Oste: The Foundation of Bones in Language and Medicine
Discover the significance of the root "Oste," meaning "bone," derived from Greek. Words like "osteoporosis" and "osteopathy" reveal its central role in understanding skeletal health and healing. From ancient medical practices to modern orthopedic innovations, "Oste" connects language to the structure and support of life.
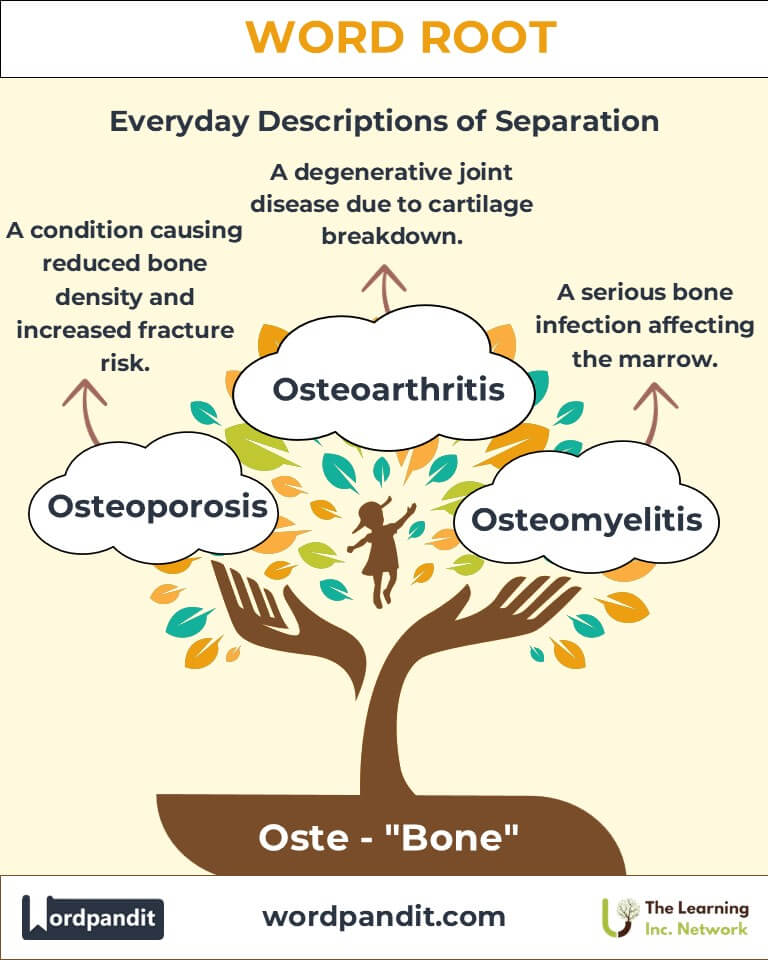
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Oste"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Oste"
- Common "Oste"-Related Terms
- "Oste" Through Time
- "Oste" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Oste" in Action
- Cultural Significance of the "Oste" Root
- The "Oste" Family Tree
- FAQs about the "Oste" Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Oste" Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Oste"
Introduction: The Essence of "Oste"
The word root "Oste" evokes images of strength, support, and life itself. Originating from the Greek word osteon (meaning "bone"), it forms the basis of medical terms and practices related to the skeletal system. Pronounced "ahs-tee" or "os-tee," this root emphasizes the importance of bones in our bodies and the language of healing.

Etymology and Historical Journey
"Oste" traces its origins to ancient Greece, where osteon referred to bones in anatomy and medicine. The Greek physician Hippocrates first explored skeletal conditions, setting the foundation for "oste"-related terminology. Through Latin adaptations, "Oste" entered medieval medical texts and modern English, influencing orthopedics and osteopathic practices worldwide.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Oste"
To remember "Oste," picture a sturdy skeleton holding a banner that reads "OSTE – Support for Life." The skeleton symbolizes the root’s meaning and the essential role of bones.
Mnemonic Device:
"Oste means bones—our body’s natural pillars!"
Common "Oste"-Related Terms
- Osteoporosis (os-tee-oh-puh-roh-sis):
Definition: A condition characterized by weakened bones due to reduced density.
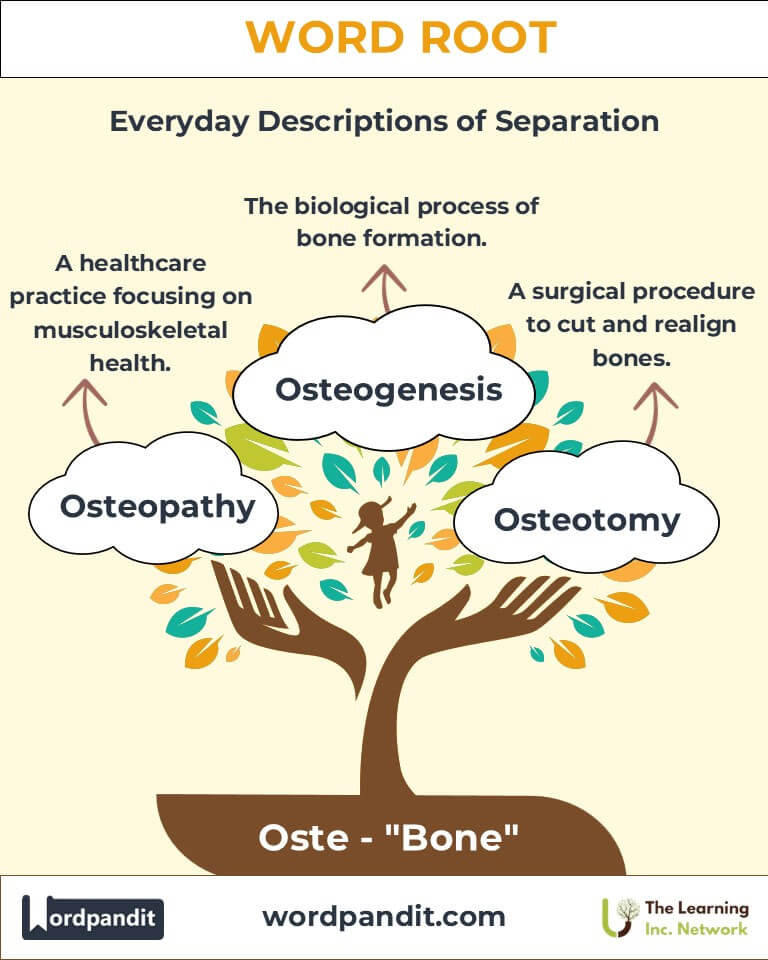
Example: "Calcium supplements can help prevent osteoporosis in older adults." - Osteopathy (os-tee-ah-puh-thee):
Definition: A medical practice focusing on diagnosing and treating skeletal and muscular issues.
