Dorm: The Root of Sleep and Serenity in Language
Discover the tranquil essence of the root "Dorm," originating from Latin, meaning "sleep." From communal spaces like "dormitories" to states of inactivity like "dormant," this root has embedded its peaceful significance into language and life.
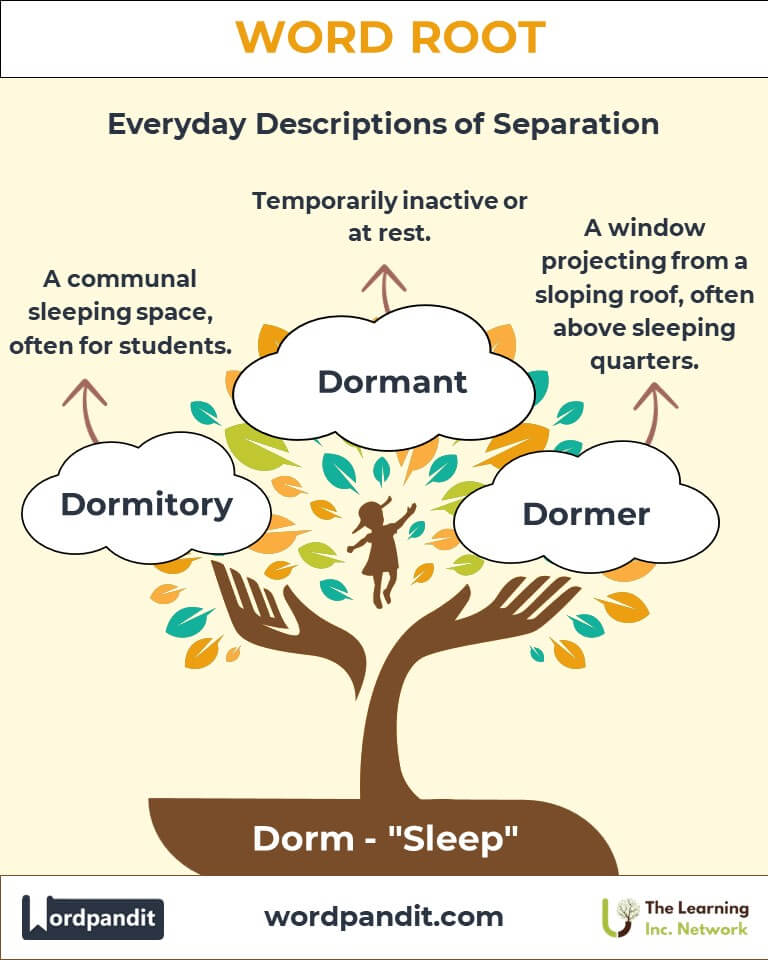
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Restful World of Dorm
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Dorm
- Common Dorm-Related Terms
- Dorm Through Time
- Dorm in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Dorm in Action
- Cultural Significance of Dorm
- The Dorm Family Tree
- FAQs about the Dorm Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Dorm Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Dorm
Introduction: The Restful World of Dorm
Picture the stillness of a snowy mountain, where nature slumbers beneath a white blanket. The word root "Dorm," pronounced "dorm," captures this serenity, symbolizing sleep and rest. Derived from the Latin word dormire (to sleep), this root is foundational in describing states of rest and inactivity, from dormitories that house sleeping students to dormant volcanoes awaiting their next eruption. Across languages and disciplines, "Dorm" serves as a reminder of the essential need for rest.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The word "Dorm" traces its origins to the Latin dormire, meaning "to sleep." As Latin influenced Romance languages, variations like the French dormir and Italian dormire emerged. The term entered English in the Middle Ages, initially describing places of communal sleeping, such as monasteries. Over time, "Dorm" expanded into metaphorical uses, reflecting states of inactivity or hibernation.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Dorm
To remember "Dorm," visualize a dormitory filled with peaceful, sleeping students. Imagine the snoozing figures as symbols of rest and rejuvenation.
Common Dorm-Related Terms
- Dormitory (dor-muh-tor-ee): A communal sleeping space, often for students.
Example: "The college dormitory buzzed with life during the day but quieted at night." - Dormant (dor-muhnt): Temporarily inactive or at rest.
Example: "The dormant volcano hadn't erupted in centuries but was closely monitored." - Dormer (dor-mer): A window projecting from a sloping roof, often above sleeping quarters.
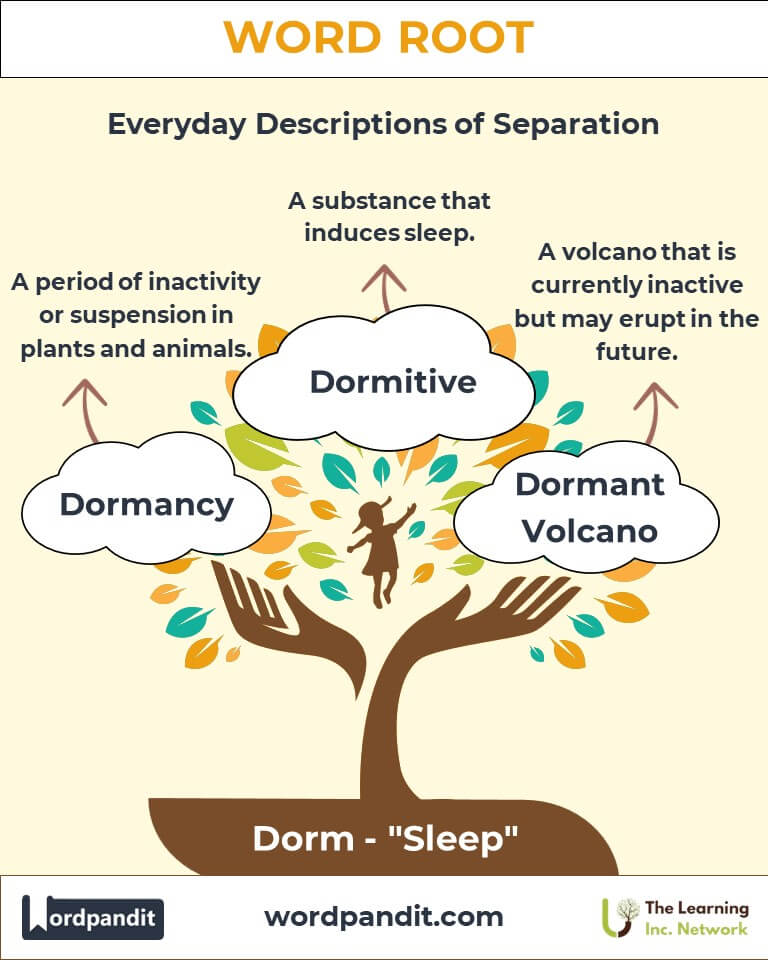
Example: "The cozy attic bedroom featured a charming dormer window." - Dormancy (dor-muhn-see): A period of inactivity or suspension.
