Mania: Exploring the Root of Obsession and Madness
Byline: Discover the dynamic and multifaceted root "mania," derived from the Greek term for madness or frenzy. From kleptomania to maniac, this powerful root has shaped words that express extreme enthusiasm or psychological disorders, bridging language, psychology, and culture.
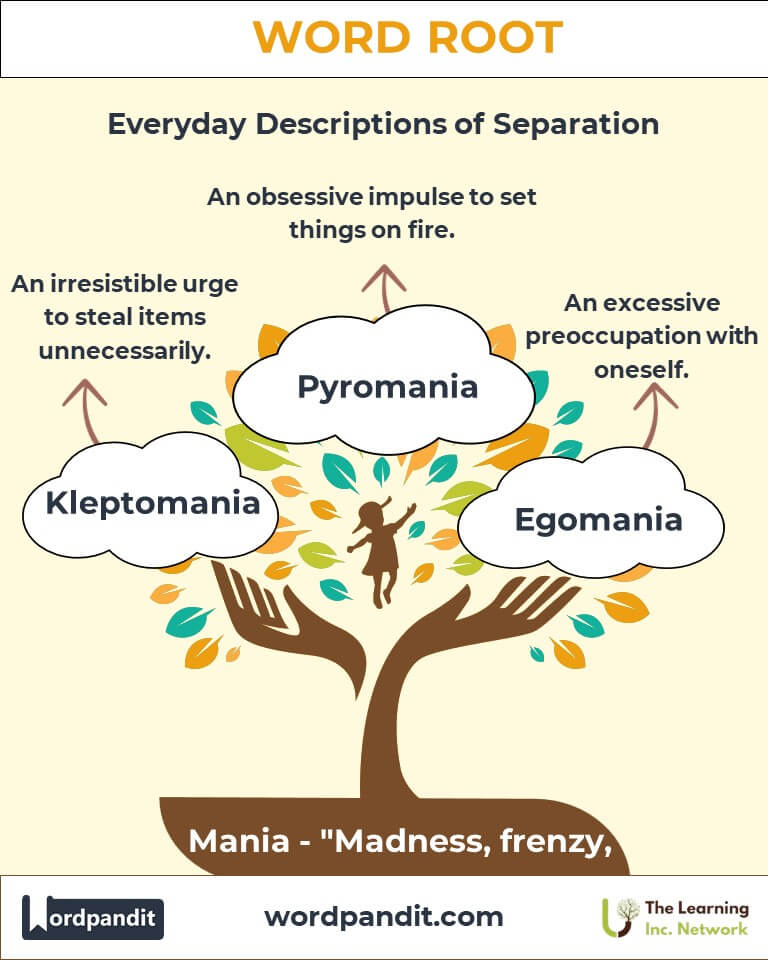
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Power of "Mania"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Mania"
- Common "Mania"-Related Terms
- "Mania" Through Time
- "Mania" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Mania" in Action
- Cultural Significance of "Mania"
- The "Mania" Family Tree
- FAQs About the Mania Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Mania Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Everlasting Impact of "Mania"
Introduction: The Power of "Mania"
Imagine an artist consumed by their craft, working day and night with fervor. Or consider someone who can't resist the urge to steal, even when unnecessary. Both examples illustrate the dual nature of "mania," a root representing extremes of obsession, enthusiasm, and madness. Originating from Greek, "mania" (pronounced may-nee-uh) forms the foundation of terms in psychiatry, popular culture, and everyday language.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "mania" originates from the Greek word manía, meaning madness, frenzy, or excessive enthusiasm. It was used in ancient Greek to describe a state of madness or divine inspiration, often attributed to the gods. Over time, the term was adopted into Latin and later English, where it expanded to describe both psychological conditions and intense passions.
Notable historical uses include its presence in Greek tragedies, where characters overcome by "mania" often faced dramatic fates. By the 19th century, "mania" gained prominence in psychiatry to denote specific mental health disorders.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Mania"
To remember "mania," picture a spinning top spinning uncontrollably, symbolizing frenzy and obsession.
Mnemonic Device: “Mania spins you into madness—whether driven by passion or disorder.”
Common "Mania"-Related Terms
- Kleptomania (klep-toh-may-nee-uh): An irresistible urge to steal items, often unnecessary.
Example: "Her kleptomania led her to pocket trinkets she didn't even need."
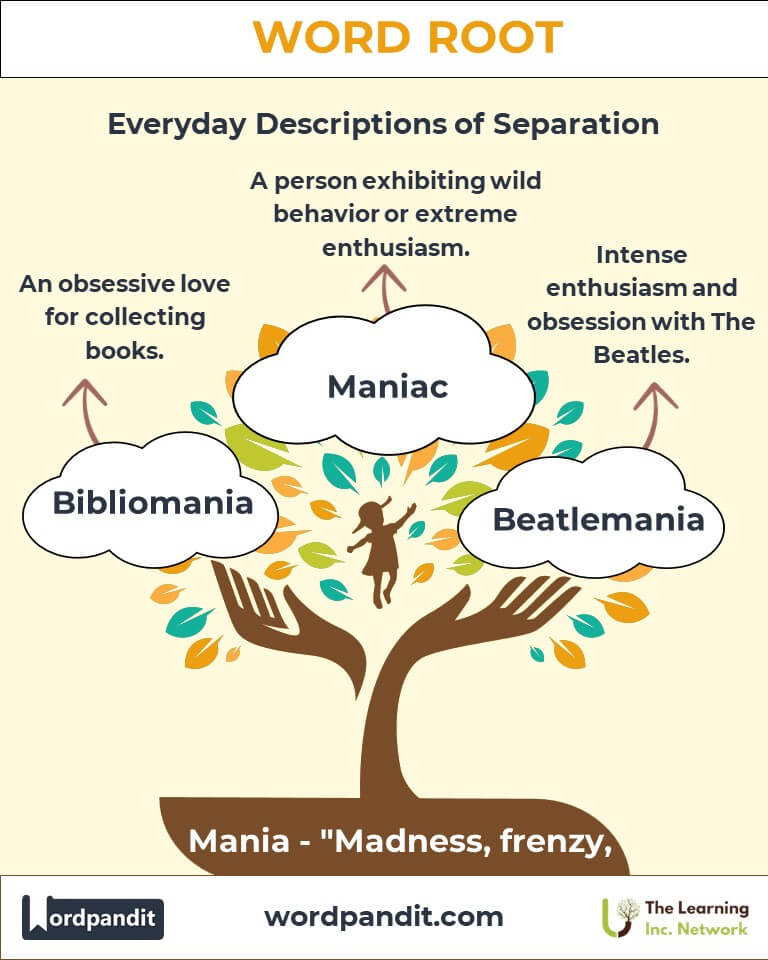
- Maniac (may-nee-ak): A person exhibiting wild or violent behavior, or extreme enthusiasm for something.