Example: "The osteopath used gentle manipulations to relieve her back pain." - Osteogenesis (os-tee-oh-jen-uh-sis):
Definition: The process of bone formation.
Example: "Osteogenesis is crucial during childhood growth." - Osteoarthritis (os-tee-oh-ahr-thry-tis):
Definition: A degenerative joint disease caused by cartilage breakdown.
Example: "Osteoarthritis often affects the knees and hips in older individuals." - Osteotomy (os-tee-ah-tuh-mee):
Definition: A surgical procedure to cut and realign bones.
Example: "The surgeon performed an osteotomy to correct the bone deformity."
"Oste" Through Time
- Ancient Greece: Hippocrates documented skeletal injuries and healing, marking the root’s first significant use.
- Renaissance Medicine: "Osteology" emerged as the study of bones, combining classical knowledge with anatomical discoveries.
- Modern Medicine: Terms like "osteoporosis" highlight advances in diagnosing and treating skeletal conditions.
"Oste" in Specialized Fields
- Medicine:
Osteoporosis: Understanding and preventing bone density loss.
Osteopathy: Emphasizing holistic approaches to musculoskeletal health. - Biology:
Osteogenesis: Studying bone formation and repair mechanisms. - Surgery:
Osteotomy: Enhancing mobility and correcting deformities through surgical intervention. - Sports Medicine:
Osteochondritis: Addressing joint and cartilage conditions in athletes.
Illustrative Story: "Oste" in Action
Dr. Elena, an osteopath, treated a patient suffering from osteoporosis. By combining dietary advice, gentle exercises, and manual therapy, she helped restore their strength and confidence. Her holistic approach showcased the profound impact of "Oste"-inspired care on skeletal health and overall well-being.
Cultural Significance of the "Oste" Root
From ancient Greece to modern healthcare, "Oste" symbolizes resilience and healing. Sculptures of skeletons in art highlight humanity’s fascination with structure, while osteopathy emphasizes balance between body and mind. These cultural connections reinforce the root’s universal relevance.

The "Oste" Family Tree
- Arthro- (Joint):
- Arthritis: Inflammation of joints.
- Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive procedure to examine joints.
- Chondro- (Cartilage):
- Chondritis: Inflammation of cartilage.
- Chondrocyte: A cell that produces cartilage.
- Myelo- (Marrow):
- Osteomyelitis: Bone infection involving the marrow.
- Myeloma: A type of bone marrow cancer.
FAQs About the Oste Word Root
Q: What does the root "Oste" mean?
A: "Oste" means "bone," derived from the Greek word osteon. It is the foundation for medical terms and practices related to skeletal health and the study of bones. This root is essential in describing the structural framework of living organisms.
Q: What is osteoporosis?
A: Osteoporosis is a medical condition characterized by reduced bone density, making bones weak and prone to fractures. It is most common in older adults and can be managed through diet, exercise, and medication.
Q: How does osteopathy differ from conventional medicine?
A: Osteopathy is a form of holistic healthcare that emphasizes the interconnection of bones, muscles, and the nervous system. Osteopaths use hands-on techniques, such as stretching and manipulation, to improve body function and address pain, distinguishing it from more medication-focused treatments.
Q: What is osteogenesis?
A: Osteogenesis refers to the biological process of new bone formation. It occurs naturally during growth and healing, involving specialized cells like osteoblasts that lay down bone material.
Q: What is the role of osteotomy in medicine?
A: Osteotomy is a surgical procedure in which a bone is cut to realign or reshape it. It is often performed to correct deformities, relieve pain from joint disorders, or improve mobility, particularly in cases of severe osteoarthritis or misaligned fractures.
Q: Can osteoarthritis be cured?
A: While there is no definitive cure for osteoarthritis, treatments like physiotherapy, medications, lifestyle changes, and in severe cases, surgery can manage symptoms effectively. Early intervention can slow its progression.
Q: What are osteoclasts and osteoblasts?
A: Osteoclasts are cells that break down old or damaged bone tissue, whereas osteoblasts are cells that build new bone material. Together, they regulate bone remodeling, ensuring bones remain strong and functional.
Test Your Knowledge: Oste Word Root Quiz
1. What does the root "Oste" signify?
2. What does osteoporosis affect?
3. What is osteopathy?
4. What process does osteogenesis describe?
5. What is an osteotomy used for?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Oste"
The root "Oste" serves as a linguistic and medical foundation for understanding bone health and healing. From ancient Greek studies to cutting-edge therapies, its influence continues to shape our knowledge and care for the skeletal system. By exploring "Oste," we celebrate the strength and resilience that bones provide, reminding us of their crucial role in supporting life.














