Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Caut"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Caut"
- Common "Caut"-Related Terms
- "Caut" Through Time
- "Caut" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Caut" in Action
- Cultural Significance of the "Caut" Root
- The "Caut" Family Tree
- FAQs about the "Caut" Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Caut" Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Caut"
Introduction: The Essence of "Caut"
Have you ever considered the connection between heat and caution? The Latin root "Caut", pronounced (kawt), embodies both the physical and metaphorical power of heat. Found in words like cauterize, which uses heat for healing, and cautious, which advises prudence, "Caut" reminds us of the transformative and protective qualities of fire and warmth.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "Caut" derives from the Latin cautus, meaning "careful" or "guarded," and cauter, meaning "branding iron." Historically, the term evolved alongside medical practices that utilized heat for sterilization and sealing wounds, as well as philosophical notions of caution in managing danger.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Caut"
Picture a glowing iron cauterizing a wound while a doctor advises, "Be cautious—heat heals but burns." The connection between heat and prudence becomes vivid through this imagery.
Mnemonic Device:
"Caut reminds us: Heat can heal, but handle with care!"
Common "Caut"-Related Terms
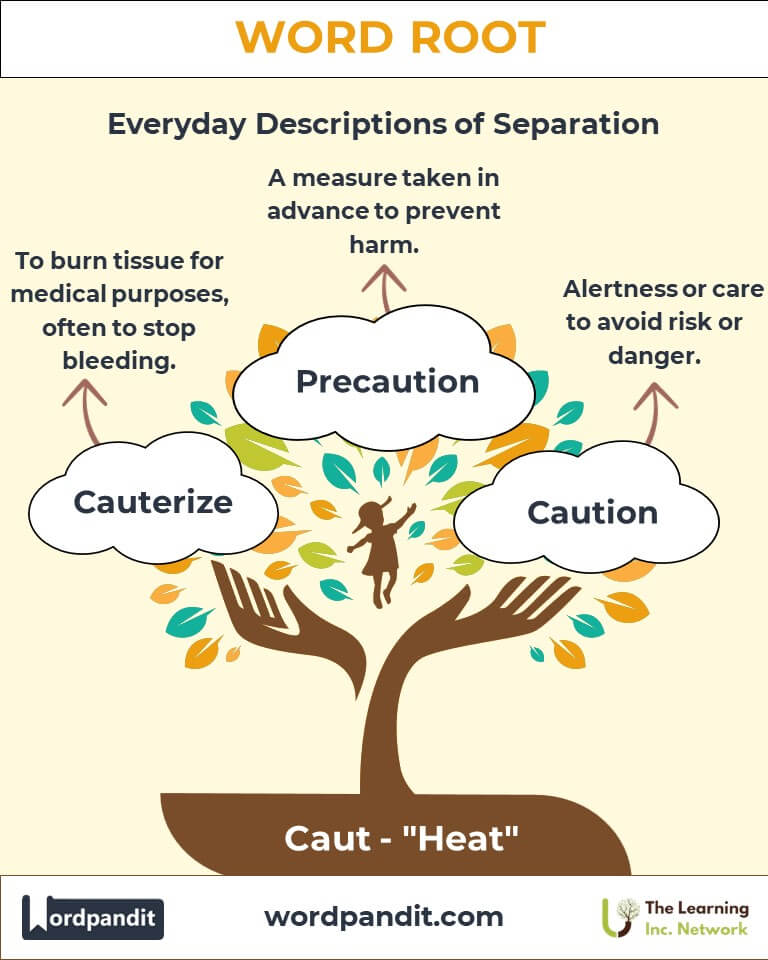
- Cauterize (kaw-tuh-rise)
- Definition: To burn tissue for medical purposes, often to stop bleeding or prevent infection.
- Example: "The surgeon used a laser to cauterize the wound and ensure it was sterile."
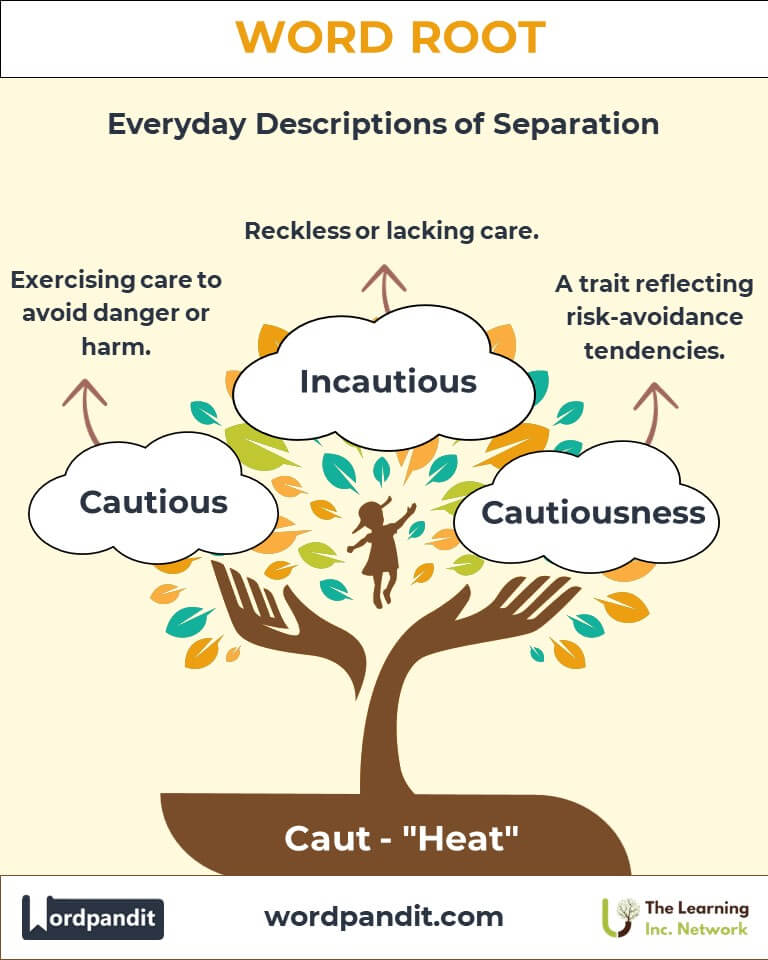
- Cautious (kaw-shus)
- Definition: Exercising care to avoid danger or harm.
