece.
Shift: Expanded to include courage and bravery in literature. -
Cardiograph (Modern): Invented in the 19th century, this device records heart activity.
Significance: Revolutionized the diagnosis of cardiac conditions.
"Cardi" in Specialized Fields
- Medicine: Cardiomyopathy addresses diseases affecting heart muscles.
Impact: Aids in understanding chronic heart conditions. - Fitness: Cardio exercises are activities that elevate heart rate.
Purpose: Promotes cardiovascular health. - Technology: Electrocardiogram (ECG) measures electrical activity of the heart.
Importance: Critical for diagnosing arrhythmias and other conditions.
Illustrative Story: "Cardi" in Action
Dr. Maya, a dedicated cardiologist, spent her days treating patients with heart conditions. One day, a young athlete arrived with unexplained chest pain. Using an ECG, Dr. Maya diagnosed early-stage cardiomyopathy. Through personalized care, she helped the athlete recover, proving the heart's resilience. The patient later won a marathon, dedicating his victory to the doctor who saved his "cardi."
Cultural Significance of "Cardi"
The heart has long been a symbol of love, courage, and life. In ancient Greece, the heart (kardia) was considered the seat of emotions. Today, phrases like "put your heart into it" or "heartfelt thanks" reflect the enduring metaphorical power of "Cardi."

The "Cardi" Family Tree
- Cor-/Cord- (Latin: Heart):
- Cordial: Warm and friendly.
- Core: The central part of something.
- Peri- (Greek: Around):
- Pericardium: Membrane surrounding the heart.
- Angio- (Greek: Vessel):
- Angiocardiogram: An imaging test of the heart and blood vessels.
FAQs About the Cardi Root
Q: What does the root "Cardi" mean?
A: The root "Cardi" comes from the Greek word kardia, meaning "heart." It forms the basis of numerous medical terms related to the heart, such as "cardiac" and "cardiovascular," as well as metaphorical expressions like having "heart" (courage) or being "heartfelt" (sincere).
Q: What is a cardiologist?
A: A cardiologist is a physician specializing in diagnosing and treating heart-related conditions. Cardiologists manage diseases like coronary artery disease, arrhythmias, and heart failure, often using diagnostic tools such as electrocardiograms (ECGs) or echocardiograms.
Q: Why is "Cardio" associated with exercise?
A: "Cardio" exercises, like running or cycling, are named for their ability to elevate heart rate and improve cardiovascular health. These activities enhance blood circulation, strengthen the heart muscle, and reduce risks of heart disease.
Q: What is the pericardium, and why is it important?
A: The pericardium is the protective double-layered membrane surrounding the heart. It prevents the heart from over-expanding, provides lubrication to reduce friction during heartbeats, and shields the heart from infections or external shocks.
Q: How is "Cardi" connected to courage or emotions?
A: Historically, the heart was considered the seat of emotions and bravery in many cultures. Expressions like "putting your heart into something" or "having a big heart" reflect this connection. Ancient Greek philosophers linked kardia to emotional strength, a metaphor that persists in language today.
Q: What does "Cardiomyopathy" mean?
A: Cardiomyopathy refers to diseases that affect the heart muscle, impairing its ability to pump blood effectively. There are various types, including dilated cardiomyopathy (where the heart enlarges) and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (where the heart muscle thickens), both of which can lead to heart failure if untreated.
Q: How does an electrocardiogram (ECG) relate to the "Cardi" root?
A: An ECG is a diagnostic test that measures the electrical activity of the heart. By recording the heart's rhythms, it helps detect conditions such as arrhythmias, heart attacks, or other abnormalities, illustrating the practical application of the "Cardi" root in modern medicine.
Test Your Knowledge: Cardi Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "Cardi" mean?
2. Which term refers to the heart and blood vessels?
3. What is a cardiologist?
4. What does "Pericardium" refer to?
5. Which device measures the heart's electrical activity?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Cardi"
The root "Cardi" beats at the center of language, culture, and medicine. From ancient beliefs to modern science, its influence underscores the heart's importance as a biological organ and a symbol of vitality and emotion. As advances in cardiology continue, "Cardi" remains a testament to the enduring power of the heart in all its forms.














