Eremo: The Root of Isolation and Solitude in Language and Nature
Byline
Dive into the depth of the root "Eremo", derived from Greek and Latin, meaning "desert" or "solitary." From scientific terms like eremology to ecological descriptors such as eremophyte, this root unveils the linguistic and natural worlds of solitude, resilience, and the art of thriving in barren spaces.
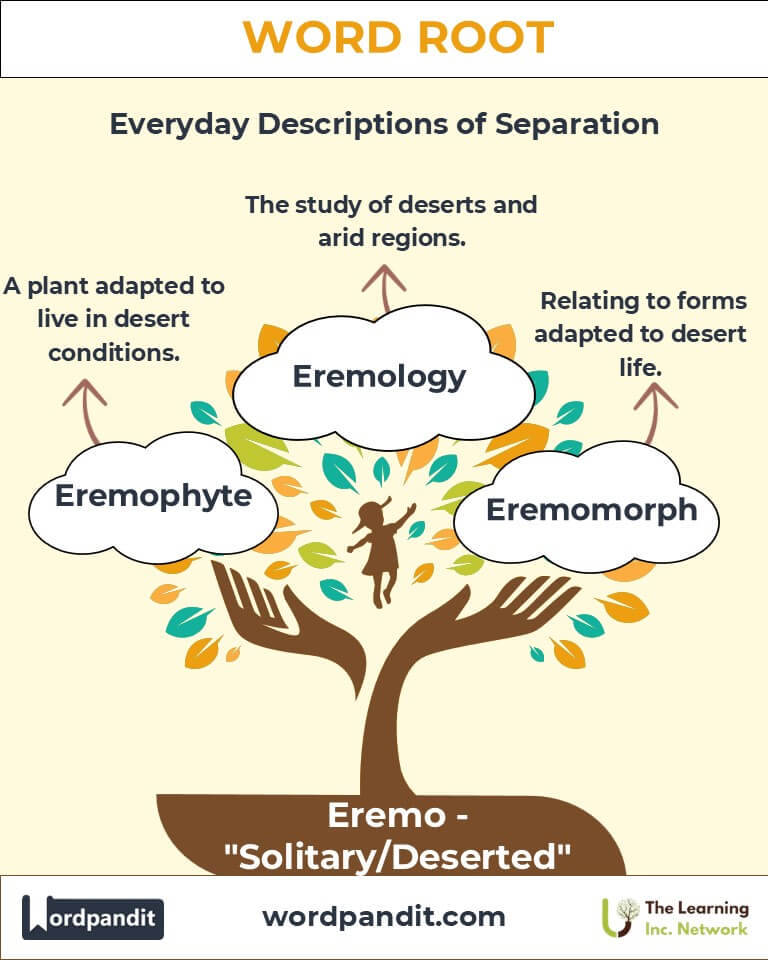
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Eremo
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Eremo
- Common Eremo-Related Terms
- Eremo Through Time
- Eremo in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Eremo in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Eremo Root
- The Eremo Family Tree
- FAQs about the Eremo Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Eremo Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Eremo
Introduction: The Essence of Eremo
What does a barren desert, a secluded hermit, and the science of arid zones have in common? They all trace their roots to "Eremo" (pronounced air-eh-moh), a word signifying solitude and desert-like qualities. Originating from Greek "erēmos" and Latin "eremus", meaning “desert” or “solitary,” the root paints a vivid picture of isolation and resilience. It finds its applications in ecology, philosophy, and even societal metaphors, making it as enduring as the deserts it describes.

Etymology and Historical Journey
- Greek "erēmos": Meaning "lonely, deserted."
- Latin "eremus": Used to describe wilderness or deserted places.
In ancient times, the desert was not just a geographical location but also a metaphor for spiritual solitude. Early Christian hermits and ascetics retreated to deserts, giving rise to terms like eremite (a hermit). This root evolved into scientific and ecological terminology as human understanding of deserts and their significance grew.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Eremo
To remember "Eremo," visualize a lone cactus standing resilient in a vast, empty desert under a blazing sun.
Mnemonic Device:
"Eremo is where the earth feels alone, but life quietly thrives."
Common Eremo-Related Terms
- Eremology (air-eh-mol-uh-jee): The study of deserts and arid regions.
Example: "Her research in eremology helped predict how climate change might affect desert ecosystems." - Eremophyte (air-eh-moh-fite): A plant adapted to live in desert conditions.
Example: "The cactus is a classic eremophyte, thriving where few other plants can." - Eremite (air-eh-mite): A person who lives in solitude, often for spiritual reasons.
