Cycl: The Root of Circles and Cycles in Language and Life
Discover the fascinating journey of the root "cycl," derived from the Greek word kyklos, meaning "circle." From bicycles to cyclones, this versatile root shapes words that describe loops, rotations, and systems in endless motion.
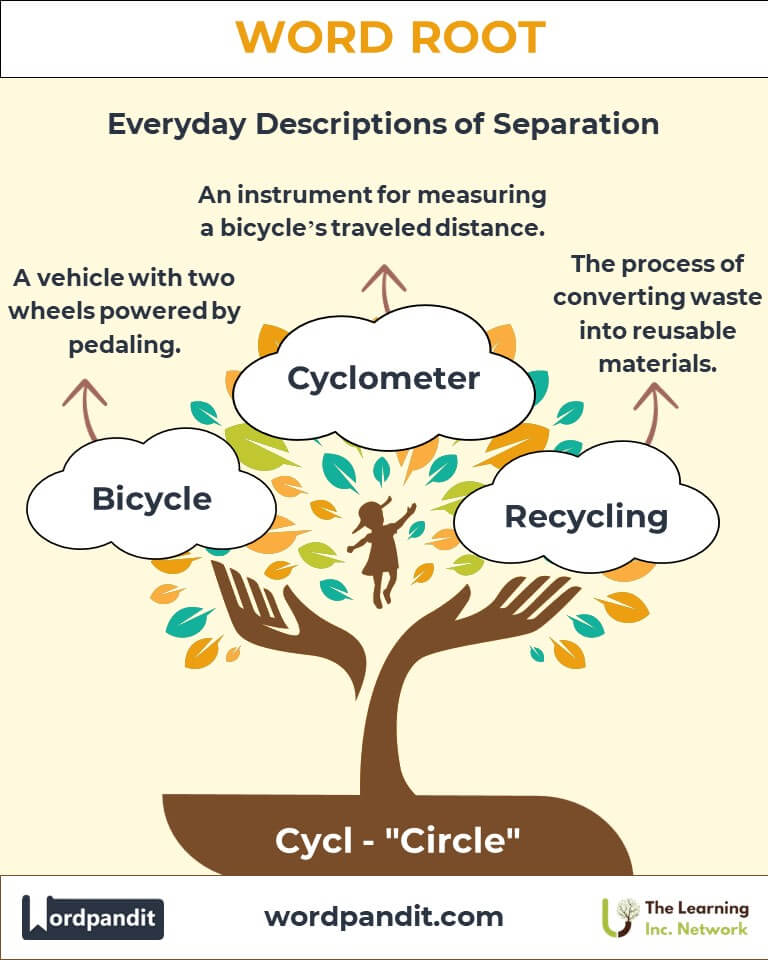
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Magic of "Cycl"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Cycl
- Common Cycl-Related Terms
- Cycl Through Time
- Cycl in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Cycl in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Cycl Root
- The Cycl Family Tree
- FAQs about the Cycl Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Cycl Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Unending Legacy of Cycl
1. Introduction: The Magic of "Cycl"
Imagine a wheel rolling endlessly down a path, symbolizing motion and continuity. This imagery encapsulates the essence of "cycl," a root that signifies circles, cycles, and rotations. Found in words like bicycle and cyclone, "cycl" represents circular motion and recurring systems, playing a pivotal role in both everyday and technical vocabularies.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "cycl" originates from the Greek kyklos, meaning "circle" or "wheel." Ancient Greeks used kyklos to describe physical wheels, circular assemblies, and even the celestial orbits of the stars. Over centuries, this root influenced Latin and English, giving rise to words that capture the essence of cycles and circularity.
Notable linguistic milestones include the Middle Ages, when "cycl-" terms described natural phenomena like whirlwinds, and the Industrial Revolution, which popularized inventions like the bicycle, embodying the root’s circular motion.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Cycl
To remember "cycl," envision a cyclist pedaling a bicycle—the wheels, a perfect metaphor for perpetual motion and cycles.
Mnemonic Device: “Cycl spins through life like a bicycle wheel, round and round, never still!”
4. Common Cycl-Related Terms
- Bicycle (bye-si-kul): A vehicle with two wheels powered by pedaling.
- Example: "She rode her bicycle through the park on a sunny afternoon."
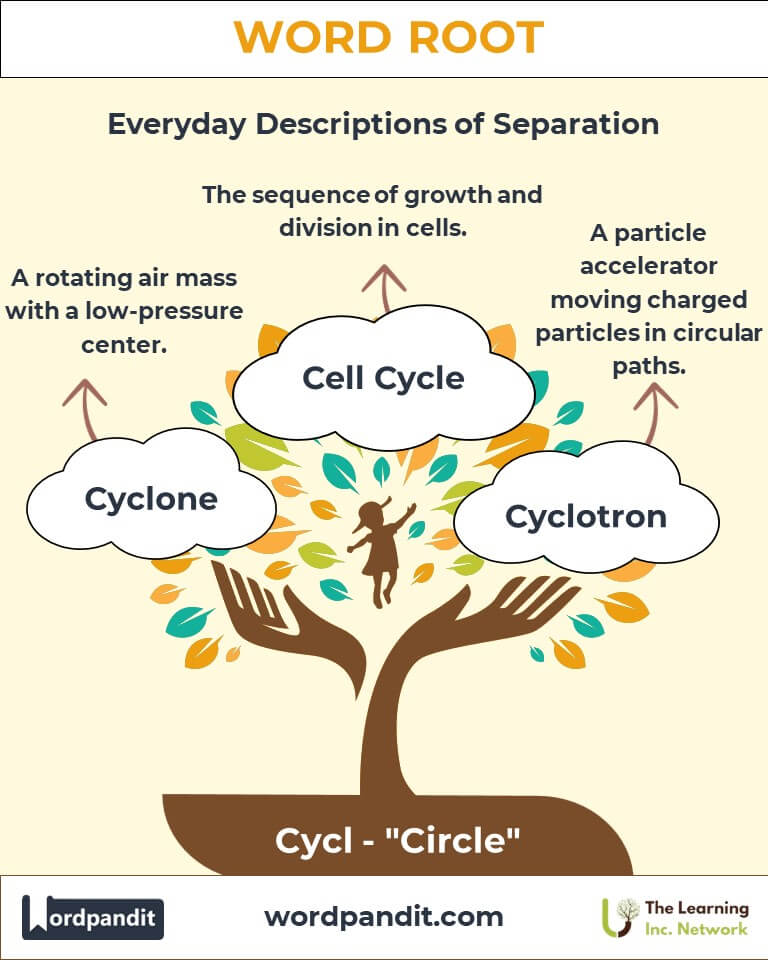
- Cyclone (sy-klone): A large-scale air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure.
