Oro: The Pinnacle of Language and Meaning
Discover the heights of the root "oro," derived from the Greek and Latin words for "mountain." From shaping scientific terminology like "orography" to depicting transformative geological processes in "orogenic," this word root symbolizes the towering importance of mountains in our lives and language.
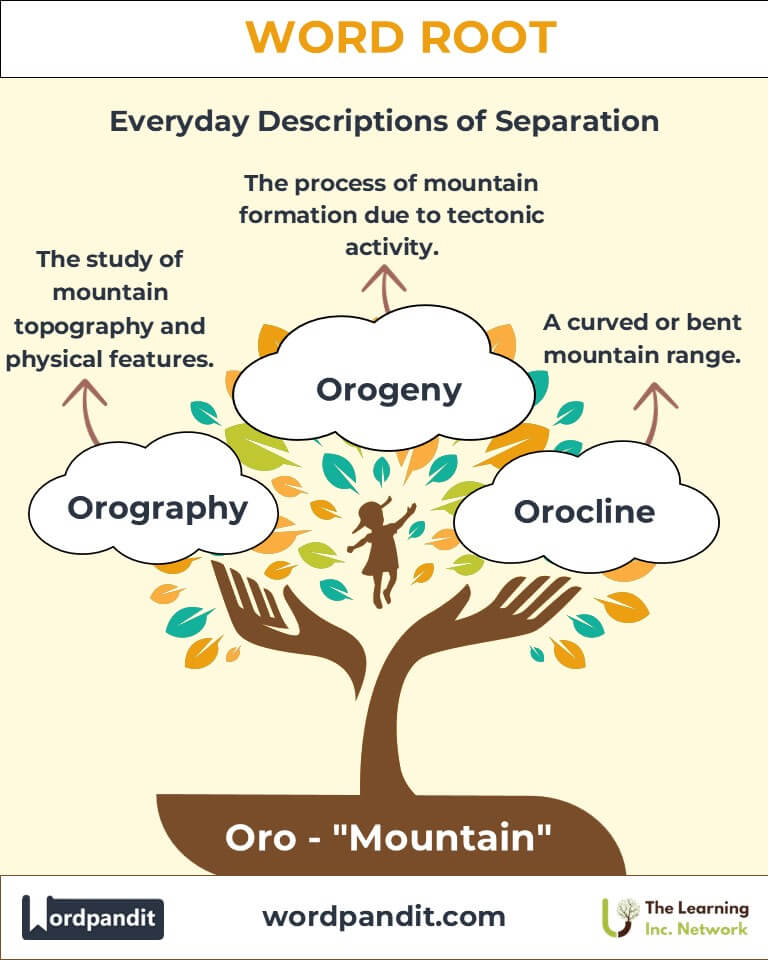
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Oro
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Oro
- Common Oro-Related Terms
- Oro Through Time
- Oro in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Oro in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Oro Root
- The Oro Family Tree
- FAQs About the “Oro”Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge:”Oro” Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Oro
Introduction: The Essence of Oro
The root "oro" (pronounced "oh-ro") carries a majestic weight, literally meaning "mountain" in Latin and Greek. Its towering imagery has inspired words across fields, from geography to geology. Whether mapping the world’s peaks through orography or studying the mountain-building forces of orogenesis, oro anchors us to the awe-inspiring power of Earth's landscapes. But the influence of this root isn’t limited to science; its echoes can be found in literature, culture, and metaphorical language.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The oro root originates from the Greek oros and the Latin or-, oro, both meaning "mountain." In ancient cultures, mountains were often regarded as sacred places, connecting the heavens and the earth. The root oro later found its way into scientific disciplines during the Renaissance, enriching the lexicon of geologists and geographers as they studied Earth’s physical features.
Over time, oro has expanded its semantic reach, symbolizing monumental achievements, challenges, and transformations in metaphorical contexts.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Oro
To remember oro, imagine a mighty mountain range stretching across a vibrant horizon. Picture yourself shouting “Oro!” as you summit the peak, celebrating the height and grandeur that this root represents.
