Phan: The Art of Showing and Revealing in Language and Expression
Discover the fascinating versatility of the root "phan," originating from Greek, meaning "to show" or "to appear." From the translucent charm of "diaphanous" to the profound clarity of an "epiphany," this root has shaped words that illuminate concepts, reveal truths, and bring ideas to light.
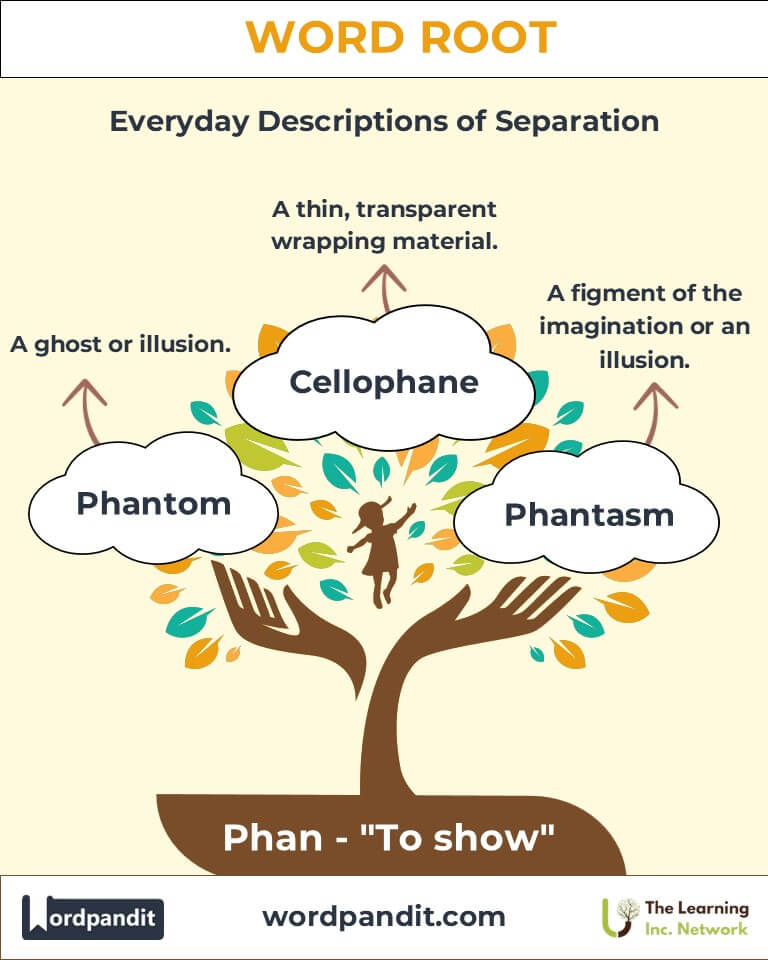
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Magic of "Phan"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Phan"
- Common "Phan"-Related Terms
- "Phan" Through Time
- "Phan" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Phan" in Action
- Cultural Significance of "Phan"
- The "Phan" Family Tree
- FAQs About the "Phan" Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Phan" Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Radiance of "Phan"
1. Introduction: The Magic of "Phan"
What connects the delicate fabric of a diaphanous gown with a life-changing epiphany? Both draw upon the Greek root phan (pronounced fan), meaning "to show" or "to appear." This root underscores words that bring clarity, display, or revelation. Whether it describes physical transparency or moments of intellectual enlightenment, phan is at the heart of illumination and understanding.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The root phan originates from the Greek word phainein, meaning "to show" or "to bring to light." It entered Latin as phan and later merged with Old French and English vocabulary. Ancient philosophers and playwrights, from Plato to Sophocles, used derivatives of phan to explore themes of revelation, truth, and appearance. Over centuries, it has continued to evolve into words used in science, art, and everyday speech.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Phan"
Imagine a beam of light passing through a curtain, creating a vivid display of shadows and forms—revealing what lies beyond. This imagery ties perfectly to phan, symbolizing the act of showing or unveiling.
Mnemonic Device: "Phan shows what’s unseen, like light through a translucent screen."
4. Common "Phan"-Related Terms
- Diaphanous (die-a-fuh-nuhs): Light, delicate, and almost transparent.
Example: "The diaphanous curtains let the morning sunlight softly filter into the room." - Epiphany (ih-pif-uh-nee): A sudden, striking realization or insight.