Example: "The eremite built a small hut in the wilderness to meditate in peace." - Eremophobia (air-eh-moh-foh-bee-uh): Fear of solitude or deserted places.
Example: "Her eremophobia made the idea of traveling alone unbearable." - Eremic (air-eh-mik): Pertaining to deserts or arid conditions.
Example: "The eremic landscape stretched endlessly, barren and silent."
Eremo Through Time
- Eremite (Ancient Context): Early Christian monks, like St. Anthony, became eremites, retreating to deserts for spiritual enlightenment.
- Eremology (Modern Science): Coined in the 20th century, it highlights humanity’s growing interest in studying deserts as ecosystems teeming with life.
Eremo in Specialized Fields
- Ecology: Eremophyte plants like cacti are pivotal in understanding adaptations to arid environments.
- Spiritual Studies: The eremite symbolizes solitude and introspection in religious and philosophical traditions.
- Geography: Eremic zones are defined by extreme aridity, crucial for climate studies and conservation.
Illustrative Story: Eremo in Action
Amira, a young ecologist, ventured into the Sahara to study eremophytes. Her mission was to understand how these resilient plants survived in harsh conditions. During her research, she met an elderly eremite, living a simple life amidst the dunes. He shared stories of the desert’s wisdom, teaching her that solitude often reveals life’s most profound lessons. Inspired, Amira used her findings to advocate for preserving these unique ecosystems, highlighting the harmony between nature and solitude.
Cultural Significance of the Eremo Root
- Religious Solitude: From Christian hermits to Hindu ascetics, deserts symbolize spiritual testing and enlightenment.
- Symbol of Resilience: Deserts and their life forms embody endurance and adaptation, resonating with human struggles and triumphs.

The Eremo Family Tree
- Arid (Latin "aridus"): Meaning dry or barren. Example: "Arid landscapes challenge even the toughest species."
- Desert (Latin "desertus"): Meaning abandoned or left behind. Example: "Deserts are ecosystems with unique biodiversity."
- Sol (Latin "solus"): Meaning alone. Example: "Solitude often leads to profound self-discovery."
FAQs About the Eremo Root
Q: What does “Eremo” mean?
A: The root "Eremo" means "desert" or "solitary," derived from the Greek word "erēmos" and the Latin word "eremus", both of which describe isolated, barren landscapes or a state of solitude. This root is the foundation for terms that connect with themes of isolation, resilience, and life in harsh environments.
Q: What is Eremology?
A: Eremology is the scientific study of deserts, their ecosystems, and their unique flora and fauna. This field focuses on understanding how organisms adapt to arid environments and the ecological importance of deserts, which cover approximately one-third of Earth’s surface.
Q: What is an Eremophyte?
A: An Eremophyte is a plant specifically adapted to survive in arid, desert-like conditions. Examples include cacti, succulents, and xerophytes. These plants demonstrate unique adaptations like water storage tissues, reduced leaf surfaces, and deep root systems, making them critical to desert ecosystems.
Q: How is Eremo used metaphorically?
A: Beyond its literal connection to deserts, Eremo symbolizes solitude, introspection, and resilience. For example, an eremite represents someone who retreats into solitude for spiritual or philosophical reasons, akin to the isolation of a desert.
Q: What does Eremophobia describe?
A: Eremophobia is the fear of solitude or deserted places. This condition can stem from anxiety about being alone, discomfort in quiet spaces, or a fear of abandonment. It contrasts sharply with the positive connotations of solitude found in spiritual or meditative practices.
Q: What is an Eremic Zone?
A: An Eremic Zone refers to regions characterized by extreme aridity, such as deserts or semi-deserts. These areas are often sparsely vegetated and experience low annual rainfall, making them challenging yet fascinating ecosystems to study.
Q: Why are deserts important despite their barrenness?
A: Deserts are vital to global biodiversity and climate regulation. They support unique species, store minerals, and play a role in atmospheric circulation. Studying eremology helps us understand these critical contributions.
Test Your Knowledge: Eremo Mastery Quiz
1. What does “Eremo” mean?
2. What is Eremology?
3. Which term describes a desert-adapted plant?
4. What does Eremophobia mean?
5. What is an Eremite?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Eremo
The root "Eremo" bridges the worlds of nature and introspection, from the barren deserts that challenge life to the solitude that fosters self-discovery. As both a scientific and cultural cornerstone, it reminds us of resilience and the quiet power of thriving against the odds. In a world often bustling with noise, Eremo inspires us to embrace solitude and uncover the profound truths within.














