Lyso: The Root of Loosening in Science and Life
Dive into the fascinating world of the root "lyso," derived from the Greek word "lysis," meaning loosening or dissolving. Found at the heart of terms like "lysosome" and "lysozyme," this root signifies breakdown and renewal, making it integral to biology, medicine, and beyond.
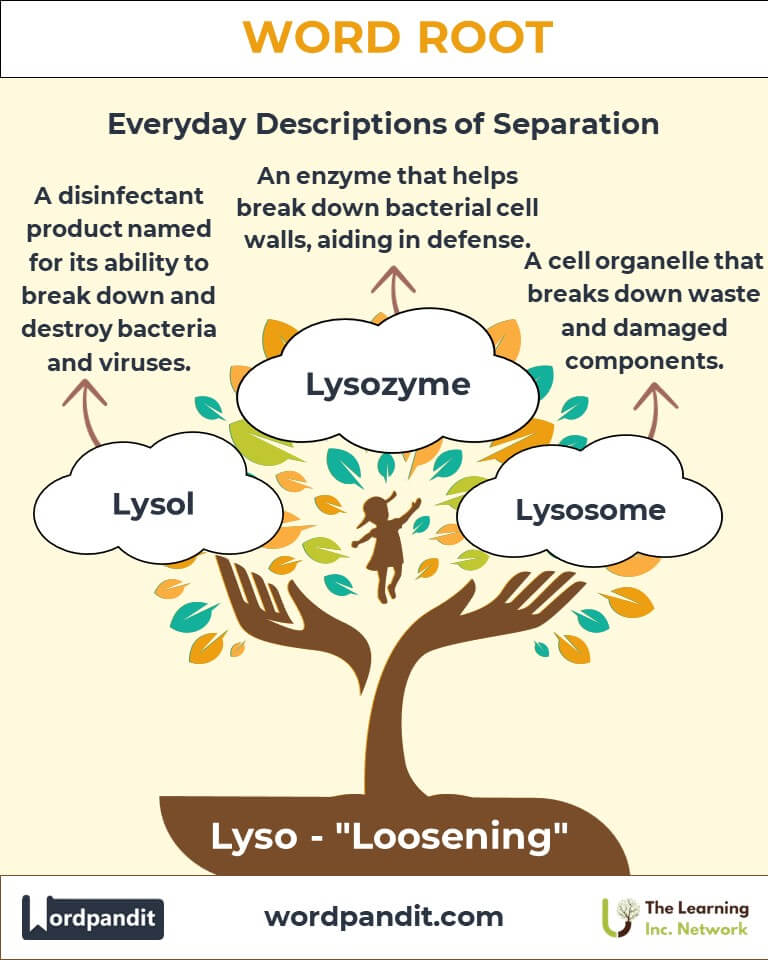
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Power of Loosening
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Lyso
- Common Lyso-Related Terms
- Lyso Through Time
- Lyso in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Lyso in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Lyso Root
- The Lyso Family Tree
- FAQs about the Lyso Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Lyso Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Transformative Power of Lyso
Introduction: The Power of Loosening
What connects the degradation of waste in cells to the destruction of bacteria? The answer lies in the word root "lyso." Pronounced “lie-so,” this Greek-derived root embodies the concept of breaking down or loosening. Whether describing cellular processes or powerful enzymes, "lyso" plays a pivotal role in understanding life's transformative mechanisms.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "lyso" originates from the Greek lysis, which means "a loosening" or "to untie." In ancient Greek thought, this term symbolized release or dissolution, concepts essential to both philosophical discussions and early scientific observations.
Over centuries, "lyso" entered modern biology, chemistry, and medicine, defining critical mechanisms such as the breakdown of molecular bonds and cellular components.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Lyso
Imagine an enzyme as a key unlocking the bonds holding a structure together. The word "lyso" symbolizes this process of breaking apart.
Mnemonic Device: "Lyso unlocks bonds, making large things small—whether in cells or walls!"
Common Lyso-Related Terms
- Lysosome (lie-so-some):
A cell organelle containing enzymes for digestion and waste removal.
Example: "Lysosomes act as the recycling centers of the cell." - Lysozyme (lie-so-zime):
An enzyme that breaks down bacterial cell walls.
Example: "Lysozymes in tears help protect the eyes from infections." - Lysis (lie-sis):
The disintegration of a cell or membrane.
Example: "Bacterial lysis occurs when antibiotics weaken the cell wall." - Autolysis (aw-toe-lie-sis):
The self-destruction of a cell through its own enzymes.