Mnemonic Device:
"Oro takes you to the top—think of towering mountains and monumental heights."
Common Oro-Related Terms
- Orography (oh-RAW-gruh-fee):
Definition: The study of the physical features and topography of mountains.
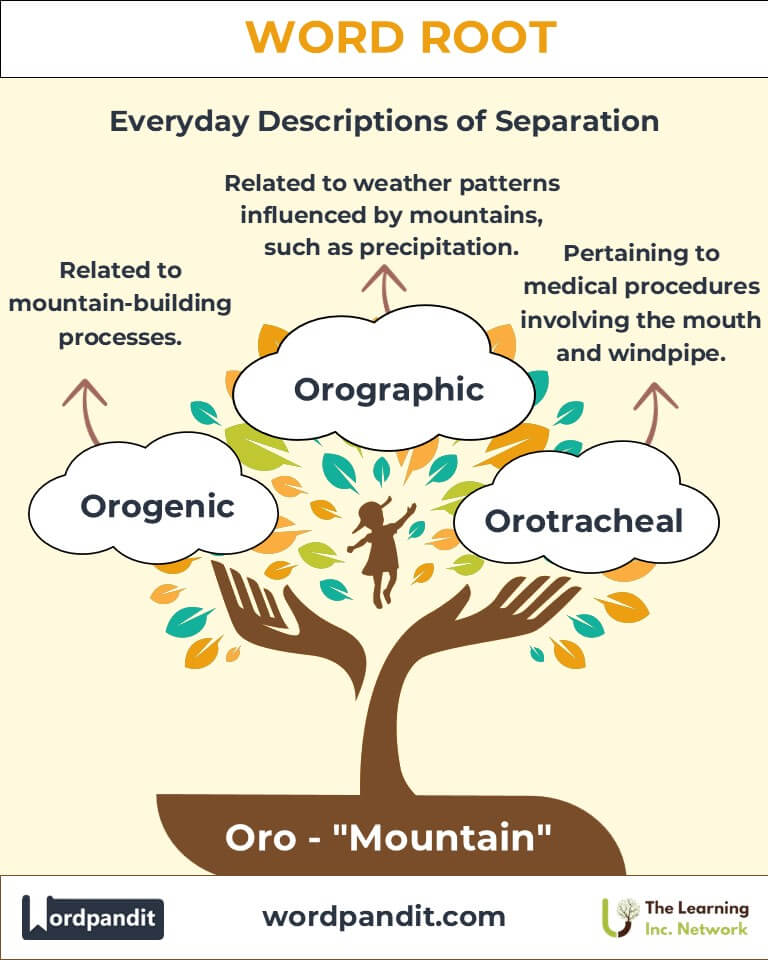
Example: "The orography of the Himalayas reveals their complex geological history." - Orogenic (or-oh-JEN-ik):
Definition: Related to mountain-building processes.
Example: "The Andes were formed by orogenic forces over millions of years." - Orocline (OR-oh-kline):
Definition: A curved or bent mountain range.
Example: "The Appalachians exhibit characteristics of an ancient orocline." - Orotracheal (OR-oh-TRAY-kee-uhl):
Definition: Pertaining to medical procedures involving the mouth and windpipe.
Example: "An orotracheal intubation was necessary during the emergency." - Orogeny (or-AWJ-uh-nee):
Definition: The process of mountain formation, especially through tectonic activity.
Example: "The orogeny of the Rockies is linked to plate tectonic movements."
Oro Through Time
- Ancient Context: The term oros in ancient Greek often symbolized divine or unreachable realms, reinforcing the sacred status of mountains.
- Scientific Evolution: By the 18th and 19th centuries, geologists used orogenic and orogeny to describe the forces that shape Earth's crust into mountain ranges.
- Modern Use: Today, oro has expanded into fields like environmental science and linguistics, illustrating its adaptability.
