Cerebro: The Brain Behind Words and Meaning
Unveil the intricate world of the word root "Cerebro," derived from Latin, meaning "brain." From everyday terms like "cerebral" to specialized medical terminology such as "cerebrospinal," this root reflects the human fascination with thought, intelligence, and the central organ of our consciousness.
1. Introduction: The Essence of Cerebro
The root "Cerebro" (pronounced seh-REE-broh) is derived from Latin, meaning "brain." This root is pivotal in words that describe both the physical structure of the brain and its metaphorical associations with intellect and analysis. Its relevance spans disciplines from medicine to philosophy and psychology.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The term "Cerebro" stems from the Latin word cerebrum, meaning "brain." In ancient Rome, this word described the physical brain and its functions, emphasizing its role as the seat of thought and control. Over time, "Cerebro" entered scientific language, shaping medical terms and intellectual descriptors alike.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Cerebro
To remember "Cerebro," picture a glowing brain lighting up like a supercomputer, symbolizing thought and intelligence.
4. Common Cerebro-Related Terms
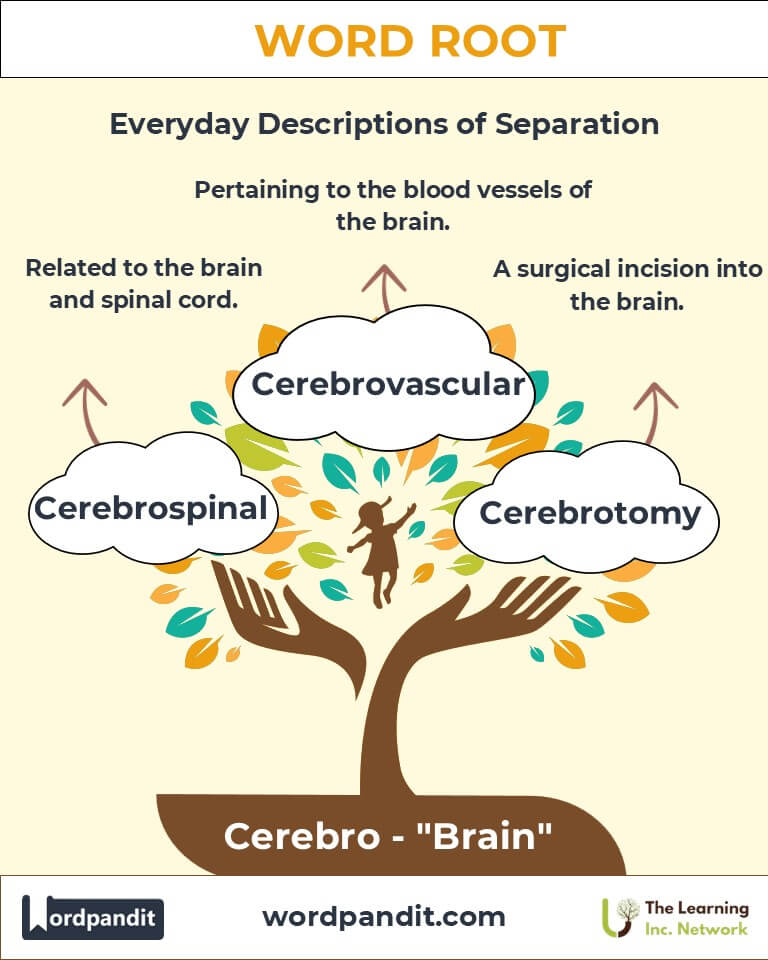
- Cerebral (seh-REE-bruhl): Related to the brain or intellect.
Example: "His cerebral approach to problem-solving impressed the team." - Cerebrospinal (seh-REE-broh-SPY-nuhl): Pertaining to the brain and spinal cord.
Example: "Cerebrospinal fluid protects and nourishes the central nervous system." - Cerebellum (seh-ruh-BEL-uhm): A part of the brain that controls motor functions.
Example: "Damage to the cerebellum can affect balance and coordination." - Cerebration (seh-ruh-BRAY-shun): The act of thinking or mental activity.
Example: "Deep cerebration is essential for solving complex problems." - Cerebrotomy (seh-REE-broh-toh-mee): A surgical incision into the brain.
