Mut: The Root of Change in Language and Life
Explore the transformative power of the word root "mut," originating from Latin and meaning "change." From biological mutations to immutable principles, this root encapsulates the essence of transformation and constancy across fields like science, philosophy, and everyday vocabulary.
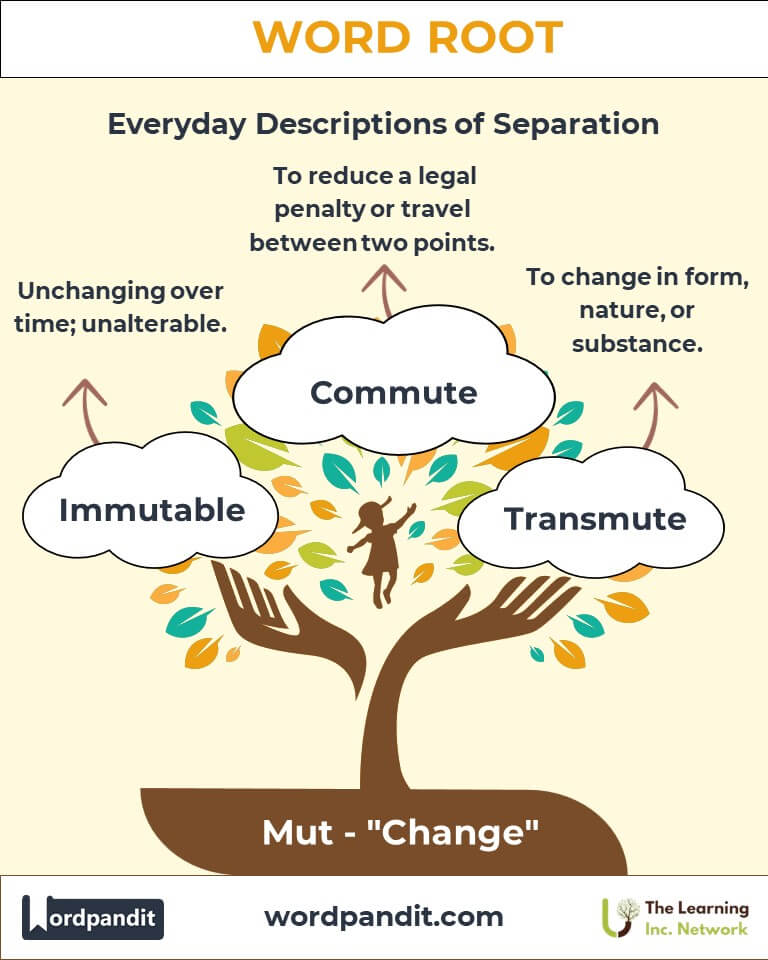
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Mut"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Mut"
- Common "Mut"-Related Terms
- "Mut" Through Time
- "Mut" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Mut" in Action
- Cultural Significance of "Mut"
- The "Mut" Family Tree
- FAQs About the "Mut" Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Mut" Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Enduring Impact of "Mut"
Introduction: The Essence of "Mut"
Change is an inevitable force in life, and the Latin root "mut" embodies this dynamic quality. Pronounced "myoot," this root forms the basis of words like "mutate" (to change) and "immutable" (unchanging). Its presence in diverse fields like genetics, philosophy, and linguistics highlights its universal relevance. Whether describing a biological mutation or an unyielding truth, "mut" anchors our understanding of transformation and constancy.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "mut" originates from the Latin word mutare, meaning "to change." It first appeared in classical texts describing physical, emotional, and situational changes. Over time, its derivatives entered English through Middle French and directly from Latin, enriching our lexicon with terms that explore both change and permanence. For example, the term "mutation" gained prominence in the 19th century with advances in biological sciences.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Mut"
To remember "mut," picture a caterpillar transforming into a butterfly—a vivid metaphor for change and growth.
Mnemonic Device:
“‘Mut’ means change, from caterpillar to butterfly, from mutable to immutable!”
Common "Mut"-Related Terms
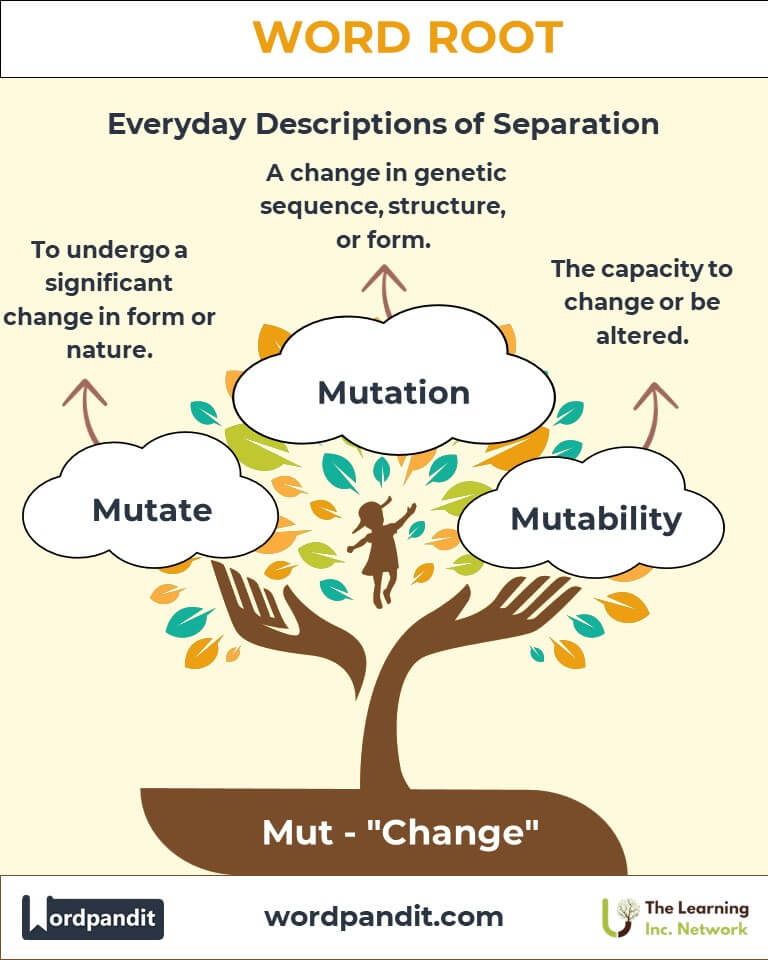
- Mutate (myoo-tayt):
Definition: To undergo a significant change, often in form or nature.