Example: "Autolysis is a critical step in tissue breakdown after death." - Electrolysis (ee-lek-tro-lie-sis):
A chemical process using electricity to break down compounds.
Example: "Electrolysis is used to extract metals like aluminum."
Lyso Through Time
- Lysimachus (Historical): In Greek mythology, this name means "one who loosens strife." It reflects the symbolic importance of "lyso" in resolving conflicts.
- Lysosome (Modern Biology): Coined in the 20th century, lysosomes exemplify how "lyso" evolved to describe cellular functions integral to life.
Lyso in Specialized Fields
- Medicine: Lysozyme: A naturally occurring enzyme that provides antimicrobial defense in saliva and tears.
Relevance: Used in pharmaceuticals to enhance immune protection. - Biochemistry: Lysosome: Essential for cellular recycling and autophagy.
Impact: Understanding lysosomes helps in treating diseases like Tay-Sachs and Parkinson’s. - Chemistry: Electrolysis: Vital for separating elements and purifying metals.
Application: Widely used in industries for material production.
Illustrative Story: Lyso in Action
Dr. Elena Martinez, a microbiologist, faced a dire challenge: a resistant bacterial infection in her patient. Using the natural power of lysozyme, she isolated and applied a purified enzyme to weaken the bacteria’s cell walls. With this treatment, the patient recovered, showcasing the life-saving potential of "lyso" in modern medicine.
Cultural Significance of the Lyso Root
The concept of "loosening" resonates beyond science, symbolizing renewal and transformation in philosophy and culture. In ancient Greek rituals, lysis represented liberation, whether of the soul, relationships, or societal bonds.

The Lyso Family Tree
- Hydro- (Water):
Hydrolysis: The breakdown of compounds using water.
Example: "Enzymes accelerate hydrolysis in digestion." - Cata- (Down):
Catalysis: Speeding up chemical reactions.
Example: "Catalysis is key in energy production." - Auto- (Self):
Autolysis: Self-decomposition of cells.
Example: "Autolysis occurs naturally in dying tissues."
FAQs About " Lyso "
Q: What does "lyso" mean?
A: The root "lyso" means "loosening" or "dissolving," derived from the Greek word "lysis." It refers to processes that break down or decompose structures, often used in biological, chemical, and medical contexts.
Q: What is a lysosome, and why is it important?
A: A lysosome is an organelle in eukaryotic cells that contains enzymes responsible for breaking down waste materials, damaged organelles, and foreign invaders like bacteria. It acts as the cell’s recycling center, maintaining cellular health by preventing the accumulation of harmful substances.
Q: How does lysozyme protect the body?
A: Lysozyme is an enzyme found in bodily fluids like tears, saliva, and mucus. It protects the body by breaking down the peptidoglycan in bacterial cell walls, causing the bacteria to lyse (burst). This makes lysozyme a critical part of the immune system’s first line of defense.
Q: What is lysis in biology?
A: Lysis refers to the disintegration or destruction of cells by rupturing their membranes. It can occur naturally, such as during apoptosis (programmed cell death), or artificially, as in the use of antibiotics to kill bacteria.
Q: How is "lyso" related to antibiotics?
A: Many antibiotics, like penicillin, induce bacterial lysis by targeting the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall. This weakens the wall, causing it to break apart under internal pressure, killing the bacteria.
Q: What is autolysis, and where does it occur?
A: Autolysis is the process of self-digestion where a cell breaks down using its own enzymes. It occurs after cell death or in certain physiological contexts, such as during tissue remodeling or decomposition.
Q: What is electrolysis, and how does it work?
A: Electrolysis is a chemical process that uses electricity to break down compounds, usually into their constituent elements. For example, it is used to separate water into hydrogen and oxygen gases or to extract metals from their ores.
Q: How are lysosomes connected to diseases?
A: Defects in lysosomes or their enzymes can lead to lysosomal storage diseases, such as Tay-Sachs and Gaucher’s disease. These occur when undigested materials accumulate in cells, causing dysfunction and severe health issues.
Test Your Knowledge: " Lyso " Mastery Quiz
1. What does "lyso" mean?
2. Which organelle is known as the cell's recycling center?
3. What does lysozyme target?
4. What is autolysis?
5. Which process uses electricity to break down compounds?
Conclusion: The Transformative Power of Lyso
The root "lyso" encapsulates the essence of transformation, breaking down the old to pave the way for renewal. From cellular health to industrial processes, its applications highlight the beauty of change and renewal. By exploring "lyso," we deepen our appreciation for the intricate balance between destruction and creation, a cornerstone of both life and language.














