Junct: The Root of Connection in Language and Beyond
Discover how the Latin root "Junct," meaning "join," forms the basis of many words that embody connection, unity, and relationships. From "junction" to "conjunction," this root highlights the importance of linking ideas, objects, and people in everyday life and specialized fields.
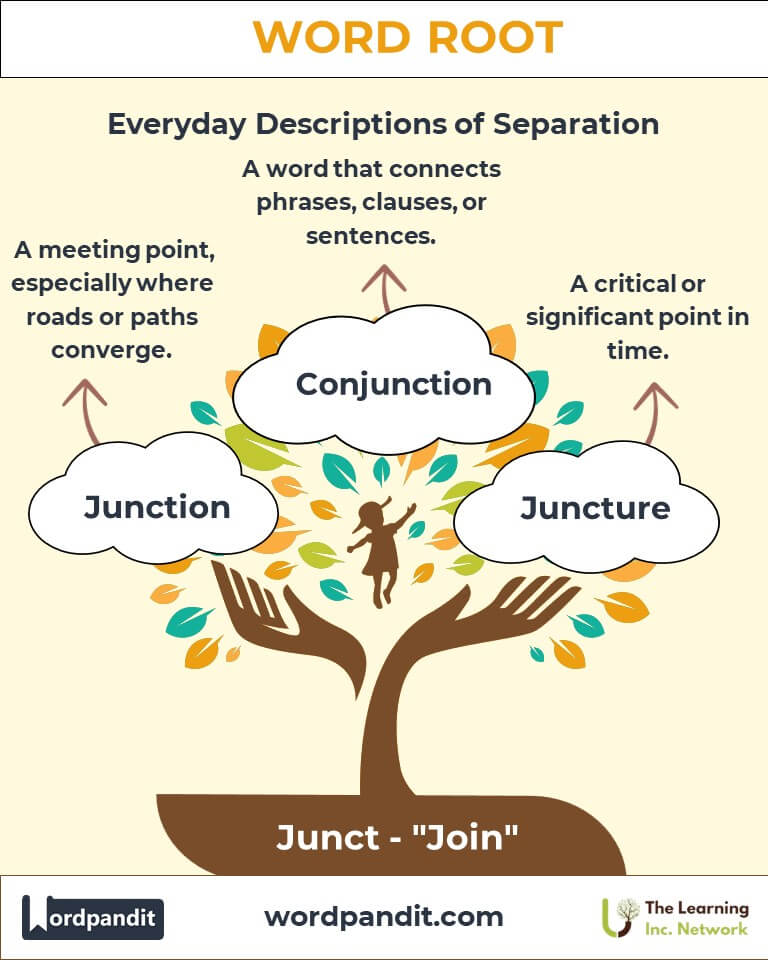
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Junct"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Junct"
- Common "Junct"-Related Terms
- "Junct" Through Time
- "Junct" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Junct" in Action
- Cultural Significance of the "Junct" Root
- The "Junct" Family Tree
- FAQs about the "Junct" Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Junct" Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Junct"
1. Introduction: The Essence of "Junct"
Every day, we encounter the power of connections—whether it’s meeting at a road junction, using conjunctions in writing, or experiencing a crucial juncture in life. The root "Junct," pronounced "juhngkt," stems from the Latin jungere, meaning "to join." Words derived from this root emphasize unity, connection, and interdependence, making "Junct" a cornerstone of communication and structure in both language and life.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "Junct" originates from the Latin jungere, evolving into junctus (joined) and spreading into English through Middle French. Early uses highlighted physical connections, such as links in a chain, before expanding to abstract concepts like relationships and unity. The root found prominence in fields like grammar (conjunctions) and infrastructure (junctions), symbolizing the enduring importance of joining elements for functionality and meaning.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Junct"
Visualize a sturdy chain with interlinked rings labeled "Junct." Each ring represents a word or idea, seamlessly joined to the next.
Mnemonic Device:
"Junct links everything—words, roads, and ideas—stronger together than apart."
4. Common "Junct"-Related Terms
- Junction (juhngk-shuhn):
- Definition: A meeting point, especially where roads or paths converge.
- Example: "The busy junction had traffic signals to manage the flow."
- Conjunction (kuhn-juhngk-shuhn):
- Definition: A part of speech connecting words, phrases, or clauses.
- Example: "She used the conjunction 'and' to link her ideas."
- Disjunction (dis-juhngk-shuhn):
- Definition: A separation or disconnection.
- Example: "There was a clear disjunction between the two arguments."
