Mandibulo: The Foundation of Speech and Nutrition
Explore the intricate role of the word root "mandibulo," derived from Latin, meaning "jaw." From its critical function in speech and eating to its linguistic connections, this root underpins fascinating terminology and concepts in anatomy, medicine, and beyond.
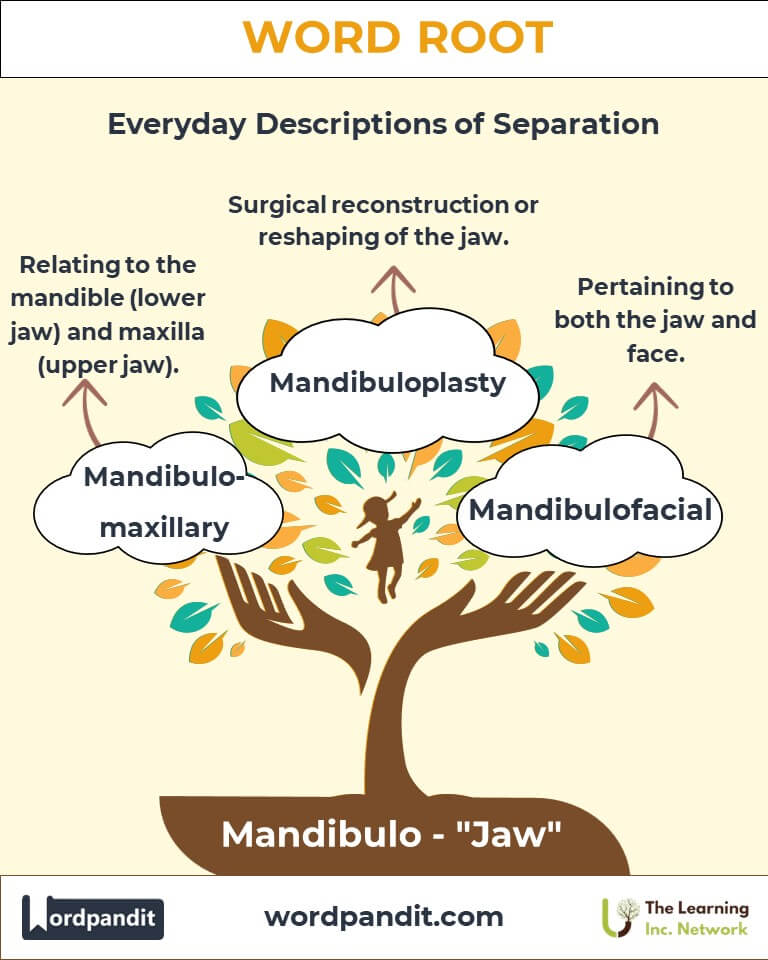
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Core of Mandibulo
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Mandibulo
- Common Mandibulo-Related Terms
- Mandibulo Through Time
- Mandibulo in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Mandibulo in Action
- Cultural Significance of Mandibulo
- The Mandibulo Family Tree
- FAQs about the Mandibulo Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Mandibulo Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Mandibulo
Introduction: The Core of Mandibulo
The jaw is more than a skeletal structure; it's a cornerstone of human communication and sustenance. The word root mandibulo, pronounced man-dib-yoo-loh, comes from Latin, meaning "jaw." It has given rise to terms that describe the jawbone's anatomy, movement, and medical conditions. Understanding "mandibulo" reveals the interconnectedness of biology, language, and technology.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The term "mandibulo" traces its origins to the Latin word mandibula, derived from mandere, meaning "to chew." This term first referred to the jawbone’s role in mastication. As anatomical studies progressed during the Renaissance, "mandibulo" became central in describing both the upper and lower jaw's structure and their associated functions.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Mandibulo
Picture a dinosaur gnashing its teeth while chewing leaves, with its strong jaw labeled “MANDIBULO.” This imagery ties the root to its primary function—chewing.
Mnemonic Device: "Mandibulo is the master of mastication, connecting jaws to their vocation!"
Common Mandibulo-Related Terms
- Mandible (man-di-buhl):
Definition: The lower jawbone, crucial for chewing and speech.
Example: "The mandible is the only movable bone in the human skull." - Mandibular (man-dib-yoo-lar):
Definition: Pertaining to the lower jaw.
Example: "Mandibular nerves play a key role in facial sensations and chewing." - Mandibulofacial (man-dib-yoo-loh-fay-shuhl):
Definition: Relating to the jaw and face.
