Etho: The Foundation of Character in Language and Culture
Dive into the world of "etho," the linguistic root of "character" that defines behavior, principles, and shared values. Originating from Greek, this root shapes words like "ethology" (the study of behavior) and "ethos" (a community's guiding spirit). Join us as we explore its etymology, applications, and cultural significance.
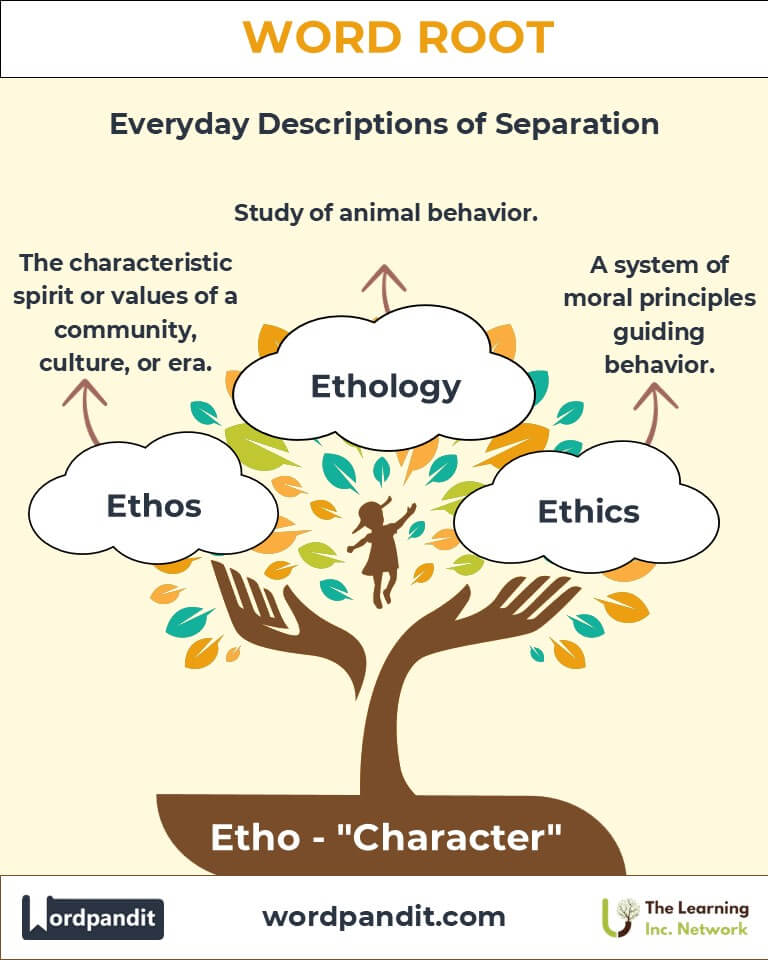
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Core of "Etho"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Etho"
- Common Etho-Related Terms
- Etho Through Time
- Etho in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Etho" in Action
- Cultural Significance of the "Etho" Root
- The "Etho" Family Tree
- FAQs about the "Etho" Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Etho Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Etho"
Introduction: The Core of "Etho"
What makes a person trustworthy or a community harmonious? The answer often lies in "etho," a root that embodies character and guiding principles. Pronounced "ee-tho," it stems from Greek and influences words that explore individual and collective behavior. From ancient philosophy to modern psychology, "etho" captures the essence of character and values.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "etho" originates from the Greek ἦθος (ēthos), meaning "custom" or "character." Initially, it referred to habitual behavior or societal norms. Greek philosophers like Aristotle expanded its use, linking ethos to moral character and persuasive rhetoric. Over centuries, "etho" embedded itself into English vocabulary, shaping concepts of ethics, behavior, and cultural identity.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Etho"
Picture a tree with deep roots labeled "ETHO." The tree represents character, with its branches spreading into behaviors and societal values.
Mnemonic Device: "Etho is the root of character—growing behaviors and values that define who we are."
Common Etho-Related Terms
- Ethology (ee-thol-uh-jee): The scientific study of animal behavior, particularly under natural conditions.
- Example: "Jane Goodall's work in ethology revolutionized our understanding of primates."
- Ethos (ee-thos): The characteristic spirit or values of a community, culture, or era.
- Example: "The company's ethos emphasizes innovation and sustainability."
- Ethics (eth-iks): A system of moral principles guiding behavior.
- Example: "Medical ethics require doctors to prioritize patient well-being."
- Ethnocentric (eth-no-sen-trik): Evaluating other cultures based on the standards of one's own.
- Example: "Her ethnocentric perspective limited her understanding of cultural diversity."
- Ethnology (eth-nol-uh-jee): The branch of anthropology that studies cultures and their relationships.
- Example: "Ethnology examines how traditions shape societal norms."
Etho Through Time
- Ancient Ethos: In Aristotle’s rhetoric, ethos referred to the speaker's credibility as a persuasive tool.
