Phag: The Root of Consumption in Language and Science
Byline:
Discover the fascinating world of the root "phag," derived from Greek, meaning "eat." From terms like "anthropophagous" to "esophagus," this root connects diverse fields, from biology to culture, highlighting the universal act of consuming and its implications.
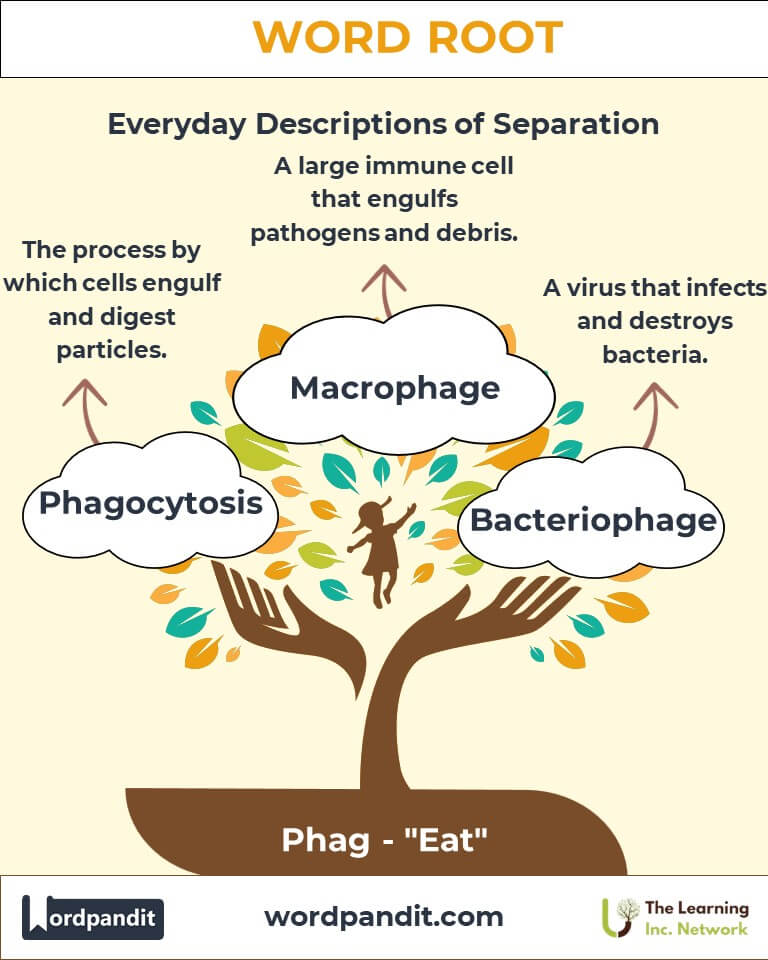
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Phag"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Phag"
- Common "Phag"-Related Terms
- "Phag" Through Time
- "Phag" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Phag" in Action
- Cultural Significance of "Phag"
- The "Phag" Family Tree
- FAQs about the "Phag" Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Phag" Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Phag"
Introduction: The Essence of "Phag"
Eating is a universal act, essential to life and rich in symbolic meaning. The word root "phag" (pronounced "fag") stems from the Greek word phagein, meaning "to eat." It serves as the foundation for numerous terms across disciplines, from biology to cultural studies. Whether describing predatory organisms or human anatomy, "phag" embodies the act of consumption in all its forms.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "phag" traces its origins to Ancient Greek. The term phagein was used to describe eating or devouring, often in a metaphorical sense. As the Greek language influenced Latin and later English, "phag" became embedded in scientific and literary vocabularies, enriching discussions about nutrition, predation, and even societal behaviors.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Phag"
To remember "phag," picture a Pac-Man figure devouring everything in its path. This iconic image mirrors the meaning of "phag"—to eat or consume.
Mnemonic:
“Phag is like a hungry Pac-Man, always eating!”
Common "Phag"-Related Terms
- Anthropophagous: Feeding on human flesh.
