Metr: The Root of Measurement in Language, Science, and Beyond
Byline: Discover the profound significance of the word root "metr," originating from the Greek "metron," meaning "measure." From shaping mathematical terms to defining harmony and balance in art and architecture, this root has established its relevance across various disciplines and fields.
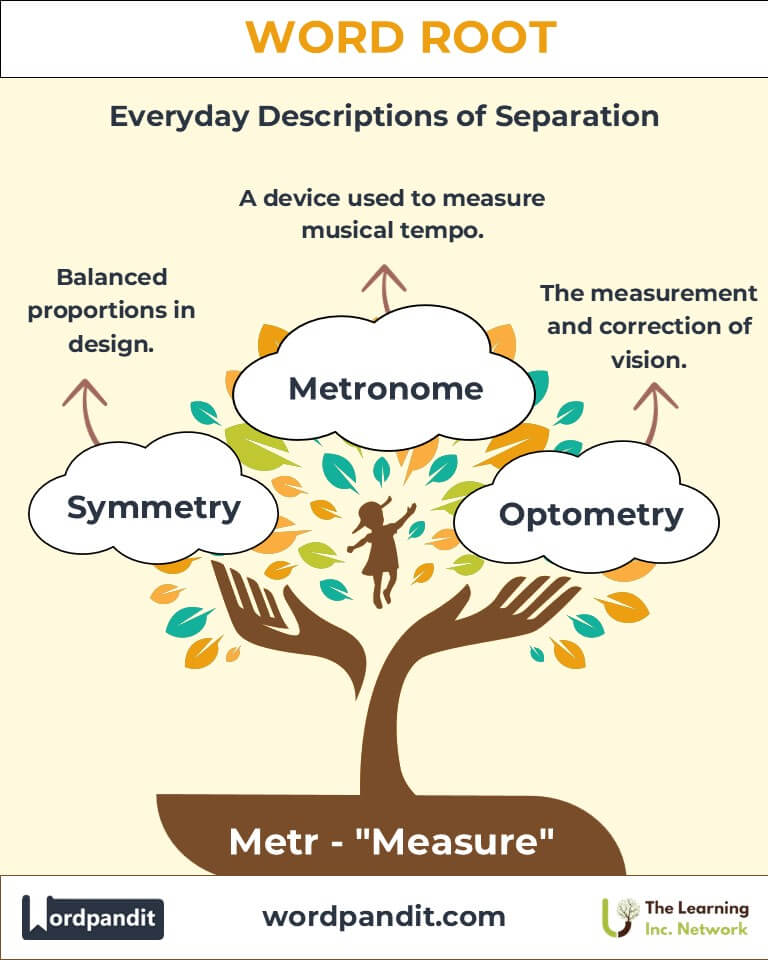
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Metr"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Metr"
- Common "Metr"-Related Terms
- "Metr" Through Time
- "Metr" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Metr" in Action
- Cultural Significance of the "Metr" Root
- The "Metr" Family Tree
- FAQs About the “Metr” Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: “Metr” Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Metr"
Introduction: The Essence of "Metr"
What unites the metric system, symmetry, and geometry? It’s the Greek root "metr," meaning "measure" or "meter." Pronounced "mee-tr" or "met-er" depending on context, this linguistic cornerstone appears in words that express precision, balance, and quantification. From mathematics to poetry, "metr" shapes how we perceive and describe the world.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "metr" derives from the Greek word metron, meaning "measure." Ancient Greek society valued precision and proportion, using "metron" to define concepts of balance in art, architecture, and philosophy. Through Latin, the root entered English, becoming integral to terms like "metric" and "geometry."
Over centuries, "metr" evolved in tandem with technological and scientific advancements, contributing to frameworks like the metric system, which standardizes measurement worldwide.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Metr"
Imagine a ruler labeled "Metr" that stretches endlessly, measuring everything from distances to ideas.
Mnemonic Device: "Metr measures the world, from symmetry in art to metrics in science."
Common "Metr"-Related Terms
- Metric (met-rik): Relating to or based on a system of measurement.
Example: "The metric system is used globally for scientific calculations." - Symmetry (sim-i-tree): Balanced proportions or harmony in arrangement.
Example: "The butterfly's wings exhibit perfect symmetry." - Geometry (jee-om-i-tree): The branch of mathematics dealing with the properties and relations of points, lines, and surfaces.
Example: "Geometry helps architects design structurally sound buildings." - Metronome (met-ruh-nohm): A device used to mark time at a selected rate by ticking.