- Adjunct (ad-juhngkt):
- Definition: Something added or joined to another entity but not essential.
- Example: "The adjunct professor taught part-time at the university."
- Juncture (juhngk-cher):
- Definition: A critical or significant point in time.
- Example: "The company faced a challenging juncture in its history."
5. "Junct" Through Time
- Juncture: Once used to describe physical joints or connections, its meaning evolved to signify critical moments in history or decision-making.
- Disjunction: Initially focused on physical separations, it gained prominence in philosophy and logic to represent breaks in thought or argument.
6. Juv in Specialized Fields
-
Biology:
- Juvenile phase: The early stage of an organism’s development.
- Example: "The juvenile stage of the butterfly is the caterpillar."
-
Psychology:
- Juvenile behavior: Traits often associated with adolescence, such as impulsivity.
- Application: Understanding juvenility helps address developmental challenges.
-
Medicine:
- Juvenile arthritis: A condition affecting young individuals.
- Relevance: Early diagnosis can lead to better outcomes.
-
Literature:
- Juvenilia: Works produced by an author during youth.
- Example: "The poet’s juvenilia reveal an early passion for nature."
7. Illustrative Story: Juv in Action
Lila, a stressed city dweller, decided to rejuvenate her spirit by visiting her childhood home. Walking through the familiar forest, she stumbled upon a group of children playing, their laughter echoing through the trees. Inspired by their youthful energy, she joined them in skipping stones, feeling the years melt away. That evening, Lila realized that the spirit of "juv" wasn’t just about age—it was about embracing joy and renewal.
8. Cultural Significance of the "Junct" Root
The root "Junct" reflects humanity's intrinsic desire for connection and unity. Whether in literature, infrastructure, or relationships, "Junct" embodies the importance of joining forces and bridging gaps.
- Literature: Famous literary conjunctions like "and" or "but" symbolize the infinite possibilities of connection.
- Infrastructure: Physical junctions in cities demonstrate the necessity of collaboration for progress.
- Relationships: The concept of junctures highlights pivotal life moments that bring people together.

9. The "Junct" Family Tree
- Jug- (Latin: "to join"):
- Subjugate: To bring under control or join forcibly.
- Conjugal: Relating to marriage (a joining of lives).
- Join- (Latin: "to link"):
- Rejoin: To come together again.
- Joinery: Craftsmanship involving connections in woodwork.
- Nex- (Latin: "to bind"):
- Annex: To add or join to something larger.
- Nexus: A central connection or link.
10. FAQs About the Junct Word Root
Q: What does "Junct" mean?
A: "Junct" means "to join" or "to connect," originating from the Latin root jungere. This concept of joining can apply to physical connections, like roads at a junction, or abstract links, like ideas in a conjunction.
Q: What is the difference between "Junction" and "Juncture"?
A: While both words involve connection, their contexts differ:
- Junction: A physical meeting point, such as where roads or railways cross or converge.
- Juncture: A critical or significant point in time, often involving decisions or turning points.
Q: How is "Conjunction" used in grammar?
A: A conjunction is a word that links two or more elements in a sentence, such as phrases or clauses. Common examples include "and," "but," and "or." These words help ideas flow logically, making writing cohesive and structured.
Q: What does "Adjunct" mean, and where is it used?
A: An adjunct refers to something added or connected to a primary structure but not essential to it.
- In grammar, an adjunct is an optional modifier (e.g., "quickly" in "He runs quickly").
- In organizational contexts, an adjunct might be a part-time or secondary role, like an adjunct professor.
Q: What is a "Disjunction" in logic?
A: In formal logic, a disjunction is an "or" statement. It presents two or more alternatives, where at least one must be true. For example, "It will rain or snow" implies that one or both conditions are possible.
Q: Can "Junct" words refer to relationships beyond physical ones?
A: Yes, many "Junct"-related words deal with abstract connections. For example, conjunctions connect ideas, junctures signify pivotal moments in life, and adjuncts add supplementary relationships to existing structures.
11. Test Your Knowledge: Junct Word Root Quiz
1. What does "Junct" signify?
2. Which word describes a critical moment in time?
3. What is the role of a conjunction in grammar?
4. What does "Adjunct" refer to?
5. Which term describes a meeting point for roads?
12. Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Junct"
The root "Junct" continues to shape our understanding of connection and unity. From linguistic links to physical junctions, it underscores the importance of joining forces for progress and harmony. As language and society evolve, "Junct" remains a testament to the enduring power of connection in all its forms.