Example: "The seeds remained in dormancy until spring rains awakened them." - Dormitive (dor-mi-tiv): Something that induces sleep.
Example: "The herbal tea acted as a natural dormitive for her sleepless nights."
Dorm Through Time
- Dormitorium (Medieval Latin): Originally referred to monastic sleeping quarters.
Evolution: This term eventually became "dormitory" in modern English, extending its use to schools and colleges. - Dormant (16th Century): Borrowed from French, it described inactive states, such as hibernating animals or idle machinery.
Modern Use: The term now applies to various fields, including biology, geology, and business.
Dorm in Specialized Fields
Biology:
Dormancy: Refers to a state where growth, development, and physical activity are temporarily halted.
Example: "Plants enter dormancy during winter to conserve energy."
Geology:
Dormant Volcanoes: Volcanoes that have not erupted recently but retain the potential to do so.
Example: "Mount Rainier is considered a dormant volcano."
Pharmacology:
Dormitive Substances: Used to induce sleep or sedation.
Example: "Dormitives like melatonin are popular for managing jet lag."
Architecture:
Dormers: Structural elements used to add light and space to upper rooms, often near sleeping quarters.
Example: "Dormer windows give the attic a quaint, inviting appearance."
Illustrative Story: Dorm in Action
In a bustling university, Clara struggled to adjust to the noisy dormitory life. One night, overwhelmed by the chaos, she sought refuge in the library’s quiet dormancy. As she sat by the dormer window, gazing at the serene campus below, she found inspiration for her essay on "Dormancy in Nature." That tranquil night not only rejuvenated her spirit but also helped her appreciate the balance between activity and rest—a harmony reflected in the root "Dorm."
Cultural Significance of Dorm
The concept of sleep and rest, encapsulated by "Dorm," is celebrated across cultures. Ancient myths often depicted gods and spirits associated with sleep, like Hypnos in Greek mythology. Architecturally, dormitories have long symbolized communal living, from monastic settings to modern universities. In literature, dormancy frequently serves as a metaphor for potential or hidden strength, as seen in phrases like "dormant talents."

The Dorm Family Tree
- Somn- (Latin: "sleep"):
Examples: Insomnia, Somnolent. - Hypno- (Greek: "sleep"):
Examples: Hypnosis, Hypnotherapy. - Narc- (Greek: "numbness or sleep"):
Examples: Narcolepsy, Narcotic.
FAQs About the Dorm Word Root
Q: What does "Dorm" mean?
A: "Dorm" means "sleep," originating from the Latin dormire. It serves as the root for words related to rest, inactivity, or dormancy, such as "dormitory" and "dormant."
Q: What is the difference between "Dormant" and "Dormitory"?
A: "Dormant" describes something inactive or at rest, such as a volcano or plant that is temporarily not active. A "dormitory" is a communal sleeping area typically used in schools or colleges.
Q: What is a Dormer Window?
A: A dormer window is a structural feature that projects from a sloping roof, usually to provide light and ventilation to an attic or upper-level sleeping quarters.
Q: Why do plants enter dormancy?
A: Plants enter dormancy to survive adverse conditions, such as cold winters or dry seasons. During dormancy, metabolic activities slow down, allowing the plant to conserve energy and water until favorable conditions return.
Q: What are dormitives?
A: Dormitives are substances that induce sleep or a state of relaxation. They can be natural, such as chamomile, or pharmaceutical, like sedatives used to treat insomnia.
Q: Are dormant volcanoes extinct?
A: No, dormant volcanoes are not extinct. They are currently inactive but still have the potential to erupt in the future. Examples include Mount Fuji in Japan and Mount Rainier in the U.S.
Q: What is dormancy in seeds?
A: Dormancy in seeds is a natural survival mechanism where germination is delayed until environmental conditions, such as temperature or moisture, are optimal for growth.
Test Your Knowledge: Dorm Mastery Quiz
1. What does "Dorm" mean?
2. Which term describes a state of temporary inactivity?
3. What is a dormitive?
4. What does "Dormitory" refer to?
5. What is dormancy in biology?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Dorm
The root "Dorm" reminds us of the vital role rest plays in life. From seeds lying dormant to students resting in dormitories, it reflects the universal need for rejuvenation and potential waiting to be unleashed. As language evolves, "Dorm" continues to symbolize the tranquil balance between rest and action, inspiring us to appreciate the cycles of activity and repose in our own lives.