- Example: "The cyclone caused widespread damage along the coast."
- Cycle (sy-kul): A series of events that repeat in a predictable order.
- Example: "The life cycle of a butterfly includes four stages."
- Recycling (ree-sy-kl-ing): The process of converting waste into reusable materials.
- Example: "Recycling reduces environmental pollution."
- Cyclometer (sy-klom-i-ter): An instrument for measuring the distance traveled by a bicycle.
- Example: "He attached a cyclometer to track his cycling workouts."
5. Cycl Through Time
- Kyklos (Ancient Greek): Initially referred to wheels and celestial spheres. Over time, it evolved into metaphors for life and cosmic cycles.
- Cyclone (19th Century): First coined to describe large weather systems with rotating winds, capturing the root’s essence of circular motion.
- Recycling (Modern Era): Emerged during the environmental movement, emphasizing the reuse of materials in a sustainable, cyclical process.
6. Cycl in Specialized Fields
- Meteorology:
- Cyclogenesis: The formation of cyclones, crucial for understanding weather patterns.
- Application: Studying cyclogenesis helps predict severe storms.
- Biology:
- Cell Cycle: The sequence of growth and division in cells.
- Application: Central to understanding organism growth and disease progression.
- Physics:
- Cyclotron: A particle accelerator that moves charged particles in circular paths.
- Application: Cyclotrons are used in medical imaging and cancer treatment.
- Engineering:
- Cycle Analysis: Used in thermodynamics to optimize systems like engines.
- Application: Maximizes energy efficiency in power plants.
7. Illustrative Story: Cycl in Action
Lila loved exploring her town on her bicycle, the spinning wheels taking her on endless adventures. One day, a powerful cyclone hit, and she watched in awe as nature mirrored the circular motion of her bike’s wheels. Later, inspired by the cycle of life she observed in her garden, she became an environmental scientist, promoting recycling to protect the planet’s ecosystems. For Lila, "cycl" was more than a root—it was a way of life.
8. Cultural Significance of the Cycl Root
From the mystical "circle of life" in ancient philosophies to the modern emphasis on recycling and sustainability, "cycl" embodies humanity’s fascination with continuity and renewal. In literature, the cycle motif often reflects themes of rebirth and transformation, while in science, it underscores our understanding of nature’s recurring patterns.

9. The Cycl Family Tree
- Circ- (Latin: circle):
- Circumference: The distance around a circle.
- Example: "The circumference of the Earth is about 40,075 kilometers."
- Orb- (Latin: wheel, disk):
- Orbit: The curved path of a celestial object.
- Example: "The Moon’s orbit around Earth takes about 27 days."
- Rot- (Latin: turn):
- Rotate: To spin around an axis.
- Example: "The Earth rotates on its axis once every 24 hours."
10. FAQs About the Cycl Word Root
Q: What does the root "cycl" mean?
A: The root "cycl" means "circle" or "wheel," originating from the Greek word kyklos. It represents anything related to circular motion, cycles, or recurring patterns.
Q: How does "cyclone" connect to the root "cycl"?
A: The word "cyclone" reflects the circular motion of air in a rotating wind system, illustrating the root’s emphasis on circularity.
Q: What is the difference between a "cycle" and a "recycle"?
A: A "cycle" is a sequence of events that repeats in the same order. "Recycle" adds the prefix re-, indicating the act of reusing materials in a closed loop.
Q: What is the role of "cycl" in scientific terms?
A: In terms like "cyclotron" and "cell cycle," the root emphasizes circular motion or repetitive processes in physics and biology.
Q: Why is "cycl" important in meteorology?
A: Terms like "cyclone" and "cyclogenesis" highlight the circular nature of atmospheric movements, central to understanding weather patterns.
11. Test Your Knowledge: Cycl Mastery Quiz
1. What does "cycl" mean?
2. Which term describes a rotating air mass?
3. What does a "cyclometer" measure?
4. Which of these relates to a life process?
5. What’s the Latin equivalent of "cycl"?
12. Conclusion: The Unending Legacy of Cycl
The root "cycl" weaves through language and life, symbolizing motion, cycles, and continuity. From ancient observations of celestial spheres to modern technological marvels like cyclotrons, it bridges the physical and conceptual, inspiring innovation and understanding. As we continue to embrace cycles in sustainability and life, the legacy of "cycl" endures—an eternal loop of meaning and application.