Example: Legends of anthropophagous creatures have fueled horror stories for centuries. - Esophagus: The muscular tube connecting the throat to the stomach.
Example: The esophagus plays a crucial role in swallowing food. - Phagocyte: A type of cell that engulfs and consumes harmful particles.
Example: Phagocytes are key players in the immune system, attacking bacteria. - Geophagy: The practice of eating soil or clay.
Example: Geophagy is a behavior observed in certain animal species and some human cultures. - Bacteriophage: A virus that infects and consumes bacteria.
Example: Scientists study bacteriophages to develop alternatives to antibiotics.
"Phag" Through Time
- Ancient Usage: The term "anthropophagous" emerged in classical Greek literature, often describing mythical man-eating creatures.
- Scientific Advances: With the rise of microbiology, "phag" became central to terms like "phagocyte" and "bacteriophage," reflecting humanity’s growing understanding of microscopic consumption.
"Phag" in Specialized Fields
- Biology: Phagocytosis describes the process by which cells engulf particles.
Example: White blood cells use phagocytosis to neutralize pathogens. - Medicine: The esophagus plays a vital role in digestion.
Example: Disorders like acid reflux affect millions worldwide. - Microbiology: Bacteriophages are studied as alternatives to antibiotics.
Example: They target bacteria without harming human cells.
Illustrative Story: "Phag" in Action
In a distant forest, a scientist named Dr. Lina studied a bacteriophage that targeted harmful bacteria infecting crops. By applying her discovery, she saved an entire village’s harvest. Meanwhile, her colleague Dr. Arjun treated a patient with esophageal cancer, emphasizing the critical role of the esophagus in health. Their work demonstrated the importance of "phag" in both microscopic and human scales.
Cultural Significance of "Phag"
"Phag" has left its mark on cultural narratives, from ancient myths of anthropophagous giants to modern discussions about food ethics and sustainability. The root reflects humanity’s complex relationship with eating—both as a necessity and a metaphor for consumption and survival.

The "Phag" Family Tree
Related Roots:
1. Vor- (Latin: "to devour")
- Voracious: Having a great appetite.
- Carnivore: An organism that eats meat.
2. Troph- (Greek: "nourishment")
- Autotroph: An organism that produces its own food.
- Atrophy: The wasting away of tissue due to lack of nourishment.
3. Caco- (Greek: "bad")
FAQs About the "Phag" Word Root
Q: What does "phag" mean?
A: The root "phag" originates from the Greek word "phagein," which means "to eat." It is widely used in terms related to consumption, digestion, and engulfing processes in both biology and medicine.
Q: What is a bacteriophage?
A: A bacteriophage is a type of virus that infects and destroys bacteria. The term combines "bacteria" with "phag" (to eat), reflecting its role in targeting and consuming bacterial cells.
Q: How does the esophagus function?
A: The esophagus is a muscular tube that connects the throat to the stomach. It uses a wave-like motion called peristalsis to transport food and liquids for digestion.
Q: What is phagocytosis?
A: Phagocytosis is a cellular process where immune cells, such as phagocytes, engulf and digest harmful particles, bacteria, or cellular debris. It is vital for maintaining the body’s health and immune defense.
Q: What is geophagy, and why is it practiced?
A: Geophagy refers to the practice of eating soil or clay. It is observed in animals and some human cultures, often linked to nutritional needs like obtaining minerals or detoxification.
Test Your Knowledge: "Phag" Word Root Quiz
1. What does "phag" mean?
2. What does "esophagus" refer to?
3. What is the role of a phagocyte?
4. What does "geophagy" describe?
5. Which field commonly uses the term "phagocytosis"?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Phag"
The root "phag" embodies the universal act of eating and its profound significance across biology, medicine, and culture. From the cells that protect our bodies to the myths that shape our imagination, "phag" connects us to the fundamental processes of life. Let "phag" inspire discoveries that deepen our understanding of consumption in all its forms.














