Jud: The Root of Judgment in Law and Language
Byline: Delve into the Latin root "jud," meaning "judge," and explore its profound influence on words relating to fairness, law, and critical thinking. From "judicial" systems to "prejudice," this root has shaped our understanding of authority and impartiality across centuries.
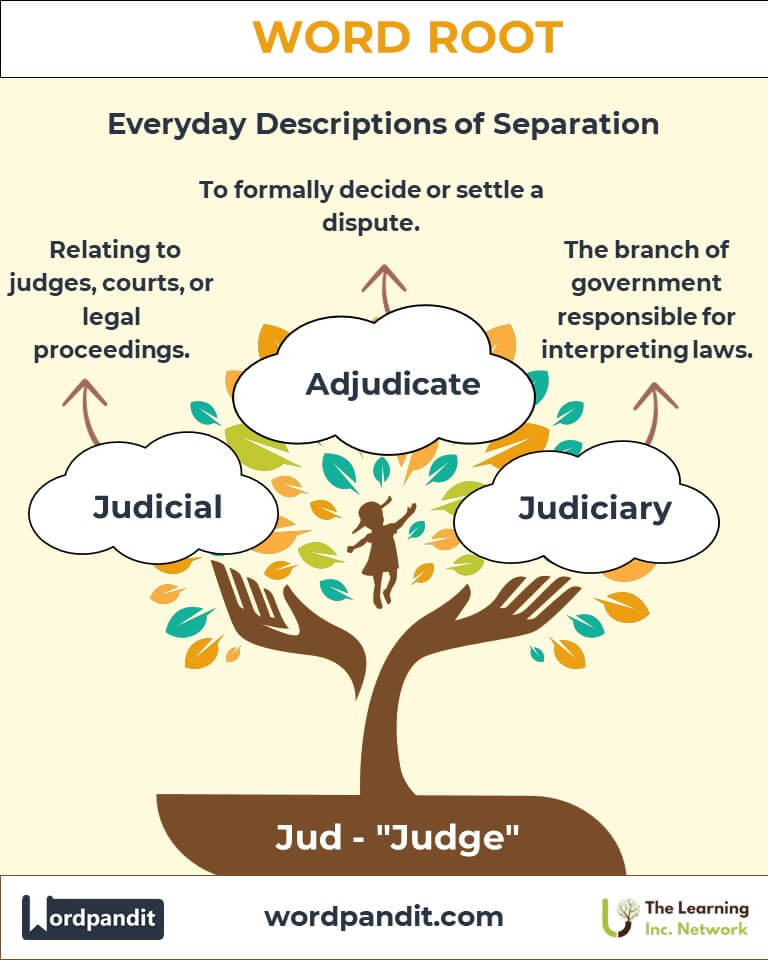
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Jud"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Jud"
- Common Jud-Related Terms
- "Jud" Through Time
- "Jud" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Jud" in Action
- Cultural Significance of "Jud"
- The "Jud" Family Tree
- FAQs about the "Jud" Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Jud" Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Jud"
1. Introduction: The Essence of "Jud"
The root "jud," pronounced "jood," originates from the Latin word judex, meaning "judge." It forms the backbone of words central to legal systems, critical reasoning, and social ethics. From ensuring justice in "judicial" proceedings to combating "prejudice," "jud" embodies the principles of fairness and discernment. This root is vital across disciplines like law, philosophy, and sociology.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The Latin root judex is a combination of jus (law, right) and dicere (to say or declare). In ancient Rome, judex referred to a person appointed to decide legal disputes. Over time, this root evolved into words used in judicial systems and moral reasoning worldwide. With the spread of Latin through Roman conquests and the development of English, "jud" became integral to legal and ethical vocabulary.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Jud"
Imagine a wise, impartial judge sitting in a courtroom, holding the scales of justice. The image of the judge reminds us of "jud" as the root of judgment, fairness, and decision-making.
Mnemonic Device:
"Jud is the root of justice, balancing rights and fairness with wise decisions."
4. Common Jud-Related Terms
- Judicial (joo-dish-uhl): Pertaining to judges, courts, or the administration of justice.
- Example: "The judicial system ensures the fair application of laws."
