Hedono: The Pursuit of Pleasure in Language and Life
Discover the allure and significance of the root "Hedono," originating from Greek, meaning "pleasure." From philosophies of hedonism to descriptions of pleasure-seekers like hedonists, this root has shaped ideas and language surrounding joy and gratification.
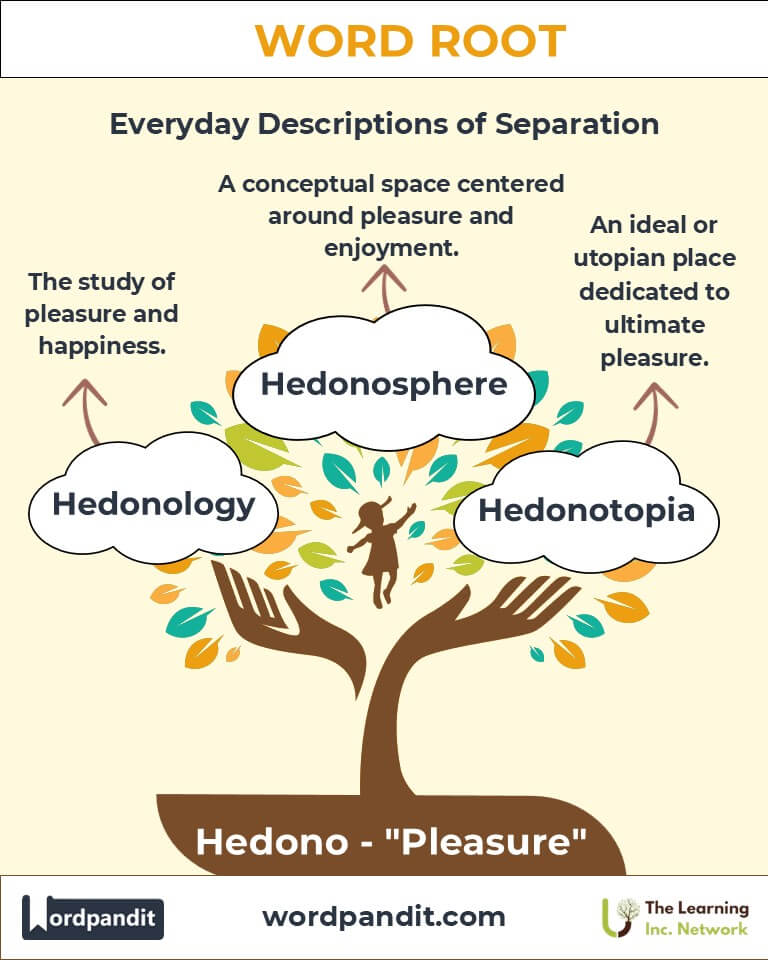
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Joyful Essence of Hedono
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Hedono
- Common Hedono-Related Terms
- Hedono Through Time
- Hedono in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Hedono in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Hedono Root
- The Hedono Family Tree
- FAQs about the Hedono Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Hedono Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Timeless Allure of Hedono
Introduction: The Joyful Essence of Hedono
The word root "hedono" resonates with joy, indulgence, and satisfaction. Derived from the Greek word hēdonē (pleasure), it forms the basis of terms that describe the pursuit of happiness, like "hedonism" (a philosophy centered on pleasure) and "hedonist" (a seeker of pleasurable experiences). This root symbolizes humanity’s enduring quest for joy across cultures, disciplines, and eras.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "hedono" comes from the Greek hēdonē, meaning pleasure or delight. Ancient Greek philosophers like Epicurus emphasized hēdonē as central to a good life, advocating a balance of physical and intellectual pleasures. Over time, "hedono" evolved into terms like "hedonism," spreading through Latin and into English, embodying the celebration and critique of pleasure-seeking behaviors.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Hedono
Imagine a garden filled with blooming flowers, soft music, and delicious treats, symbolizing the sensory delights of life. A sign in the garden reads: "Welcome to Hedono—the place of pleasure and joy."
Mnemonic Device: "Hedono is where happiness grows—a garden of pleasures for all to know."
Common Hedono-Related Terms
- Hedonism (hee-duh-niz-uhm):
- Definition: A philosophy or way of life focused on the pursuit of pleasure as the highest good.
