Narr: The Power of Storytelling in Language and Expression
Discover the rich world of the root "narr," derived from Latin, meaning "to tell." From weaving intricate narratives to narrating compelling stories, this root has shaped the language of storytelling, communication, and expression.
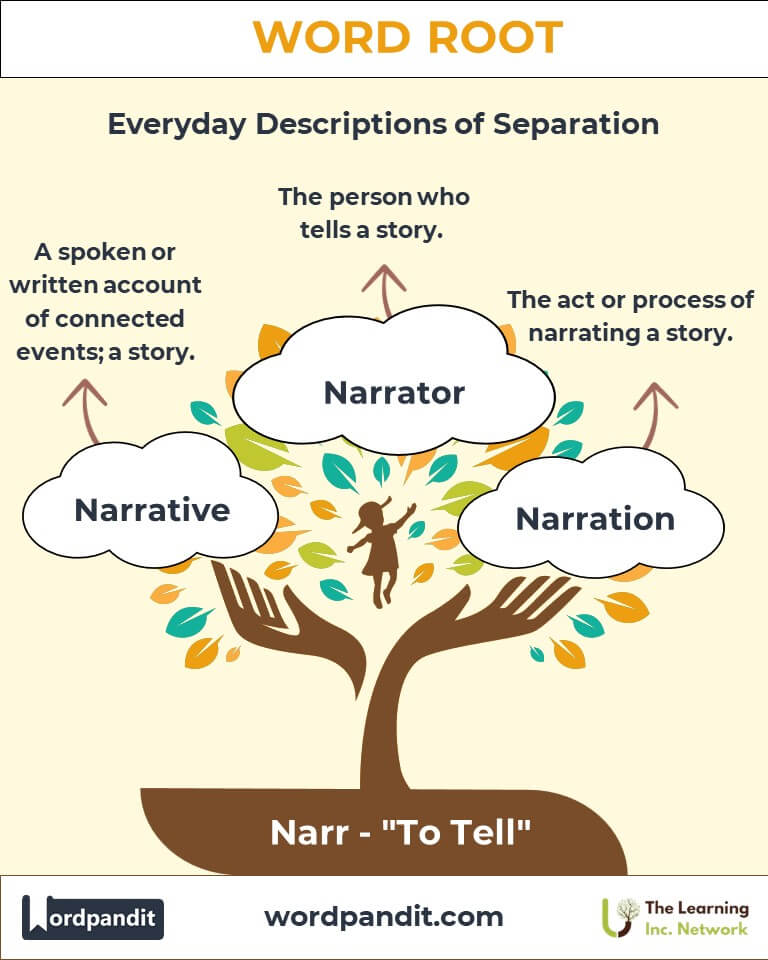
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Narr"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Narr"
- Common "Narr"-Related Terms
- "Narr" Through Time
- "Narr" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Narr" in Action
- Cultural Significance of the "Narr" Root
- The "Narr" Family Tree
- FAQs About the "Narr" Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Narr" Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Narr"
Introduction: The Essence of "Narr"
What makes a story captivating? The word root "narr" (pronounced "nahr"), meaning "to tell," is at the heart of storytelling. Originating from Latin, "narr" has given rise to words that encapsulate the art of sharing tales, whether through oral traditions, literature, or modern media. From the spoken word to cinematic storytelling, the "narr" root connects us through narratives that inform, entertain, and inspire.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "narr" traces its origins to the Latin word narrāre, meaning "to relate" or "to tell." In classical Rome, storytelling was a revered art, with "narrators" recounting tales of history, mythology, and culture. As Latin evolved into Old French and Middle English, "narr" words entered the English language, bringing with them a tradition of verbal and written expression.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Narr"
Picture a storyteller weaving magic with words, their audience captivated around a glowing campfire. Think of "Narr" as the flame that kindles tales.
Mnemonic Device:
"‘Narr’ is the spark of stories, lighting up minds with every word."
Common "Narr"-Related Terms
- Narrative (NAIR-uh-tiv):
Definition: A spoken or written account of connected events; a story.
Example: "The novel’s narrative captivated readers with its twists and turns." - Narrator (NAIR-ray-ter):
Definition: The person who tells a story.
