Hedon: The Pursuit of Pleasure in Language and Life
Discover the captivating essence of the root "Hedon," derived from the Greek word for pleasure. Whether highlighting lifestyles of indulgence (hedonist) or examining the absence of joy (anhedonism), this root has shaped how we discuss emotions, well-being, and the human condition.
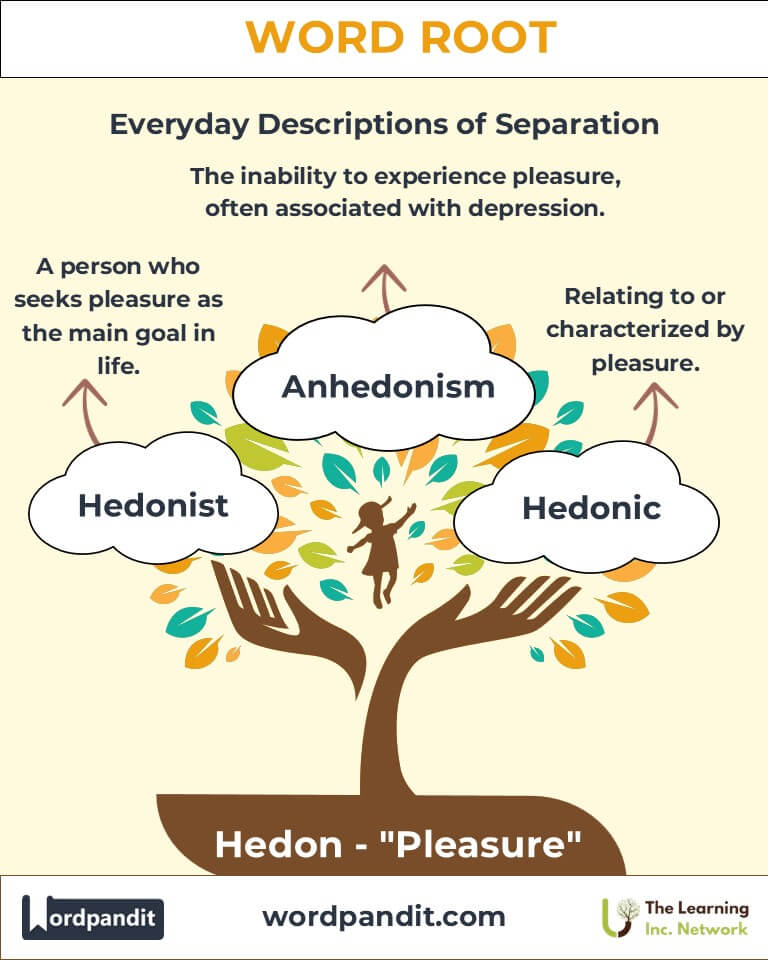
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Hedon
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Hedon
- Common Hedon-Related Terms
- Hedon Through Time
- Hedon in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Hedon in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Hedon Root
- The Hedon Family Tree
- FAQs About the Geo Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Geo Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Hedon
Introduction: The Essence of Hedon
What does it mean to truly enjoy life? The word root "Hedon" (pronounced "hee-don") represents pleasure and is derived from the Greek word hēdonē. This root enriches our language with terms that explore human desires, happiness, and well-being. From hedonists embracing life’s pleasures to medical discussions of anhedonism, the absence of joy, Hedon shapes our understanding of satisfaction and its pursuit.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "Hedon" traces its origin to the Greek word hēdonē (pleasure), used by philosophers like Epicurus to explore the nature of happiness and the role of sensory experiences in a fulfilling life. Over centuries, the term evolved, influencing English words that describe both indulgence and its opposite, reflecting the complexity of human emotions and values.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Hedon
Imagine a sunny beach, with someone lounging under an umbrella, sipping a drink, and reading their favorite book. The scene embodies the root "Hedon", synonymous with the pursuit of joy and relaxation.
Mnemonic Device: "Hedon is where happiness hides, in the sunshine of life's pleasures."
Common Hedon-Related Terms
- Hedonist (hee-duhn-ist): A person who prioritizes pleasure as the primary goal in life.
