Histo: The Building Blocks of Life and Medicine
Explore the fascinating world of the root "Histo," derived from Greek, meaning "tissue." From the intricate study of histology to the vital role of histamine in the human body, this root unveils the microscopic wonders that sustain life and drive medical science forward.
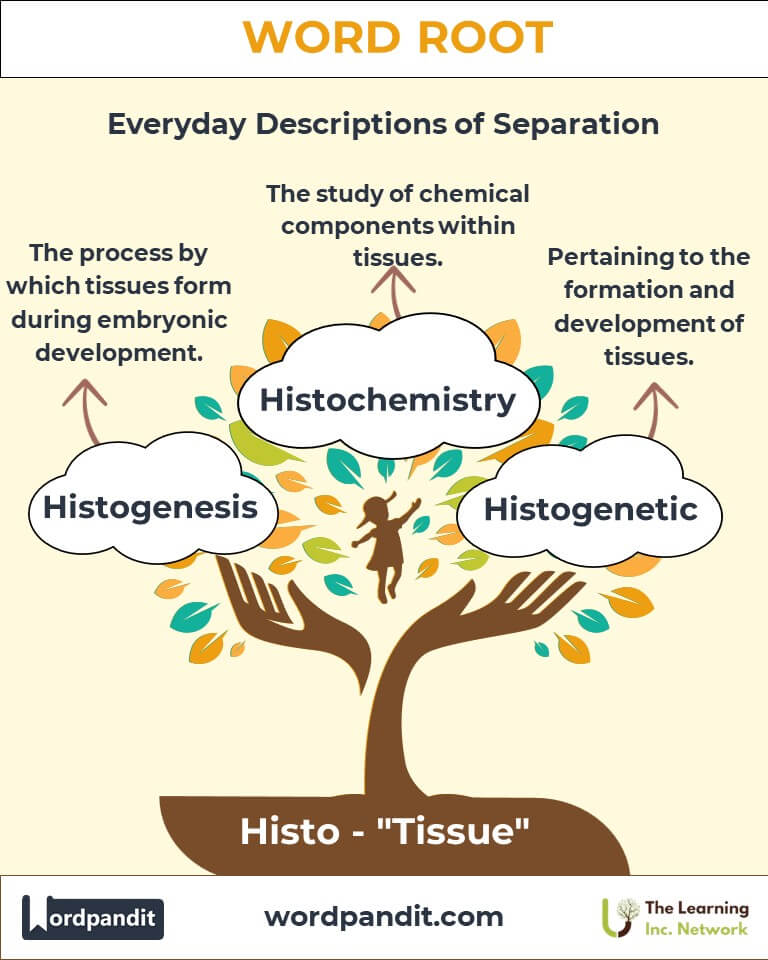
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Histo"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Histo"
- Common "Histo"-Related Terms
- "Histo" Through Time
- "Histo" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Histo" in Action
- Cultural Significance of the "Histo" Root
- The "Histo" Family Tree
- FAQs about the "Histo" Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Histo" Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Histo"
Introduction: The Essence of "Histo"
Imagine peering into a microscope to uncover the intricate web of life within tissues. The root "Histo," pronounced HIS-toh, captures this wonder, originating from the Greek word histos, meaning "web" or "tissue." It forms the basis of crucial terms in biology and medicine, such as histology (the study of tissues) and histamine (a key compound in immune response). "Histo" underscores the complex interactions and structures that define living organisms.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "Histo" stems from the Greek histos, originally used to describe a woven structure, akin to a fabric's threads. Over time, its meaning shifted to denote biological tissues, reflecting their web-like arrangement. The scientific field of histology emerged in the 19th century, revolutionizing biology and medicine by enabling the detailed examination of tissues at the cellular level.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Histo"
To remember "Histo," visualize a spider weaving an intricate web, each thread representing the complex structures of tissues.
Mnemonic Device: "Histo weaves the story of life, one tissue thread at a time."
Common "Histo"-Related Terms
- Histology (HIS-tuh-loh-jee): The study of tissues and their structure.
Example: "The pathologist used histology to diagnose the disease." - Histamine (HIS-tuh-meen): A compound involved in immune responses, such as inflammation.
Example: "An antihistamine reduced her allergy symptoms." - Histopathology (HIS-tuh-puh-thol-uh-jee): The microscopic study of diseased tissues.
