Hapl: The Root of Simplicity in Biology and Beyond
Byline: Discover the profound simplicity embedded in the root "hapl," derived from Greek, meaning "simple" or "single." From biological concepts like haploid to genetic classifications like haplotype, this root illustrates the elegance of singularity in science and language.
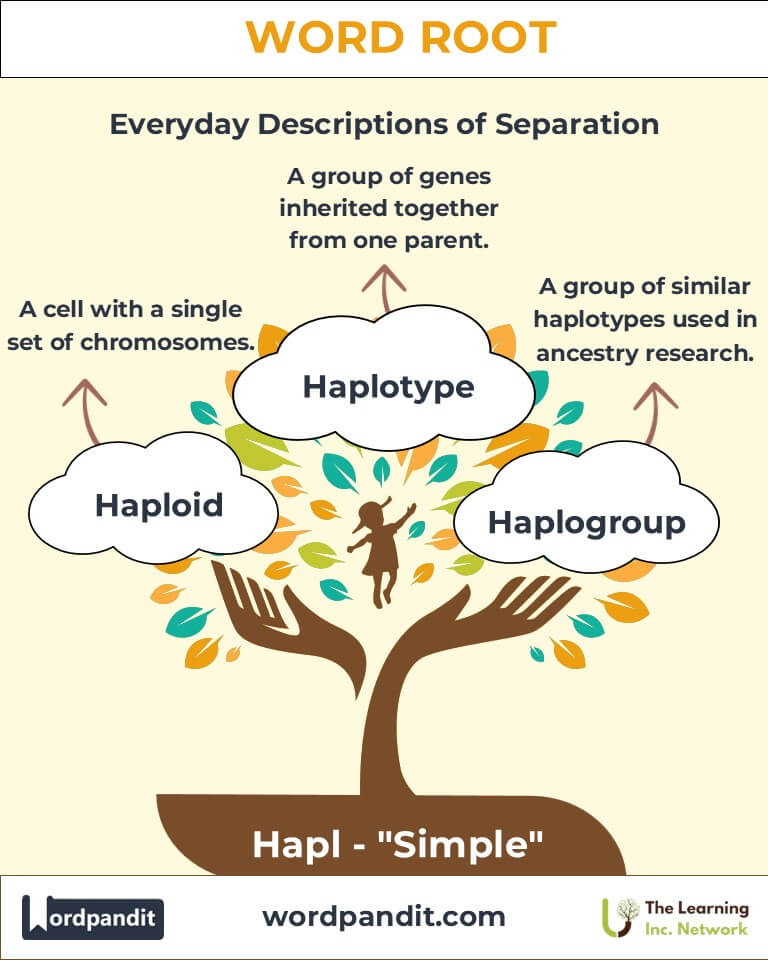
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Power of Simplicity in Hapl
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Hapl
- Common Hapl-Related Terms
- Hapl Through Time
- Hapl in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Hapl in Action
- Cultural Significance of Hapl
- The Hapl Family Tree
- FAQs About the Geo Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Geo Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Enduring Elegance of Hapl
Introduction: The Power of Simplicity in Hapl
What makes simplicity so powerful? The word root hapl, pronounced "hap-l," encapsulates this idea. Originating from Greek, it means "simple" or "single." This root is integral to scientific vocabulary, particularly in biology and genetics, where it helps describe phenomena that rely on singular or uncomplicated structures, such as haploid cells or haplotypes. Its usage extends beyond science, reminding us of the beauty in simplicity.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root hapl comes from the Greek word haplous, meaning "single" or "simple." Early uses of the term appeared in classical Greek texts to contrast complexity with simplicity. In the 19th century, as scientific terminology grew, the root was adopted to describe concepts in genetics and cell biology, such as haploid cells—those containing a single set of chromosomes.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Hapl
To remember hapl, think of a simple, single-leaf sprout emerging from the ground. This lone sprout embodies the idea of simplicity and singularity.
Mnemonic Device: "Hapl = Happy in being Simple."
Common Hapl-Related Terms
- Haploid (hap-loid): A cell or organism with a single set of chromosomes.
Example: "Gametes, such as sperm and egg cells, are haploid, containing half the genetic material of a diploid cell." - Haplotype (hap-loh-type): A group of genes inherited together from a single parent.
Example: "Scientists studied the haplotypes of a population to trace genetic diseases." - Haplogroup (hap-loh-groop): A group of similar haplotypes, often used in ancestry research.