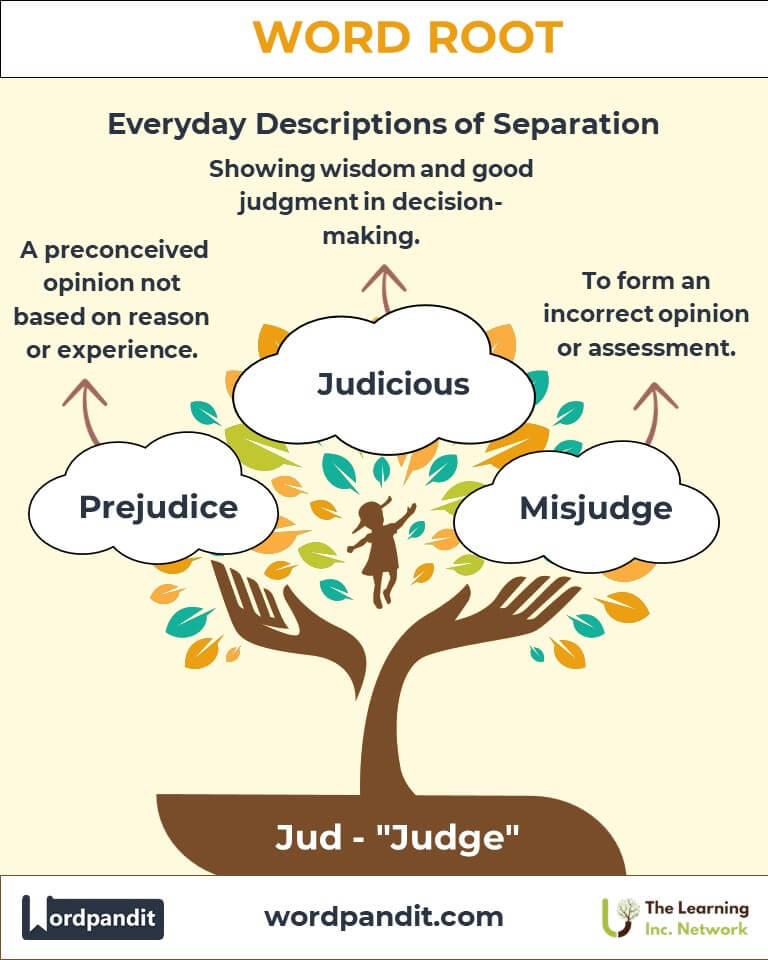
- Prejudice (prej-uh-dis): A preconceived opinion not based on reason or experience.
- Example: "Overcoming prejudice requires education and empathy."
- Judicious (joo-dish-uhs): Having, showing, or done with good judgment.
- Example: "A judicious decision often leads to favorable outcomes."
- Adjudicate (uh-joo-di-kate): To make a formal judgment or decision about a dispute.
- Example: "The panel was asked to adjudicate the case impartially."
- Misjudge (mis-juhj): To form an incorrect opinion or conclusion.
- Example: "He misjudged the situation and acted prematurely."
5. "Jud" Through Time
- Judex (Ancient Rome): Denoted a Roman judge tasked with interpreting laws and resolving disputes.
- Prejudice (Middle Ages): Originally meant "prior judgment," later evolving into its current meaning of biased or unfair judgments.
- Judicial (Modern): Today, this term encompasses all aspects of courts, judges, and legal systems worldwide.
6. "Jud" in Specialized Fields
- Law:
- Judiciary: Refers to the branch of government responsible for interpreting laws and administering justice.
- Sociology:
- Prejudice: Highlights biases that affect societal interactions and equality.
- Philosophy:
- Judicious decision-making: A key concept in ethics and moral philosophy.
7. Illustrative Story: "Jud" in Action
In a small town, a wise judge named Maria was known for her judicious rulings. One day, two farmers brought a land dispute to her court. While examining the evidence, she uncovered a misunderstanding fueled by prejudice. By resolving the issue with fairness and empathy, Maria not only restored justice but also fostered harmony in the community.
8. Cultural Significance of "Jud"
The root "jud" transcends linguistic boundaries, symbolizing the universal quest for justice. Across cultures, fairness in judicial systems and overcoming prejudice are seen as essential for societal progress. The balance of impartiality and moral judgment remains a cornerstone of civilization.

9. The "Jud" Family Tree
- Jus/Jur (Law):
- Jurisprudence: The theory or philosophy of law.
- Dic/Dict (Say, Declare):
- Dictate: To lay down authoritatively.
- Cred (Believe):
- Credibility: The quality of being trustworthy.
10. FAQs About the Jud Word Root
Q: What does the root "jud" mean?
A: The root "jud" comes from the Latin judex, meaning "judge." It forms the foundation of words related to judgment, decision-making, and fairness. This root highlights the process of weighing evidence or opinions to reach a conclusion.
Q: Is "prejudice" always a negative term?
A: Originally, "prejudice" was a neutral term meaning "prior judgment." Over time, it has developed a predominantly negative connotation, referring to biased opinions formed without proper reasoning or experience. However, the word can still imply any preconceived opinion, not necessarily a harmful one.
Q: What is the difference between "judicial" and "judicious"?
A: While both derive from the "jud" root, their meanings differ significantly:
- Judicial relates to judges, courts, or the legal system. For example, a judicial decision refers to a ruling made in a court of law.
- Judicious refers to showing good judgment or wisdom in decision-making. For instance, a judicious action is a wise and thoughtful choice.
Q: What does "adjudication" involve?
A: Adjudication is the formal process of resolving disputes, often within a legal context. It involves a judge or appointed arbitrator examining evidence, applying laws, and making a binding decision.
Q: How is "jud" connected to morality?
A: Words like judicious and misjudge emphasize the moral dimensions of judgment. They reflect the importance of fairness, wisdom, and integrity in assessing situations or making decisions, crucial to ethics and justice.
Q: What is the role of the judiciary?
A: The judiciary is the branch of government responsible for interpreting laws and ensuring justice. It applies legal principles impartially, resolving disputes, protecting rights, and maintaining the rule of law.
11. Test Your Knowledge: Jud Word Root Quiz
1. What does the root "jud" signify?
2. Which term means "preconceived opinion"?
3. What does "adjudicate" mean?
4. Which word relates to good judgment?
5. What is the role of the judiciary?
12. Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Jud"
The root "jud" embodies the principles of fairness, law, and judgment. From ancient Roman judges to modern judicial systems, its legacy continues to shape how we think, act, and ensure justice in society. Let the enduring power of "jud" inspire fairness and good judgment in all aspects of life.