Example: "A hedonist, Emma spent her weekends traveling to exotic destinations to savor life’s delights." - Anhedonism (an-hee-doh-niz-uhm): The inability to experience pleasure.
Example: "The therapist diagnosed him with anhedonism, a common symptom of depression." - Hedonic (hee-don-ik): Relating to or characterized by pleasure.
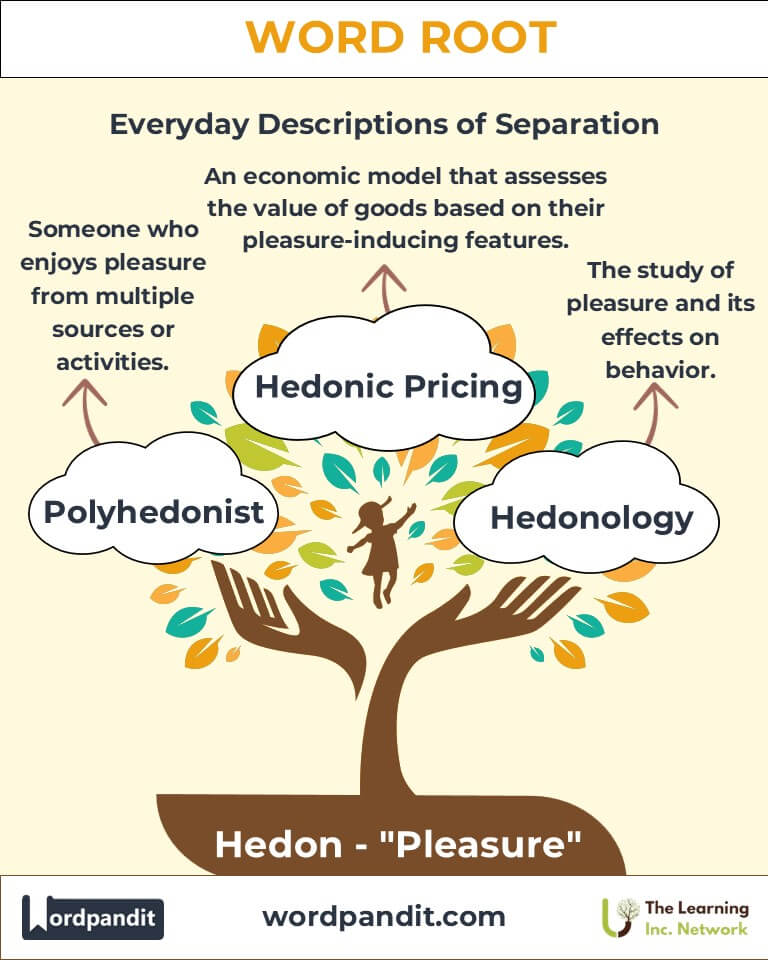
Example: "The hedonic treadmill suggests that people quickly adapt to changes in happiness." - Polyhedonist (pol-ee-hee-duhn-ist): Someone who derives pleasure from multiple activities or sources.
Example: "As a polyhedonist, she found joy in art, music, and travel." - Hedonology (hee-don-ol-uh-jee): The study of pleasure and its effects on human behavior.
Example: "Hedonology explores how pleasure motivates decision-making."
Hedon Through Time
- Hēdonē in Ancient Greece: Initially a philosophical term, it sparked debates on the ethics of pleasure, with proponents like Epicurus emphasizing moderation and critics like Plato warning against excess.
- Hedonic Psychology (20th Century): Modern psychology introduced "hedonic adaptation" to describe how people adjust to new levels of happiness, shaping concepts in well-being and economics.
Hedon in Specialized Fields
- Psychology:
Anhedonia (an absence of pleasure) is a key indicator in diagnosing mood disorders. Understanding hedonic responses can guide treatments for depression and anxiety. - Economics:
The hedonic pricing model evaluates goods and services based on pleasure-driven attributes, such as location for real estate or design in consumer products. - Philosophy:
Hedonism remains central in ethical debates, examining whether maximizing pleasure leads to a meaningful life.