Example: "Scientists observed how the virus mutated into a new strain." - Immutable (ih-myoo-tuh-buhl):
Definition: Unchanging over time; unalterable.
Example: "The laws of physics are considered immutable." - Mutation (myoo-tay-shun):
Definition: A change in form, structure, or genetic sequence.
Example: "The mutation in the gene led to a unique trait in the organism." - Mutability (myoo-tuh-bil-uh-tee):
Definition: The capacity to change.
Example: "The mutability of fashion trends is astonishing." - Commute (kuh-myoot):
Definition: To travel regularly between two points or to reduce a penalty.
Example: "She commutes daily from the suburbs to the city."
"Mut" Through Time
- Mutation in Genetics: Initially a broad term, "mutation" became more specific with the advent of Mendelian genetics in the 19th century, denoting changes in DNA sequences.
- Mutable in Literature: In Renaissance literature, "mutable" was often used metaphorically to explore human frailty and the ever-changing nature of life.
"Mut" in Specialized Fields
- Genetics:
Mutation: Refers to a change in genetic material, critical in evolution and medicine.
Example: "Mutations can lead to genetic diversity or hereditary diseases." - Law:
Commute: To reduce a legal penalty.
Example: "The governor commuted the prisoner’s death sentence to life imprisonment." - Philosophy:
Immutable Truths: Refers to universal, unchanging principles.
Example: "The concept of immutable laws is central to metaphysics."
Illustrative Story: "Mut" in Action
Lila, a geneticist, worked tirelessly to study mutations in plants to enhance crop resistance. After years of experiments, she discovered a natural mutation that increased drought resistance. Across the globe, Anna, a philosopher, debated the immutable nature of human rights. Though their fields were vastly different, both women’s work revolved around the root "mut"—exploring change and constancy to make the world a better place.
Cultural Significance of "Mut"
The root "mut" captures the human experience of change. From myths about metamorphoses to scientific advancements in genetics, it symbolizes transformation and adaptability. Conversely, the concept of immutability provides a counterbalance, reminding us of enduring truths and universal constants.

The "Mut" Family Tree
- Trans- (Across):
Transmute: To change in form, nature, or substance.
Example: "Alchemists attempted to transmute lead into gold." - Meta- (Change):
Metamorphosis: A complete change of form.
Example: "The metamorphosis of a tadpole into a frog is fascinating." - Mob-/Mot- (Move):
Motion: The action of moving or changing position.
Example: "The planet’s motion around the sun is constant."
FAQs About the "Mut" Word Root
Q: What does "mut" mean?
A: The root "mut" means "change," derived from the Latin word mutare. It describes transformation, variation, or alteration in form, nature, or state. For example, "mutation" in biology signifies a change in DNA, while "mutable" denotes something capable of change.
Q: Is "mutate" only used in biology?
A: No, while "mutate" is common in biology to describe changes in genetic material, it is also used metaphorically in other contexts. For instance, a situation or policy can "mutate" when it changes dramatically over time.
Q: What is the opposite of mutable?
A: The opposite of "mutable" is "immutable," which means unchanging or unable to be altered. For example, in philosophy, the laws of nature are often considered immutable truths.
Q: What does "mutation" mean in everyday language?
A: Beyond genetics, "mutation" can refer to any significant or unusual change. For instance, a city might undergo a "mutation" in its cultural identity as it modernizes.
Q: How is "commute" related to "mut"?
A: The word "commute" comes from the idea of changing or transforming. It can mean changing a sentence in law (e.g., commuting a death sentence to life imprisonment) or traveling back and forth between two places (a change in location).
Test Your Knowledge: Mut Mastery Quiz
1. What does "mut" mean?
2. Which word means "unchanging"?
3. What is a mutation?
4. Which term relates to reduced penalties?
5. What is the philosophical concept of unchanging truths?
Conclusion: The Enduring Impact of "Mut"
The root "mut" captures the duality of life: the inevitability of change and the comfort of constancy. From the microscopic changes in DNA to philosophical debates on unyielding truths, "mut" remains a cornerstone of language and thought. Let the transformative power of "mut" inspire you to embrace change and seek enduring truths in your journey of growth.