- Example: "Epicurus’ version of hedonism emphasized mental tranquility over excessive indulgence."
- Hedonist (hee-duh-nist):
- Definition: A person who seeks pleasure as their primary goal.
- Example: "As a self-declared hedonist, Mia sought happiness through travel and art."
- Hedonic (hee-don-ik):
- Definition: Relating to or characterized by pleasure.
- Example: "The hedonic design of the spa made it a perfect place to relax."
- Anhedonia (an-hee-doh-nee-uh):
- Definition: The inability to feel pleasure.
- Example: "Anhedonia is a common symptom of depression."
- Hedonophobia (hee-doh-noh-foh-bee-uh):
- Definition: Fear or aversion to experiencing pleasure.
- Example: "His hedonophobia made him wary of enjoying life’s small joys."
Hedono Through Time
- Hedonism in Antiquity: Epicureanism emphasized rational pleasures, contrasting with the excesses of Cyrenaic hedonism.
- Modern Interpretations: Today, hedonism has expanded into fields like psychology, exploring hedonic well-being and pleasure metrics.
Hedono in Specialized Fields
- Psychology: Hedonic Adaptation: Understanding this helps improve strategies for lasting happiness.
- Economics: Hedonic Pricing: Determines values based on pleasure-related attributes, like scenic views.
- Philosophy: Hedonistic Utilitarianism: Suggests actions are right if they maximize pleasure.
Illustrative Story: Hedono in Action
Amelia, a stressed professional, took a retreat to rediscover joy. Immersed in the serene environment, she embraced her inner hedonist, savoring gourmet meals, meditating by the sea, and reconnecting with simple pleasures. Returning home, she carried the lesson of balanced hedonism—finding delight in both grand and everyday moments.
Cultural Significance of the Hedono Root
The concept of "hedono" reflects diverse cultural attitudes toward pleasure:
- Ancient Greece: Valued moderation in hedonistic pursuits.
- Renaissance: Celebrated earthly pleasures in art and literature.
- Modern Times: Explores pleasure in wellness, entertainment, and consumer behavior.

The "Hedono" Family Tree
- Sympathy: Compassion for another’s suffering.
- Prelude: A playful introduction.
- Gaudy: Excessively showy or joyful.
FAQs About the "Hedono" Root
Q: What does "hedono" mean?
A: "Hedono" originates from the Greek word hēdonē, which translates to "pleasure" or "delight." It represents the idea of joy and gratification, often associated with sensory, emotional, or intellectual enjoyment.
Q: Is hedonism only about indulgence?
A: Not at all. While some interpretations of hedonism focus on sensory indulgence, Epicurean hedonism advocates for a balanced pursuit of pleasure. It emphasizes intellectual satisfaction and avoiding pain, rather than excessive indulgence in fleeting pleasures.
Q: What is hedonic adaptation?
A: Hedonic adaptation refers to a psychological phenomenon where people return to a baseline level of happiness after experiencing significant positive or negative changes. For instance, winning the lottery might make someone very happy initially, but over time, they adjust and return to their usual emotional state.
Q: How does "hedonic" differ from "hedonistic"?
A: "Hedonic" pertains to experiences or phenomena related to pleasure, such as hedonic happiness (derived from enjoyable activities). "Hedonistic," on the other hand, describes behaviors or lifestyles focused on seeking pleasure as a primary goal.
Q: Can hedonism have negative consequences?
A: Yes, if hedonism is practiced in excess or without consideration of long-term well-being, it can lead to negative consequences. Overindulgence in pleasures like food, luxury, or leisure can result in physical or mental health issues, financial problems, or diminished satisfaction over time.
Test Your Knowledge: Hedono Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "hedono" signify?
2. Which term describes the inability to feel pleasure?
3. What is hedonic adaptation?
4. Who emphasized balanced hedonism?
5. What field uses "hedonic pricing"?
Conclusion: The Timeless Allure of Hedono
The root "hedono" reminds us of life’s joys and our pursuit of happiness. From ancient philosophies to modern sciences, its significance endures in shaping how we understand pleasure and fulfillment. By exploring "hedono," we celebrate the timeless human connection to joy—an aspiration that continues to inspire and enrich our lives.