- Modern Ethics: During the Enlightenment, "ethics" evolved into a formal discipline studying morality.
- Behavioral Studies: In the 20th century, "ethology" emerged, blending biological and psychological insights.
Etho in Specialized Fields
- Behavioral Science: Ethology examines innate and learned behaviors in humans and animals, bridging biology and psychology.
- Rhetoric: Ethos forms one of Aristotle's rhetorical appeals, emphasizing credibility in persuasion.
- Cultural Studies: Ethnology explores cultural patterns and their impact on identity and society.
Illustrative Story: "Etho" in Action
In a bustling village, a teacher named Elena embodied the ethos of her community—honesty and kindness. Her lessons often included tales of animal behavior (ethology), drawing parallels between nature and human morality. One day, a student asked, “Why do we trust you so much?” Elena replied, “Because I live by our values.” Her character became a beacon, proving that ethos isn’t just taught—it’s lived.
Cultural Significance of the "Etho" Root
From philosophical treatises to modern branding, "etho" underscores the importance of character and values. It shapes literature, art, and even political ideologies, emphasizing the shared principles that define communities.

The "Etho" Family Tree
- Ethn- (Nation or People): Root of words like ethnography (cultural study).
- Ethic- (Moral Principles): Root of words like bioethics (morality in biology).
- Pathos (Emotion): Complementary to ethos, focusing on emotional appeal.
FAQs About the "Etho" Root
Q: What does "etho" mean?
A: "Etho" means "character" or "custom." It originates from the Greek root ἦθος (ēthos).
Expanded Explanation: Initially referring to habitual behavior or societal norms, it has come to encompass moral or ethical character, influencing individual and collective actions.
Q: How is "etho" connected to "ethics"?
A: Ethics is derived from the same root and focuses on moral principles that govern behavior.
Expanded Explanation: While "etho" refers broadly to character or guiding customs, ethics specifically deals with questions of right and wrong, providing frameworks for personal and professional decision-making.
Q: What is ethology, and why is it significant?
A: Ethology is the study of animal behavior, particularly in natural conditions.
Expanded Explanation: It bridges biology and psychology, helping us understand how behavior evolves and adapts. Its applications range from conservation efforts to insights into human behavior from an evolutionary perspective.
Q: What is the difference between ethos and ethics?
A: Ethos refers to the characteristic spirit or shared values of a group, while ethics focuses on moral principles guiding behavior.
Expanded Explanation: For example, a company’s ethos might emphasize sustainability, while its ethics ensure fair treatment of workers and customers.
Q: Why is ethos important in rhetoric?
A: In rhetoric, ethos establishes the speaker's credibility and moral character, making their argument more persuasive.
Expanded Explanation: Aristotle identified ethos as one of the three rhetorical appeals (along with logos and pathos). A speaker with strong ethos is trusted and respected by the audience.
Q: What does ethnology study?
A: Ethnology examines the relationships between cultures, their traditions, and their interactions.
Expanded Explanation: It focuses on understanding cultural diversity and the ways societies organize their lives, often comparing them to find commonalities and differences.
Q: How has the root "etho" influenced modern language?
A: "Etho" has given rise to words like ethics, ethos, and ethology, foundational in philosophy, behavioral science, and cultural studies.
Expanded Explanation: Its influence helps articulate principles, behaviors, and values central to human and societal development.
Q: What are some real-world examples of ethos?
A: A company’s ethos might focus on sustainability, like Patagonia’s environmental responsibility. Similarly, Mahatma Gandhi’s ethos of nonviolence shaped India’s independence movement.
Expanded Explanation: These examples demonstrate how ethos guides behavior and decisions in impactful ways.
Q: Why is ethology relevant today?
A: Ethology is crucial for studying the behavior of animals, especially in conservation efforts.
Expanded Explanation: Understanding migration patterns or mating habits helps protect endangered species and provides insights into human psychology through evolutionary behavior.
Q: How do ethics influence society?
A: Ethics form the foundation of laws, professional conduct, and interpersonal relationships.
Expanded Explanation: They promote trust, cooperation, and fairness in societies. For example, medical ethics ensure doctors prioritize patient welfare, while business ethics prevent fraud and promote accountability.
Quiz: Test Your Knowledge About the "Etho" Root
1. What does the root "etho" mean?
2. Which term refers to the study of animal behavior in natural conditions?
3. What does ethos represent in rhetoric?
4. What is the primary focus of ethics?
5. Which term describes the shared values and spirit of a group or culture?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Etho"
The root "etho" bridges past and present, linking ancient philosophical ideals to modern discussions on behavior and values. Its influence spans disciplines, reminding us that character shapes individuals and societies alike. Embrace "etho" in your vocabulary and life, letting its lessons inspire character-driven growth and understanding.














