Electro: The Spark of Energy in Language and Innovation
Discover how the root "electro," originating from the Greek word for amber, powers a vocabulary of innovation and energy. From "electricity" to "electron," this root connects the ancient with the modern, shaping the way we understand the natural world and technology alike.
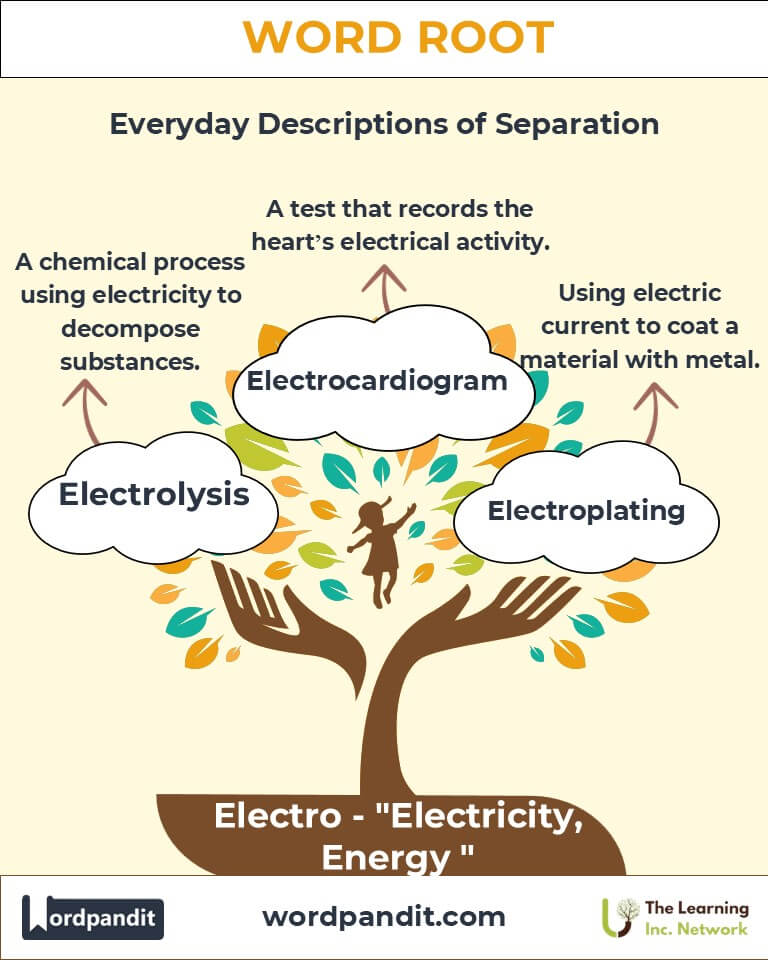
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Electro
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Electro
- Common Electro-Related Terms
- Electro Through Time
- Electro in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Electro in Action
- Cultural Significance of Electro
- The Electro Family Tree
- FAQs about the Electro Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Electro Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Electro
Introduction: The Essence of Electro
What do a crackling lightning storm, your favorite gadget, and the word "electricity" have in common? They all draw from the root "electro," a term derived from the Greek word ēlektron (amber). Pronounced "ee-lek-tro," this root represents the natural forces of energy and charge that sparked both ancient wonder and modern technological revolutions.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "electro" traces back to the Greek word ēlektron, meaning amber. Amber, a fossilized tree resin, was known in ancient times for producing static electricity when rubbed against cloth. This phenomenon inspired William Gilbert in the 1600s to coin the term "electricus," laying the foundation for the modern study of electricity. Over centuries, "electro" became a key component of scientific and technological vocabulary, encapsulating energy, charge, and electronic innovation.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Electro
Imagine a glowing amber stone radiating sparks of energy, a symbol of ancient discovery lighting the way to modern science.
Mnemonic Device: “Electro ignites energy, from amber’s glow to electronic flow!”
Common Electro-Related Terms
- Electricity (ee-lek-tri-si-tee): A form of energy resulting from the movement of charged particles.