Illustrative Story: Hedon in Action
Lila, a dedicated artist, sought solace in creating vibrant paintings after a period of anhedonism following a personal loss. As her passion reignited, she found joy in small pleasures—morning sunrises, shared laughter, and the rhythmic strokes of her brush. Lila’s journey reflected the duality of Hedon: the absence of pleasure as a challenge and its rediscovery as a triumph.
Cultural Significance of the Hedon Root
From literary works like Oscar Wilde’s The Picture of Dorian Gray to modern self-care movements, Hedon influences our perceptions of indulgence and balance. Its dualities—hedonism versus restraint, pleasure versus void—capture the eternal human quest for happiness.

The Hedon Family Tree
Related Roots:
- Phil- (Love or Affection):
Example: Philosophy (love of wisdom). - Path- (Feeling or Emotion):
Example: Empathy (the ability to share feelings). - Eu- (Good or Well):
Example: Euphoria (a state of intense happiness).
FAQs About the Hedon Word Root
Q: What does "Hedon" mean?
A: The root "Hedon" means pleasure, originating from the Greek word hēdonē. It represents the idea of enjoyment, satisfaction, and happiness, forming the basis of words that describe both the pursuit of joy (hedonism) and its absence (anhedonia).
Q: What is hedonism?
A: Hedonism is a philosophical belief that pleasure or happiness is the ultimate purpose of life. While some view it as indulgent or excessive, philosophers like Epicurus advocated a moderate form of hedonism, focusing on simple pleasures, good health, and mental peace rather than uncontrolled indulgence.
Q: What is anhedonism?
A: Anhedonism refers to the inability to experience pleasure. It is a clinical symptom often associated with mental health conditions like depression, where activities that once brought joy fail to do so. It’s a key focus in psychotherapy and neuroscience, as understanding it can lead to better treatments for mood disorders.
Q: What is hedonic adaptation?
A: Hedonic adaptation is the psychological phenomenon where people quickly return to a baseline level of happiness after major positive or negative life changes. For example, winning the lottery may bring temporary happiness, but over time, people adjust, and the joy diminishes.
Q: Is hedonism always negative?
A: No, hedonism is not inherently negative. When practiced with moderation, it can enhance well-being by encouraging individuals to seek happiness and avoid unnecessary suffering. Epicurean hedonism, for instance, focuses on cultivating long-term happiness through thoughtful choices.
Q: What is the hedonic treadmill?
A: The hedonic treadmill refers to the cycle where people continuously seek more material possessions or achievements, believing they will bring lasting happiness. However, they often find themselves returning to their previous level of happiness, prompting further pursuit in a never-ending loop.
Q: What is hedonic pricing?
A: Hedonic pricing is an economic method used to evaluate the value of products or services based on their pleasure-inducing attributes. For instance, real estate with scenic views or high-end appliances often fetches higher prices due to their added appeal.
Q: How does hedonism relate to psychology?
A: In psychology, hedonism explores the role of pleasure in human behavior and mental health. Concepts like hedonic well-being focus on how positive experiences and emotions contribute to overall happiness, while anhedonia provides insights into conditions like depression.
Q: Who was Epicurus, and what was his stance on hedonism?
A: Epicurus was a Greek philosopher who emphasized the pursuit of moderate pleasures as a path to happiness. Unlike indulgent hedonists, Epicurus believed in simple living, good friendships, and freedom from fear or pain as the key to lasting joy.
Q: What is the difference between hedonic and eudaimonic well-being?
A: Hedonic well-being focuses on experiencing pleasure and avoiding pain, emphasizing short-term happiness. In contrast, eudaimonic well-being centers on living a meaningful and fulfilling life, prioritizing personal growth, purpose, and contributions to others.
Test Your Knowledge: Hedon Mastery Quiz
1. What does "Hedon" signify?
2. What is anhedonism?
3. Which field studies hedonic pricing?
4. What does "polyhedonist" mean?
5. Who promoted moderate hedonism in philosophy?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Hedon
The root "Hedon" encapsulates the human pursuit of joy and its complexities. Whether illuminating the philosophies of ancient Greece or guiding modern psychology, it underscores the value of pleasure in our lives. Embracing Hedon reminds us to balance indulgence with intention, shaping a meaningful journey toward happiness.














