Nom: The Root of Names and Laws in Language and Science
Byline:
Explore the fascinating journey of the root "nom," derived from Latin and Greek origins meaning "name" or "law." This versatile root has shaped words spanning disciplines, from governance and naming conventions to celestial studies like astronomy.
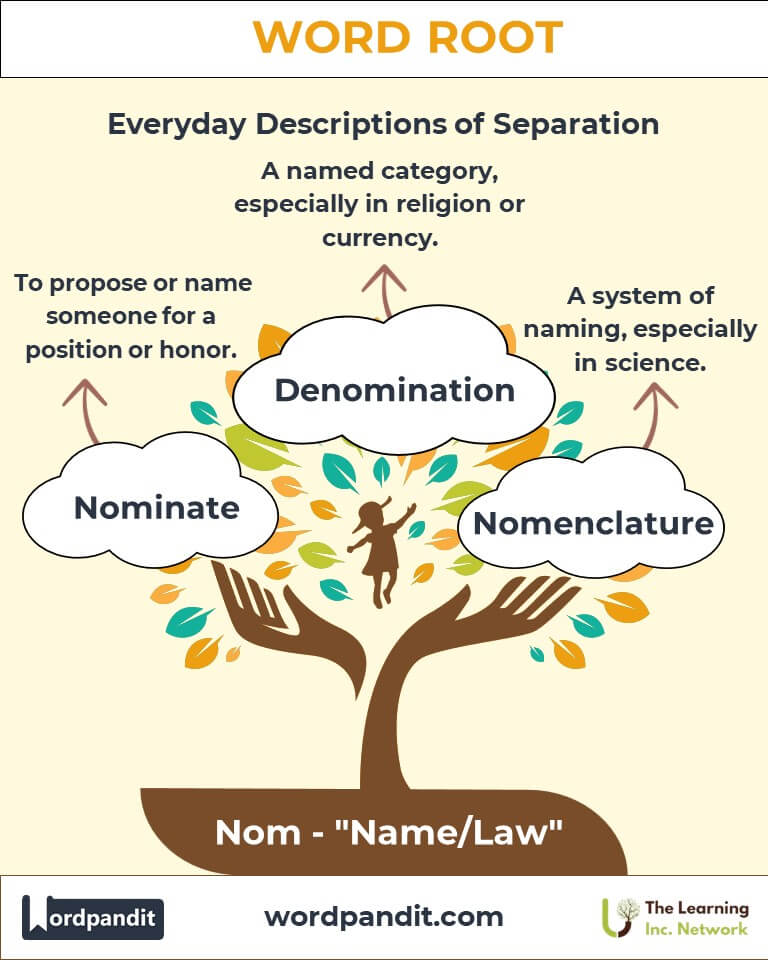
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Significance of "Nom"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Nom"
- Common "Nom"-Related Terms
- "Nom" Through Time
- "Nom" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Nom" in Action
- Cultural Significance of the "Nom" Root
- The "Nom" Family Tree
- FAQs about the "Nom" Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Nom" Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Nom"
Introduction: The Significance of "Nom"
The root "nom," pronounced as "nom," embodies the essence of naming and order. Derived from Latin and Greek roots, it weaves through language and science, signifying the act of naming (nominate) and the laws governing the cosmos (astronomy). Its dual role in linguistics and structure highlights its impact on human understanding and organization.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "nom" stems from the Latin nomen (name) and Greek nomos (law or custom). Ancient civilizations utilized "nomos" to describe societal regulations and divine laws. Over centuries, it evolved into terms reflecting order, classification, and naming in diverse languages.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Nom"
Picture a judge holding a gavel labeled "NOM," signifying both the authority to enforce laws and the power to bestow names.
Mnemonic Device: "Nom gives names and enforces norms."
Common "Nom"-Related Terms
- Nominate
Pronunciation: nom-i-nate
Definition: To propose or name someone for a position or honor.
Example: "The committee will nominate a candidate for the award." - Astronomy
Pronunciation: as-tron-o-mee
Definition: The scientific study of celestial objects and the laws governing them.
Example: "Astronomy reveals the mysteries of the universe." - Nominal
Pronunciation: nom-i-nal
Definition: Relating to names or existing in name only.
Example: "She was the nominal head of the organization." - Denomination
Pronunciation: de-nom-i-nation
Definition: A named category, especially in religion or currency.