Example: "The maniac raced through the streets, yelling incoherently."
- Pyromania (pie-roh-may-nee-uh): An obsessive urge to set things on fire.
Example: "The investigator suspected pyromania as the cause of the repeated arsons."
- Bibliomania (bib-lee-oh-may-nee-uh): An excessive love for collecting books.
Example: "His bibliomania filled every corner of his home with rare manuscripts."
- Egomania (ee-go-may-nee-uh): An obsessive preoccupation with oneself.
Example: "The celebrity's egomania made it difficult for them to form genuine connections."
"Mania" Through Time
- Hippocratic Era: Mania was viewed as a medical condition requiring balancing of the body's humors.
- Middle Ages: Mania took on a religious connotation, sometimes associated with demonic possession.
- Modern Psychiatry: Terms like bipolar mania distinguish clinical conditions from everyday enthusiasm.
"Mania" in Specialized Fields
- Psychiatry:
- Manic Episode: A period of heightened mood, energy, and activity, often seen in bipolar disorder.
- Importance: Understanding mania is critical for diagnosing and managing mental health.
- Literature:
- Manic Prose: Describes writing imbued with frenetic energy or chaotic structure.
- Example: Many Romantic poets explored themes of mania and inspiration.
- Marketing and Pop Culture:
- Terms like "mania" describe widespread enthusiasm, e.g., "Beatlemania" or "Pokemon-mania."
- Relevance: Demonstrates society's collective obsessions.
Illustrative Story: "Mania" in Action
Sofia, an art student, found herself consumed by bibliomania. Her love for rare books led her to spend countless hours hunting down first editions. One day, she stumbled upon a shop housing a rare Shakespeare folio. Overwhelmed by her obsession, she bartered her savings to acquire it. Though her friends thought her a maniac, Sofia’s passion became the cornerstone of her blossoming career as a curator.
Cultural Significance of "Mania"
The root "mania" resonates deeply across cultures, capturing humanity's extremes—from divine inspiration in ancient Greece to modern fandoms. "Mania" highlights how obsession, whether pathological or celebratory, drives innovation, creativity, and connection.

The "Mania" Family Tree
- Phren- (Greek: "mind"):
- Schizophrenia: A mental disorder involving distorted thinking.
- Phrenology: The study of skull shapes to determine mental traits.
- Psych- (Greek: "soul, mind"):
- Psychology: The scientific study of the mind.
- Psychosis: A severe mental disorder affecting reality perception.
- Path- (Greek: "suffering, disease"):
- Pathology: The study of diseases.
- Apathy: Lack of feeling or interest.
FAQs About the Mania Word Root
Q: What does "mania" mean?
A: Mania originates from the Greek word manía, meaning madness, frenzy, or intense enthusiasm. While it often describes extreme psychological states, it can also refer to excessive passion or excitement, depending on context.
Q: What is the difference between "mania" and "enthusiasm"?
A: While enthusiasm denotes positive, controlled energy and interest, mania suggests an overwhelming, uncontrollable obsession that can sometimes have negative or pathological implications. For example, being passionate about a hobby is enthusiasm, while obsessively engaging in it to the detriment of one’s well-being may be described as mania.
Q: What is kleptomania?
A: Kleptomania is a psychological disorder characterized by a compulsive urge to steal items, even when they have no personal or monetary value. It is not driven by financial need or greed but rather by a lack of control over impulses.
Q: Can mania occur without mental illness?
A: Yes, mania can describe an intense passion or cultural phenomenon, such as "Beatlemania" or "sports mania," without implying a medical condition. However, in a clinical context, mania typically refers to heightened energy, mood, and activity levels associated with disorders like bipolar disorder.
Q: What causes mania in a psychological context?
A: Mania can result from underlying conditions like bipolar disorder or certain medical conditions, medication side effects, or substance use. It often requires medical evaluation and treatment to address its root causes and symptoms.
Test Your Knowledge: Mania Word Root Quiz
1. What does "mania" mean?
2. Which term describes the uncontrollable urge to steal?
3. What is pyromania?
4. What is a manic episode?
5. What does bibliomania describe?
Conclusion: The Everlasting Impact of "Mania"
The root "mania" embodies the spectrum of human passion and disorder. From clinical diagnoses to cultural phenomena, it continues to shape language and understanding. By embracing its complexities, we gain deeper insight into the extremes that drive human behavior and creativity.