- Electron (ee-lek-tron): A subatomic particle with a negative charge.
- Electrolysis (ee-lek-trol-uh-sis): A chemical process that uses electricity to decompose substances.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): A medical test that measures the electrical activity of the heart.
- Electromagnetic (ee-lek-troh-mag-net-ik): Relating to electric and magnetic fields and their interactions.
Electro Through Time
- Electrometer (1700s): Devices measured small electric charges.
- Electromotive Force (1800s): Drove advancements in energy research.
- Electronics (1900s–Present): The root "electro" now powers an array of modern innovations.
Electro in Specialized Fields
- Medicine: Electroencephalogram (EEG) records brain electrical activity.
- Physics: Electrodynamics studies charge interactions.
- Chemistry: Electroplating deposits metal using electric current.
- Environmental Science: Electrostatic precipitators reduce pollution using electric charge.
Illustrative Story: Electro in Action
In a small lab, Dr. Elena Alvarez was working on a breakthrough in sustainable energy storage. Inspired by the natural properties of amber and the flow of electrons, she developed an innovative electrochemical cell. This battery promised to revolutionize renewable energy, proving that the ancient root "electro" still sparks innovation in modern times.
Cultural Significance of Electro
The root "electro" symbolizes humanity’s fascination with energy and its harnessing. From ancient myths about lightning bolts to the life-changing advent of electricity, it has illuminated paths of progress. Today, "electro" also permeates pop culture, influencing music genres (electronic dance music) and technology-driven art forms.

The Electro Family Tree
- Phon (Sound): Microphone, Telephone
- Magnet (Magnetic): Magnetism, Electromagnet
- Volt (Electric Potential): Voltage, Voltmeter
FAQs About the Electro Word Root
Q1: What does "electro" mean, and where does it come from?
A1: "Electro" means "energy," "electricity," or "charge." It originates from the Greek word ēlektron, which means "amber." Ancient Greeks discovered that rubbing amber created static electricity, which later inspired the study and naming of electrical phenomena.
Q2: Why is amber significant in the history of electricity?
A2: Amber is a fossilized tree resin that, when rubbed, can attract small objects like feathers or dust. This observation, made by the Greeks, was one of the earliest recorded phenomena of static electricity. This connection between amber and electricity laid the groundwork for the term "electro."
Q3: How is the root "electro" used in medicine?
A3: In medicine, "electro" appears in terms like electrocardiogram (ECG) and electroencephalogram (EEG). These technologies measure the electrical activity of the heart and brain, respectively, helping diagnose conditions like arrhythmias or epilepsy.
Q4: What’s the difference between electricity and electronics?
A4: Electricity refers to the flow of energy resulting from charged particles. Electronics, on the other hand, involves devices that control, manipulate, and utilize this flow of energy, such as computers, smartphones, and appliances.
Q5: What is electrolysis, and where is it used?
A5: Electrolysis is a chemical process that uses an electric current to break down substances. For example, it splits water into hydrogen and oxygen or is used in refining metals like aluminum and copper. It is also employed in beauty treatments like hair removal.
Q6: What is electromagnetism, and why is it important?
A6: Electromagnetism is the interaction between electric currents and magnetic fields. It forms the basis of countless technologies, including electric motors, generators, and wireless communication systems.
Q7: What role do electrons play in electricity?
A7: Electrons are negatively charged particles that move through conductive materials to create an electric current. Their flow powers everything from lightbulbs to advanced computing systems.
Test Your Knowledge: Electro Mastery Quiz
1. What does "electro" mean?
2. What particle carries a negative charge?
3. What is electroplating used for?
4. What field studies electric and magnetic interactions?
5. What is an electrocardiogram (ECG) used for?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Electro
From amber’s mysterious glow to the boundless innovations of modern electronics, the root "electro" embodies energy, discovery, and progress. As technology continues to advance, "electro" remains at the forefront, sparking ideas that shape the future. Explore its applications and feel the charge of inspiration it provides!