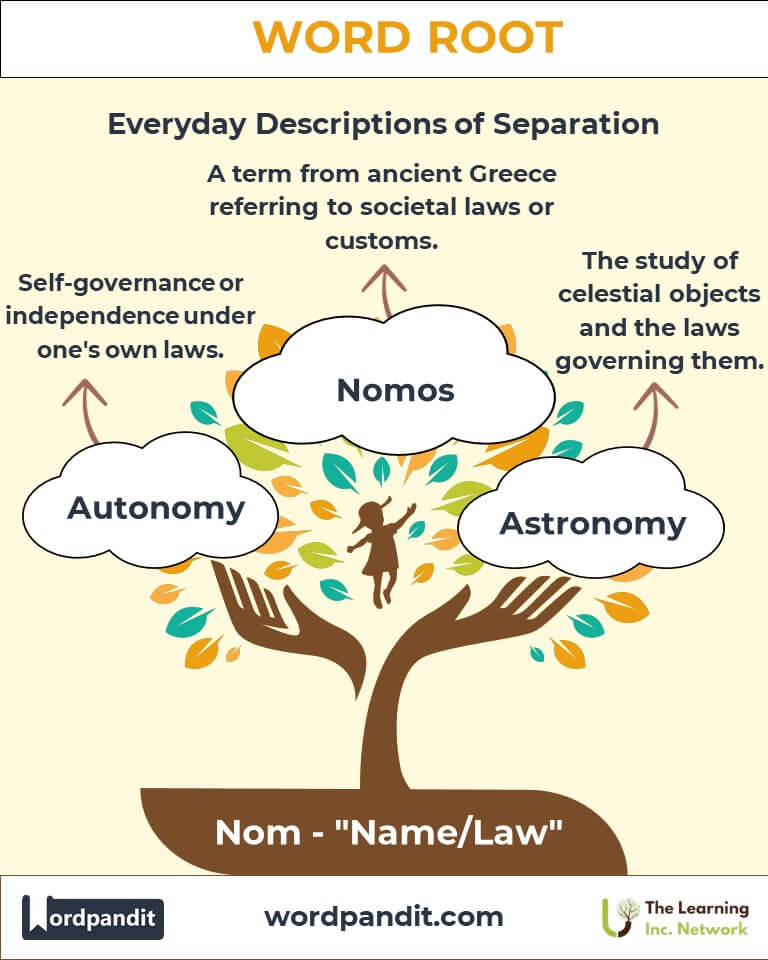
Example: "Various denominations of currency are in circulation." - Autonomy
Pronunciation: aw-ton-o-mee
Definition: Self-governance or independence under one's own laws.
Example: "The region sought autonomy from the central government."
"Nom" Through Time
- Nomos: In ancient Greece, "nomos" referred to societal laws or divine ordinances.
Example: Philosophers like Plato discussed "nomos" as central to governance. - Nomenclature: The system of naming in sciences like taxonomy, formalized in the 18th century.
Example: Carolus Linnaeus revolutionized biological nomenclature.
"Nom" in Specialized Fields
- Science:
- Astronomy: Study of the laws governing celestial objects and their movements.
- Nomenclature: Naming systems in taxonomy, chemistry, and more.
- Law and Governance:
- Autonomy: Legal independence of entities.
- Denomination: Categories in religion and financial systems.
- Linguistics:
- Nominal: Relating to names or noun forms in grammar.
Illustrative Story: "Nom" in Action
In a bustling medieval town, a council gathered to nominate a new leader. The astronomer among them argued that their laws, like the stars, should follow natural order. Inspired, they developed a system where nominees were chosen based on wisdom and alignment with communal laws—echoing the balance found in both "nomos" and the stars.
Cultural Significance of the "Nom" Root
"Nom" embodies humanity's need for order and identity, from naming systems in ancient rituals to the laws governing societies and sciences. Its presence in religious, scientific, and legal contexts highlights its role in shaping civilizations.

The "Nom" Family Tree
- Nomen (Latin: "name"):
- Nomenclature: System of naming.
- Denominator: The part of a fraction below the line.
- Nomos (Greek: "law"):
- Economy: From "oikos-nomos," meaning household management.
- Autonomy: Self-rule or independence.
- Onoma (Greek: "name"):
- Synonym: Words with similar meanings.
- Anonymous: Without a name.
FAQs About the "Nom" Word Root
Q: What does the root "nom" mean?
A: The root "nom" means "name" or "law," derived from the Latin "nomen" (name) and Greek "nomos" (law). It encapsulates concepts of identity (through naming) and structure or regulation (through laws), which are fundamental to language, governance, and science.
Q: How is "nom" connected to naming systems in science?
A: In science, "nom" appears in "nomenclature," which refers to the systematic naming of entities. For instance, in biology, the binomial nomenclature system assigns scientific names to organisms, ensuring global consistency and clarity.
Q: What does "nominal" mean, and how is it used?
A: "Nominal" relates to names or existing in name only. It can describe something small or symbolic (e.g., "a nominal fee") or indicate an official designation without real authority (e.g., "a nominal leader").
Q: What is the relationship between "nomos" and laws?
A: The Greek word "nomos" signifies laws or customs. It underscores societal and natural regulations, evident in words like "economy" (household management, derived from "oikos-nomos") and "astronomy" (laws of celestial objects).
Q: Why is "autonomy" derived from the root "nom"?
A: "Autonomy" combines "auto" (self) with "nomos" (law) to mean "self-rule" or independence. It refers to an individual’s or entity’s ability to govern themselves under their own laws, emphasizing the concept of internal regulation or sovereignty.
Test Your Knowledge: "Nom" Word Root Quiz
1. What does the root "nom" signify?
2. Which word refers to naming systems in science?
3. What is the study of celestial laws called?
4. What does "autonomy" mean?
5. What is the difference between "nominate" and "denominate"?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Nom"
From naming celestial bodies to codifying human laws, the root "nom" connects humanity’s quest for identity and order. Its continued presence in language and specialized fields underscores its enduring relevance, inspiring us to name, define, and explore the world with precision and creativity.