Example: "Histopathology revealed abnormalities in the biopsy sample." - Histogenesis (HIS-toh-jen-uh-sis): The process by which tissues form during embryonic development.
Example: "Histogenesis is crucial for organ formation." - Histochemistry (HIS-toh-kem-uh-stree): The study of chemical components within tissues.
Example: "Histochemistry helped identify specific proteins in the tissue sample."
"Histo" Through Time
- Ancient Roots: The term "histos" was originally used to describe woven fabrics, reflecting early observations of biological tissues' appearance.
- Modern Science: The advent of histology in the 19th century introduced methods like staining and microscopy, enabling breakthroughs in diagnosing diseases like cancer.
"Histo" in Specialized Fields
- Medicine: Histopathology is indispensable in diagnosing diseases by examining tissue samples.
- Pharmacology: Histamine blockers are widely used in allergy treatments, showcasing the role of "Histo" in pharmacological advances.
- Developmental Biology: Histogenesis offers insights into how tissues and organs develop in embryos, aiding regenerative medicine.
Illustrative Story: "Histo" in Action
Dr. Priya, a histologist, examined a tissue sample from a patient experiencing chronic inflammation. Using histochemistry, she identified elevated histamine levels and pinpointed the root cause: an autoimmune disorder. Her findings allowed the patient’s physician to tailor an effective treatment plan, showcasing the transformative power of "Histo" in medical science.
Cultural Significance of the "Histo" Root
"Histo" reflects humanity's enduring curiosity about life's structures. Ancient philosophers mused on the fabric of life, while modern medicine uses histology to unravel the mysteries of disease. The root embodies the intersection of art and science, symbolizing the intricate "web" of existence.

The "Histo" Family Tree
- Cyto- (Cell):
- Cytology: The study of cells.
- Cytoplasm: The fluid within cells.
- Patho- (Disease):
- Pathology: The study of diseases.
- Pathogen: An agent causing disease.
- Chemo- (Chemical):
- Chemotherapy: Drug treatment targeting cancer.
- Biochemistry: The study of chemical processes in living organisms.
FAQs About the Histo Word Root
Q: What does "Histo" mean?
A: The root "Histo" means "tissue," originating from the Greek word histos, which initially referred to a "web" or "woven structure." This imagery captures the interconnected and organized structure of biological tissues, essential to the makeup of living organisms.
Q: What is histology?
A: Histology is the scientific study of tissues at the microscopic level. It involves examining how tissues are organized, their cellular composition, and how they function together to form organs. This field is critical for understanding both healthy and diseased states.
Q: How is histamine significant in the body?
A: Histamine is a compound released by cells during immune responses. It plays key roles in inflammation, allergic reactions, and regulating physiological functions like gastric acid secretion. For example, when exposed to allergens, histamine causes symptoms such as itching, swelling, or redness.
Q: What is histopathology?
A: Histopathology involves the microscopic examination of diseased tissues to diagnose conditions. For instance, a biopsy taken from a patient may be analyzed through histopathology to identify cancer or infections.
Q: What are histochemical techniques?
A: Histochemical techniques use dyes and stains to identify specific chemical components within tissues. These methods help researchers and clinicians visualize proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates to understand tissue structure and function at a molecular level.
Q: What is histogenesis, and why is it important?
A: Histogenesis is the process by which tissues form and develop during the embryonic stage. It is fundamental to the creation of organs and systems within the body, providing a foundation for life. Any disruption in histogenesis can lead to developmental abnormalities.
Q: What role do histologists play in medicine?
A: Histologists prepare and analyze tissue samples to assist in diagnosing diseases. They use staining techniques and microscopy to identify abnormalities, contributing vital information to medical diagnoses and treatment planning.
Q: How does histology differ from cytology?
A: While histology focuses on tissues, cytology studies individual cells. Both fields are interconnected, as tissues are made up of cells. Histology provides a broader perspective on how cells function collectively within tissues.
Test Your Knowledge: Histo Mastery Quiz
1. What does "Histo" mean?
2. Which term refers to the study of tissues?
3. What does histamine do in the body?
4. What is histogenesis?
5. What is the role of histopathology?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Histo"
The root "Histo" offers a lens to explore the intricate structures of life, from healthy tissues to diseased states. As histological techniques evolve, they continue to drive breakthroughs in medicine, biology, and beyond. Understanding "Histo" reminds us of the interconnectedness of all life, woven together like the threads of a tapestry.