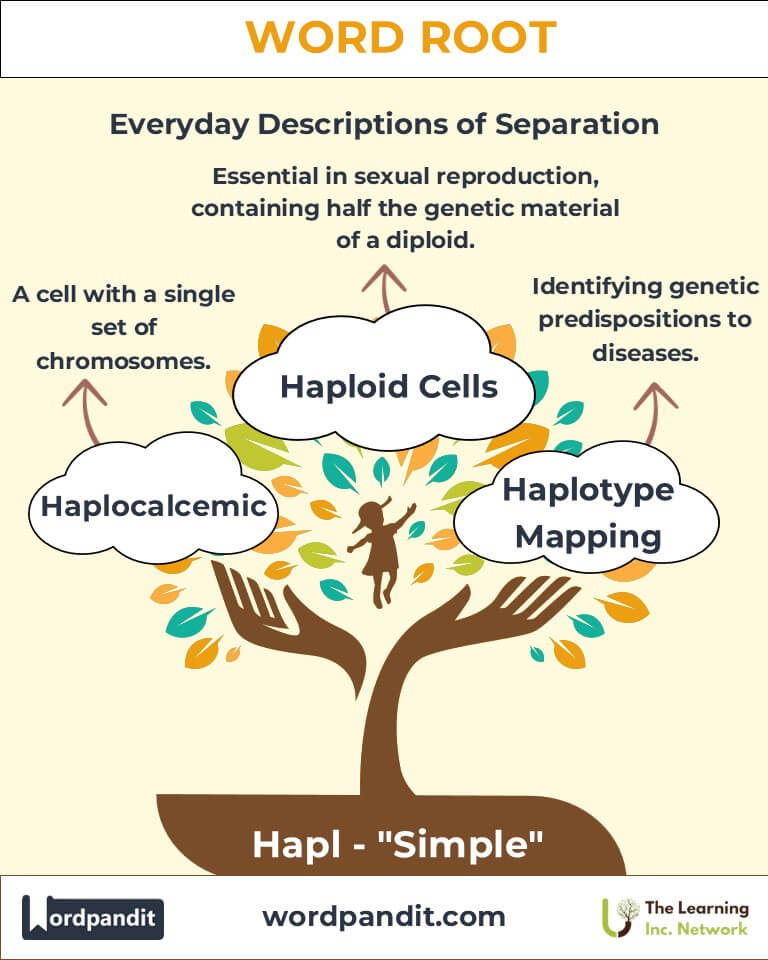
Example: "My ancestry test revealed my haplogroup originated in ancient Europe." - Haplocalcemic (hap-loh-kal-see-mik): Describes a state of having a single center of calcium control, often used in scientific research.
Example: "The haplocalcemic properties of the organism simplified calcium regulation studies."
Hapl Through Time
- Haploid (1800s): First used in biology to describe single-set chromosome cells in reproduction.
- Haplotype (1900s): Introduced in genetics to describe a set of genes inherited from one parent.
- Haplogroup (Modern Era): Expanded into ancestry studies, where genetic patterns reveal human migrations.
Hapl in Specialized Fields
- Biology:
Haploid Cells: Crucial for understanding sexual reproduction and genetic diversity. - Genetics:
Haplotypes: Essential for tracking hereditary diseases and personalized medicine. - Anthropology:
Haplogroups: Used in tracing human evolutionary history and migrations. - Medicine:
Haplotype Mapping: Helps identify genetic predispositions to diseases.
Illustrative Story: Hapl in Action
Dr. Emily Carter, a geneticist, was on a mission to find the genetic basis of a rare disorder affecting a small village. By analyzing the villagers' haplotypes, she discovered a mutation carried by a single haplogroup. Her breakthrough led to a targeted treatment plan that saved countless lives. The simplicity of focusing on one haplotype illuminated the path to complex solutions.
Cultural Significance of Hapl
While primarily scientific, the idea of hapl—simplicity—resonates culturally. Philosophers and minimalists alike celebrate the power of singularity and simplicity. In literature and art, the concept of reducing complexity to its essence often mirrors the root's significance.

The Hapl Family Tree
Related Roots:
- Mono- (Greek: single):
Examples: Monochrome (one color), Monologue (a single speech). - Uni- (Latin: one):
Examples: Unilateral (involving one side), Unique (one of a kind). - Simplex (Latin: simple):
Examples: Simplify (to make simple), Simpleton (a person of simplistic thinking).
FAQs About the Hapl Word Root
Q: What does the root "hapl" mean?
A: The root "hapl" originates from the Greek word haplous, meaning "simple" or "single." It is used in scientific contexts to describe things that are uncomplicated, singular, or possessing a single structure or function, such as a haploid cell with one set of chromosomes.
Q: What is a haploid cell, and why is it important?
A: A haploid cell contains a single set of chromosomes, unlike diploid cells, which have two sets. Haploid cells are essential in sexual reproduction since they combine during fertilization to create a diploid zygote, restoring the full chromosome number in an organism. Examples include sperm and egg cells in humans.
Q: What is a haplotype, and how is it different from a gene?
A: A haplotype is a group of genes or DNA sequences that are inherited together from a single parent due to their proximity on a chromosome. Unlike an individual gene, which represents a single unit of heredity, a haplotype captures a pattern of inheritance across multiple genes or markers, often used in genetic research to study ancestry or disease predisposition.
Q: What is the significance of haplogroups in ancestry research?
A: Haplogroups are classifications of related haplotypes that share a common ancestor. They are often used in genetic testing to trace human migrations and ancestral origins. For instance, mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroups trace maternal lineage, while Y-chromosome haplogroups trace paternal lineage.
Q: How do haplotypes aid in medical research?
A: Haplotypes help identify genetic variations linked to specific diseases. By studying haplotypes, researchers can uncover genetic predispositions to conditions like diabetes or heart disease and develop targeted therapies. They also assist in personalized medicine, tailoring treatments based on a patient's genetic makeup.
Q: How does "hapl" contrast with related terms like "diplo"?
A: While "hapl" refers to "single" or "simple," "diplo" means "double." For example, diploid cells have two sets of chromosomes, one from each parent, whereas haploid cells have only one. The contrast highlights the distinction between stages of cell division and reproduction.
Q: Is the root "hapl" used outside of biology?
A: Though primarily used in scientific contexts like biology and genetics, "hapl" can metaphorically represent simplicity or singularity. In broader usage, it may signify reduction to essential elements, such as simplifying a concept or idea.
Test Your Knowledge: Hapl Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "hapl" mean?
2. Which describes a single set of chromosomes?
3. A haplogroup is used in which field of study?
4. What is a haplotype?
5. Which prefix also means "single"?
Conclusion: The Enduring Elegance of Hapl
The root hapl reminds us that simplicity often holds the key to profound insights. From genetics to philosophy, its significance spans disciplines, reflecting the elegance of singularity. As science and language evolve, hapl continues to guide our understanding of the simple structures underpinning complex phenomena.