- Example: "The hiker was cautious while navigating the rocky trail."
- Caution (kaw-shun)
- Definition: Alertness or care to avoid risk or danger.
- Example: "The warning sign urged caution near the construction site."
- Precaution (pree-kaw-shun)
- Definition: A measure taken in advance to prevent harm.
- Example: "Wearing sunscreen is a precaution against sunburn."
- Incautious (in-kaw-shus)
- Definition: Reckless or lacking care.
- Example: "His incautious remarks offended the audience."
"Caut" Through Time
- Ancient Medicine: The practice of cauterization began in ancient Greece, where heated instruments were used to seal wounds and treat injuries.
- Modern Usage: The metaphorical extension of "Caut" led to terms like "cautious," reflecting careful deliberation and foresight, akin to managing the power of heat.
"Caut" in Specialized Fields
Medicine
- Cauterize: Essential in surgical procedures to stop bleeding or sterilize wounds.
- Example: Modern lasers perform cauterization with precision and minimal scarring.
Psychology
- Cautiousness: A trait studied in behavioral psychology, assessing risk-avoidance tendencies.
- Application: Critical in understanding decision-making under stress.
Safety Engineering
- Precautionary Measures: Related to fire safety protocols, emphasizing caution in hazardous environments.
Illustrative Story: "Caut" in Action
Dr. Elena, a skilled trauma surgeon, faced an emergency requiring immediate cauterization. A patient with a deep wound arrived, bleeding profusely. Using advanced laser tools, Dr. Elena quickly sealed the injury, saving the patient’s life. Her cautious approach and mastery of cauterization underscored the delicate balance of heat as a life-saving tool.
Cultural Significance of the "Caut" Root
From ancient healers wielding fire to modern safety campaigns emphasizing caution, the "Caut" root embodies humanity's respect for the duality of heat—both nurturing and destructive. It symbolizes prudence in embracing powerful tools while acknowledging their risks.

The "Caut" Family Tree
Calor (heat)
- Calorie: A unit of heat energy.
- Calorimeter: A device measuring heat.
Therm (heat)
- Thermometer: An instrument measuring temperature.
- Thermal: Relating to heat.
Ignis (fire)
- Ignition: The act of setting something on fire.
- Ignite: To catch fire.
FAQs About the Caut Word Root
Q: What does "Caut" mean, and what is its origin?
A: The root "Caut" means "heat" and is derived from the Latin words cautus (careful or guarded) and cauter (branding iron). It reflects both the physical properties of heat and the metaphorical caution associated with managing something powerful and potentially dangerous.
Q: What is cauterization, and where is it used?
A: Cauterization is a medical technique where heat is used to burn tissue. This procedure is often employed to stop bleeding, prevent infections, or close wounds. It dates back to ancient times when heated tools were used for sterilization. Modern cauterization uses lasers or electric currents for precise, minimally invasive treatment.
Q: How is "Caut" related to caution?
A: The metaphorical use of "Caut" in words like "cautious" reflects the need to handle heat carefully. Just as fire can heal or harm, caution emphasizes thoughtful action to avoid negative outcomes.
Q: Why does "Caut" symbolize both danger and care?
A: Heat has a dual nature: it can provide warmth and healing or cause burns and destruction. This duality made "Caut" an ideal root to convey the concepts of both physical and metaphorical prudence, especially in contexts requiring careful handling.
Q: What is the difference between caution and precaution?
A: While "caution" refers to exercising care to avoid danger, "precaution" emphasizes proactive measures taken in advance to prevent potential risks. For instance, a warning sign urges caution, while wearing protective gloves is a precaution.
Test Your Knowledge: Caut Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "Caut" mean?
2. Which word means "to burn tissue for medical purposes"?
3. What is the opposite of "Cautious"?
4. Which field prominently uses "Cauterize"?
5. What does "Precaution" imply?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Caut"
The root "Caut" illustrates the enduring significance of heat in language, science, and culture. From its literal use in medicine to its metaphorical application in everyday caution, "Caut" bridges the ancient and modern worlds. As technology evolves, the principles of "Caut"—respect for heat’s power and the wisdom of careful application—remain vital to our understanding and progress.