Oro in Specialized Fields
- Geology:
Orogenesis: Describes the collision and folding of Earth’s crust.
Impact: Critical in understanding plate tectonics and Earth's history. - Medicine:
Orotracheal Intubation: Highlights the root’s use beyond geology, referring to medical procedures involving the mouth and trachea.
Relevance: Essential in emergency and surgical care. - Geography:
Orographic Precipitation: Occurs when moist air rises over mountains, cooling and condensing into rain or snow.
Application: Vital for understanding climate patterns.
Illustrative Story: Oro in Action
Lila, a geologist, embarked on an expedition to study the orogenic forces that shaped the Andes. As she climbed higher, she marveled at the interplay of geology and time. Her findings revealed how ancient orogenies sculpted the rugged peaks and valleys, influencing local ecosystems and cultures. Inspired by her research, Lila wrote a book, sharing the story of Earth's mountains with the world.
Cultural Significance of the Oro Root
Mountains have always been symbols of strength, resilience, and spirituality. The oro root encapsulates this cultural significance. From the sacred Mount Olympus in Greek mythology to the towering Himalayas revered by Buddhists and Hindus, oro connects us to humanity’s shared reverence for these majestic landforms.

The Oro Family Tree
- Geo- (Earth):
- Geology: Study of Earth’s physical structure.
- Geography: Study of Earth’s surfaces and human interactions.
- Mont- (Mountain):
- Montane: Pertaining to mountainous regions.
- Mont Blanc: The highest mountain in the Alps.
- Alp- (Mountain):
- Alpine: Related to high mountains or their ecosystems.
- Alpinist: A climber specializing in high-altitude mountains.
FAQs About the Oro Word Root
Q: What does "oro" mean?
A: The root "oro" means "mountain" and is derived from the Greek word oros and the Latin or- or oro. It is often used to describe anything related to mountains or high elevations, such as mountain-building processes (orogeny) or the study of mountainous terrains (orography).
Q: What is orography?
A: Orography is the scientific study of the topography and physical features of mountains. Geographers and geologists use this term to understand the formation, structure, and climate interactions of mountain ranges. For example, orography helps map the effects of mountains on local weather patterns, such as rainfall distribution.
Q: How does orogenic relate to geology?
A: Orogenic refers to mountain-building processes that occur due to tectonic plate interactions. These processes, called orogenies, involve folding, faulting, and uplift of the Earth's crust. The term is vital in geology because orogenic events shape some of the most prominent landscapes on Earth, such as the Himalayas and the Rockies.
Q: What is orographic precipitation?
A: Orographic precipitation occurs when moist air masses are forced to rise over a mountain range. As the air rises, it cools and condenses, resulting in rain or snow on the windward side of the mountain. This phenomenon explains why mountain regions often experience heavy rainfall on one side (the windward side) and drier conditions on the other (the leeward side).
Q: Is "oro" used outside of geology and geography?
A: Yes, the root "oro" extends into fields like medicine and meteorology. For example, in medicine, "orotracheal" refers to procedures involving the mouth and trachea. The root’s versatility underscores its importance in describing relationships between elevation, structure, and even human anatomy.
Q: What is orogeny?
A: Orogeny refers to the geological process through which mountains are formed. It typically involves plate tectonics, where two plates collide, causing the crust to fold and uplift. Examples of significant orogenic events include the formation of the Alps and the Andes. Orogeny is central to understanding the Earth's dynamic crust.
Test Your Knowledge: Oro Word Root Quiz
1. What does the root "oro" signify?
2. Which term describes the process of mountain-building?
3. What causes orographic precipitation?
4. What does "orotracheal" refer to?
5. Which term describes a curved mountain range?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Oro
The root oro stands as a linguistic monument to the majesty of mountains. From describing Earth’s peaks to metaphorically symbolizing life’s challenges, it inspires us to explore and overcome. As we continue to study and respect the natural world, the legacy of oro will undoubtedly remain as enduring as the mountains it represents.