Example: "The pianist practiced with a metronome to maintain rhythm." - Barometer (buh-rom-i-ter): An instrument measuring atmospheric pressure.
Example: "The barometer predicted an approaching storm." - Optometry (op-tom-uh-tree): The practice of examining eyes and prescribing corrective lenses.
Example: "Optometry helps millions maintain clear vision."
"Metr" Through Time
- Ancient Use: Early Greeks used "metron" in geometry to define balance and proportion.
Example: Symmetry in the Parthenon's design reflects their mathematical precision. - Modern Evolution: The metric system, established in 18th-century France, standardized global measurements.
Significance: It simplified international scientific communication and trade.
"Metr" in Specialized Fields
- Science: Barometer and thermometer rely on "metr" for quantifying environmental changes.
- Medicine: Optometry measures visual acuity, enhancing eye health.
- Engineering: Geometric principles underpin design and construction.
- Music: The metronome ensures rhythmic accuracy for musicians.
- Business: Metrics track performance, guiding strategic decisions.
Illustrative Story: "Metr" in Action
Lila, an aspiring architect, admired symmetry in ancient structures. Inspired, she enrolled in geometry classes, where she mastered the principles of measurement. Later, using metrics and symmetry, she designed a sustainable housing project that balanced aesthetics and functionality. Her work, a testament to "metr," harmonized human need with environmental care.
Cultural Significance of the "Metr" Root
In cultures worldwide, measurement symbolizes order and balance. Ancient Egyptians used geometry to build pyramids, while Greek philosophers like Pythagoras linked symmetry to universal harmony. Today, "metr" continues to influence art, architecture, and science, reflecting humanity’s quest for precision.

The "Metr" Family Tree
- Meter (Greek: "measure")
Thermometer: Measures temperature.
Speedometer: Measures speed. - Mens (Latin: "measure")
Immense: Beyond measurable size.
Dimension: A measurable extent. - Mod (Latin: "limit, measure")
Moderate: Kept within limits.
Modern: Relating to recent times.
FAQs About the "Metr" Root
Q: What does "metr" mean, and where does it come from?
A: The root "metr" means "measure" or "meter" and comes from the Greek word metron. It reflects concepts of quantification, balance, and precision. This root has shaped terms in science, mathematics, art, and even music, emphasizing humanity’s desire to understand and organize the world.
Q: How is "metr" used in science?
A: In science, "metr" appears in terms like barometer (measures atmospheric pressure), thermometer (measures temperature), and geometric principles that calculate shapes and spatial relationships. These tools and concepts help scientists quantify and analyze the natural world with precision.
Q: How is "symmetry" related to "metr"?
A: Symmetry comes from the Greek words syn (together) and metron (measure), meaning "measured together." It refers to balanced proportions or harmony in design, emphasizing evenness or equivalence in arrangement. This concept is prevalent in art, architecture, and nature.
Q: What is the difference between "metric" and "meter"?
A: "Metric" refers to a standardized system of measurement, such as the metric system, which is widely used globally for scientific and everyday purposes. "Meter," on the other hand, is a unit of length in the metric system, equal to 100 centimeters or approximately 39.37 inches.
Q: What is a barometer, and why is it important?
A: A barometer is an instrument used to measure atmospheric pressure. It is crucial in weather forecasting, as changes in atmospheric pressure can indicate upcoming storms, clear skies, or other weather conditions.
Q: How is the root "metr" used in music?
A: In music, the root appears in metronome, a device that helps musicians maintain a steady tempo by marking time with audible ticks. The concept of measuring rhythm is essential for synchronizing performance and creating harmonious compositions.
Q: Why is "metr" important in geometry?
A: Geometry, derived from geo (earth) and metron (measure), focuses on the measurement and relationships of shapes, angles, and spaces. It is fundamental in architecture, engineering, and sciences that require spatial reasoning and precision.
Test Your Knowledge: "Metr" Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "metr" mean?
2. Which term describes harmony in proportions?
3. What instrument measures atmospheric pressure?
4. What field uses optometry?
5. How does "metr" appear in geometry?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Metr"
The root "metr" continues to measure humanity’s progress across disciplines. From ancient geometry to modern metrics, its applications demonstrate our enduring pursuit of precision and balance. As new technologies and ideas emerge, "metr" will remain at the heart of innovation, guiding us toward harmony in science, art, and life.