Example: "Mandibulofacial anomalies may require corrective surgery." - Mandibulomaxillary (man-dib-yoo-loh-mak-sil-uh-ree):
Definition: Pertaining to the mandible and maxilla (upper jaw).
Example: "Mandibulomaxillary alignment affects oral health." - Mandibularis (man-dib-yoo-lar-is):
Definition: A muscle involved in jaw movement.
Example: "The mandibularis muscle aids in opening and closing the mouth."
Mandibulo Through Time
- Past: Ancient anatomists used "mandibula" to denote chewing bones.
- Present: Today, "mandibular" also refers to modern surgical techniques, such as mandibular osteotomy.
Mandibulo in Specialized Fields
- Dentistry: Mandibular Block Anesthesia—A nerve block used to numb the lower jaw during dental procedures.
- Orthodontics: Mandibular Advancement Devices—Appliances that reposition the jaw to treat sleep apnea.
- Forensic Science: Mandibular Measurements—Used in identifying individuals through skeletal remains.
- Speech Pathology: Mandibular Dysfunctions—Diagnosed in patients with impaired speech due to jaw issues.
Illustrative Story: Mandibulo in Action
Dr. Sofia, a maxillofacial surgeon, was tasked with treating a patient suffering from mandibular misalignment. Through innovative mandibular realignment surgery, she restored the patient’s ability to eat and speak normally. Meanwhile, her dental team used mandibular imaging to craft a custom implant, showcasing the jaw's pivotal role in modern medicine.
Cultural Significance of Mandibulo
In various cultures, the jaw symbolizes strength and determination. In traditional Chinese medicine, the jaw's health reflects overall vitality. Additionally, idiomatic expressions like "jaw-dropping" emphasize its role in communication and emotional expression.

The Mandibulo Family Tree
- Maxilla (Latin: Upper jaw):
Example: Maxillary sinus relates to the upper jaw’s air-filled spaces. - Gnatho (Greek: Jaw):
Example: Prognathic describes an extended jaw shape. - Cheil (Greek: Lip):
Example: Cheiloplasty involves lip surgery, often paired with mandibular treatments.
FAQs About " Mandibulo "
Q: What does "mandibulo" mean, and where does it originate from?
A: The root "mandibulo" refers to the jaw, specifically the lower jawbone or mandible. It comes from the Latin word mandibula, which is derived from mandere, meaning "to chew." This highlights its functional association with mastication, the essential process of breaking down food.
Q: What is the mandible, and how does it differ from the maxilla?
A: The mandible is the lower jawbone and the only movable bone in the human skull, allowing for chewing and speaking. In contrast, the maxilla is the upper jawbone, which is fixed and forms part of the skull. Together, they create the structure of the mouth and face.
Q: Why is the mandible crucial for daily functions?
A: The mandible plays a vital role in chewing, speech, and facial structure. It anchors teeth, provides a platform for tongue movement, and supports lower facial muscles. Its mobility makes it indispensable for eating and articulating sounds in language.
Q: What are mandibular disorders, and what causes them?
A: Common mandibular disorders include temporomandibular joint (TMJ) dysfunction, fractures, and mandibular misalignments. Causes range from injuries, arthritis, and muscle tension to congenital defects. These conditions can lead to pain, difficulty in chewing, and restricted jaw movement.
Q: What is mandibular advancement, and why is it used?
A: Mandibular advancement refers to moving the lower jaw forward to correct sleep apnea, jaw misalignment, or bite problems. This procedure can involve dental appliances or surgical techniques to improve airflow, balance facial proportions, and restore function.
Q: How does the mandible contribute to speech?
A: The mandible’s movement facilitates the positioning of the tongue and lips, which are essential for articulating sounds and forming words. Without proper jaw function, speech can be slurred or impeded.
Q: What medical fields focus on the mandible?
A: The mandible is studied in multiple disciplines:
- Dentistry: Examining bite alignment, mandibular nerves, and oral health.
- Maxillofacial Surgery: Treating fractures, jaw deformities, and structural issues.
- Orthodontics: Correcting bite-related problems through braces or jaw repositioning.
Test Your Knowledge: " Mandibulo " Mastery Quiz
1. What does "mandibulo" mean?
2. Which term relates to the lower jaw?
3. What is a mandibular block?
4. Which root word relates to the upper jaw?
5. What is mandibular realignment used for?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Mandibulo
The root "mandibulo" stands as a testament to the jaw's critical role in health, communication, and identity. From ancient anatomical studies to cutting-edge medical technologies, it remains central to understanding human function and expression. As science and language evolve, "mandibulo" continues to anchor our exploration of the jaw’s complexities and capabilities.