Example: "During her walk, she had an epiphany about the solution to her problem." - Phantom (fan-tum): A ghost or illusion.
Example: "The sailors were haunted by the phantom of a shipwrecked vessel." - Phenomenon (fuh-nom-uh-non): An observable fact or event, often extraordinary.
Example: "The northern lights are a natural phenomenon that captivates viewers worldwide." - Cellophane (sel-uh-fane): A thin, transparent wrapping material.
Example: "She wrapped the gift in colorful cellophane for a festive touch."
5. "Phan" Through Time
- Phantasm (Ancient): A figment of the imagination or an illusion.
Context: Common in medieval literature to describe supernatural visions. - Phenomenal (Modern): Remarkable or extraordinary.
Context: The word has shifted from strictly observable phenomena to describing awe-inspiring achievements.
6. "Phan" in Specialized Fields
- Literature: Phantom: A recurring symbol for unresolved conflict in Gothic novels.
- Physics: Phenomena: Refers to observable events, such as the bending of light or sound waves.
- Art: Diaphanous: Used to describe ethereal qualities in visual compositions or textiles.
- Psychology: Epiphany: Moments of sudden understanding in cognitive therapy or creativity.
7. Illustrative Story: "Phan" in Action
Lila was designing her first collection for a fashion show. As she held a piece of diaphanous fabric against the light, an epiphany struck her—she could blend this material with bold patterns to create something truly phenomenal. Her designs became the highlight of the show, proving how "phan" illuminates creativity.
8. Cultural Significance of "Phan"
In mythology, phan is tied to moments of divine revelation, such as when gods appear to mortals. In modern times, it continues to symbolize clarity and enlightenment, appearing in poetry, philosophy, and even pop culture, where phantoms and phenomena captivate audiences.

9. The "Phan" Family Tree
Explore related roots and their meanings:
- Fan (Latin): To show or reveal.
Example: Fantasy: Imaginative ideas or stories. - Luc (Latin): Light.
Example: Lucid: Clear and easily understood. - Spec (Latin): To look or see.
Example: Spectacle: A visually striking performance or display.
10. FAQs About the "Phan" Word Root
Q: What does "phan" mean, and how is it relevant in language?
A: The root "phan" comes from Greek, meaning "to show" or "to appear." It is foundational in words that convey revelation, display, or visibility. For instance, "diaphanous" describes something light and transparent, while "epiphany" captures moments of profound realization.
Q: What is the origin of "epiphany," and how is it used today?
A: "Epiphany" originates from the Greek word epiphaneia, meaning "manifestation" or "appearance." Traditionally referring to divine revelations, it now describes personal moments of clarity, such as solving a problem or gaining deep insight.
Q: Why is "phenomenon" significant, and how has its meaning evolved?
A: A "phenomenon" refers to any observable fact or event, often extraordinary. Derived from the Greek phainomenon (that which appears), it originally described natural occurrences. Its meaning has since broadened to include cultural phenomena and remarkable human achievements.
Q: What is the difference between "phantom" and "phantasm"?
A: A "phantom" generally refers to a ghost or specter, often depicted as a shadowy figure. A "phantasm" is more abstract, referring to illusions, hallucinations, or figments of imagination. While "phantom" may be physical, "phantasm" is typically psychological.
Q: How does "diaphanous" connect to the root "phan"?
A: "Diaphanous" combines the Greek roots dia- (through) and phan (to show), meaning "to show through." It describes materials that allow light to pass through, such as sheer fabrics, emphasizing their delicate and translucent qualities.
Q: What role does "phan" play in scientific terms like "phenomenon"?
A: In science, "phan" describes observable facts or events. A "phenomenon" includes physical occurrences like gravity or cultural patterns like the spread of technology, emphasizing visibility and study across diverse fields.
11. Test Your Knowledge: "Phan" Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "phan" signify?
2. Which word describes a sudden realization or insight?
3. What does "diaphanous" mean?
4. Which term relates to supernatural visions or illusions?
5. What is the meaning of "phenomenon"?

12. Conclusion: The Radiance of "Phan"
The root "phan" continues to light up language with its association with clarity and revelation. From diaphanous designs to phenomenal achievements, its influence spans disciplines, enriching our ability to express the act of showing and appearing. Let "phan" inspire you to unveil new insights and appreciate the light in language.