Example: "The narrator’s voice added depth to the audiobook." - Narrate (NAIR-rate):
Definition: To tell a story or give an account of something.
Example: "She was chosen to narrate the documentary due to her expressive voice." - Narration (NAIR-ray-shun):
Definition: The act or process of narrating a story.
Example: "His narration brought the characters to life." - Narcolepsy (NAHR-koh-lep-see):
Definition: A condition characterized by sudden, uncontrollable sleep episodes.
Example: "Though seemingly unrelated, the connection lies in narcolepsy’s association with lapses in consciousness, akin to 'drifting into a narrative' state."
"Narr" Through Time
- Narrative (Middle Ages): Evolved to represent written accounts, particularly in historical chronicles.
- Narration (19th Century): Gained prominence with the rise of novels and oral storytelling traditions.
- Narrate (Modern Era): Expanded into digital formats, such as podcasts and audiobooks, showcasing the evolution of storytelling mediums.
"Narr" in Specialized Fields
- Literature:
Narrative Arc: The structure of a story, including exposition, climax, and resolution.
Application: Helps writers craft compelling plots. - Film & Media:
Narration: Adds depth to documentaries and animated features.
Example: A famous example is Morgan Freeman’s narration in nature documentaries. - Psychology:
Narrative Therapy: A counseling approach that encourages individuals to rewrite their personal stories.
Impact: Empowers clients by reframing challenges as stories of resilience.
Illustrative Story: "Narr" in Action
In a small village, an elderly storyteller named Maria narrated tales to eager children. One day, a young girl named Elena asked Maria to teach her the art of narration. Through years of practice, Elena became a renowned narrator, bringing the village's stories to the world. Her narrative united distant communities, proving that the root "narr" is more than a word—it’s a bridge between hearts.
Cultural Significance of the "Narr" Root
The art of storytelling has been integral to human culture since prehistoric times. Oral narratives preserved histories, values, and traditions. Today, "narr" remains vital in literature, film, and digital media, embodying humanity's timeless need to connect through shared experiences.

The "Narr" Family Tree
- Scrib/Scrip (Latin: to write):
Examples: Manuscript, describe. - Log (Greek: word, study):
Examples: Dialogue, monologue. - Tell (Old English: to count, relate):
Examples: Tale, telltale.

FAQs About the "Narr" Word Root
Q: What does the root "narr" mean, and where does it come from?
A: The root "narr" means "to tell" or "to relate." It originates from the Latin word narrāre, meaning "to recount" or "to explain." This root underpins words associated with storytelling and the communication of ideas, making it fundamental to literature, media, and human interaction.
Q: How is "narration" different from "narrative"?
A: Narration refers to the act or process of telling a story, often describing how a story is conveyed, such as through a narrator's voice in an audiobook. Narrative, on the other hand, refers to the content of the story itself, encompassing the sequence of events and the structure in which they are presented.
Q: What role does a narrator play in storytelling?
A: A narrator guides the audience through a story, providing context, insight, and perspective. They can be part of the story (first-person narrator) or an external observer (third-person narrator). Their tone, reliability, and style can significantly shape how a narrative is perceived.
Q: Can "narrate" apply outside of storytelling?
A: Yes, narrate is not limited to fictional storytelling. It can refer to recounting factual events, like narrating a documentary or describing real-life occurrences in an engaging or structured manner. It’s widely used in news, media, and even legal contexts where events are explained in detail.
Q: What is a "narrative arc," and why is it important?
A: A narrative arc describes the structure of a story, including its introduction, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution. It’s vital because it gives coherence and flow to a story, engaging the audience and ensuring that events unfold logically and emotionally.
Test Your Knowledge: Narr Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "narr" signify?
2. Which term describes the person telling a story?
3. What is a narrative arc?
4. How is "narrate" used in media?
5. Which field uses narrative therapy?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Narr"
The root "narr" weaves through history, connecting generations through the art of storytelling. From ancient oral traditions to modern digital media, its legacy continues to evolve. As long as humans have stories to share, "narr" will remain a vital part of our linguistic and cultural heritage. Let it inspire you to tell your own tale, adding your voice to the grand narrative of life.