Example: "The cerebrotomy was performed to remove the tumor safely."
5. Cerebro Through Time
- Ancient Understanding: Romans viewed the cerebrum as the center of thought.
- Modern Science: The 19th century saw advances in neuroscience, linking "cerebro" to terms like "cerebrovascular," referring to brain blood flow.
6. Cerebro in Specialized Fields
- Medicine: Cerebrovascular health is critical in preventing strokes.
- Psychology: Cerebration highlights deep thinking.
- Education: "Cerebral" pursuits describe intellectual activities.
7. Illustrative Story: Cerebro in Action
Dr. Alice Carter, a neurosurgeon, faced a critical challenge: a patient suffering from cerebrovascular blockage. Using advanced imaging techniques, she mapped the brain’s blood flow and performed a delicate surgery, restoring function. Her work showcased the vital connection between the brain’s physical structure and its life-sustaining processes.
8. Cultural Significance of Cerebro
The brain, symbolized by the root "Cerebro," has long been a metaphor for intellect, creativity, and control. From Renaissance art depicting the brain as the seat of the soul to modern AI systems named after it, "Cerebro" captures the human desire to understand and emulate the mind’s complexity.

9. The Cerebro Family Tree
- Neuro- (nerve): Neurology – The study of the nervous system.
- Psycho- (mind): Psychology – The study of the mind and behavior.
- Vascul- (vessel): Vascular – Related to blood vessels.
10.FAQs About the Cerebro Word Root
Q1: What does "Cerebro" mean?
A: "Cerebro" means "brain" and comes from the Latin word cerebrum. It is commonly used in words that refer to the brain’s physical structure, its functions, or intellectual activities.
Q2: What is cerebrospinal fluid?
A: Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear liquid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord, acting as a cushion to protect these structures from injury. It also delivers nutrients and removes waste, playing a crucial role in maintaining the brain’s health.
Q3: Is "Cerebro" used outside of medicine?
A: Yes, "Cerebro" appears in non-medical contexts. For example, the term "cerebral" often describes intellectual pursuits or deep thinking. It reflects the metaphorical association of the brain with intelligence and analysis.
Q4: What is cerebration?
A: Cerebration refers to the act of thinking or engaging in mental activity. It highlights the role of the brain in processing information, solving problems, and generating ideas.
Q5: How is "Cerebro" linked to modern technology?
A: The root "Cerebro" inspires terms in technology, such as artificial intelligence systems and computational tools modeled after the brain’s structure and functionality. These advancements seek to replicate the brain’s efficiency and problem-solving abilities.
Q6: What is the difference between "Cerebrum" and "Cerebellum"?
A: The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain, responsible for higher functions like thought, memory, and voluntary movement. The cerebellum, located at the back of the brain, controls coordination, balance, and fine motor skills.
Q7: What does "Cerebrovascular" refer to?
A: "Cerebrovascular" pertains to the blood vessels of the brain and their role in circulation. Conditions like strokes are often linked to cerebrovascular health.
Q8: What happens during a cerebrotomy?
A: A cerebrotomy is a surgical procedure involving an incision into the brain. It is typically performed to treat brain injuries, remove tumors, or address neurological conditions.
Q9: Why is "Cerebro" associated with intelligence?
A: The brain is seen as the center of thought and reasoning. Over centuries, "Cerebro" became a metaphorical representation of intellect, analysis, and critical thinking.
Q10: What does "Cerebral" mean in non-medical contexts?
A: In non-medical contexts, "cerebral" often describes something intellectual or abstract, like a cerebral novel or discussion. It implies depth, analytical thinking, or a focus on ideas rather than emotions.
11.Test Your Knowledge: Cerebro Word Root Quiz
1. What does "Cerebro" mean?
2. What does "Cerebrospinal" refer to?
3. What is cerebration?
4. What part of the brain controls balance?
5. What protects the brain and spinal cord?

12. Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Cerebro
The root "Cerebro" connects us to the mysteries of the brain, the organ that defines thought, emotion, and identity. Its influence spans ancient philosophy to modern neuroscience.













