Phys: The Root of Nature in Language and Science
Byline:
Dive into the fascinating world of "phys," a root derived from the Greek word "physis," meaning "nature." From "physical" to "physiology," this root highlights our understanding of the natural world and its workings, connecting science, health, and human existence in profound ways.
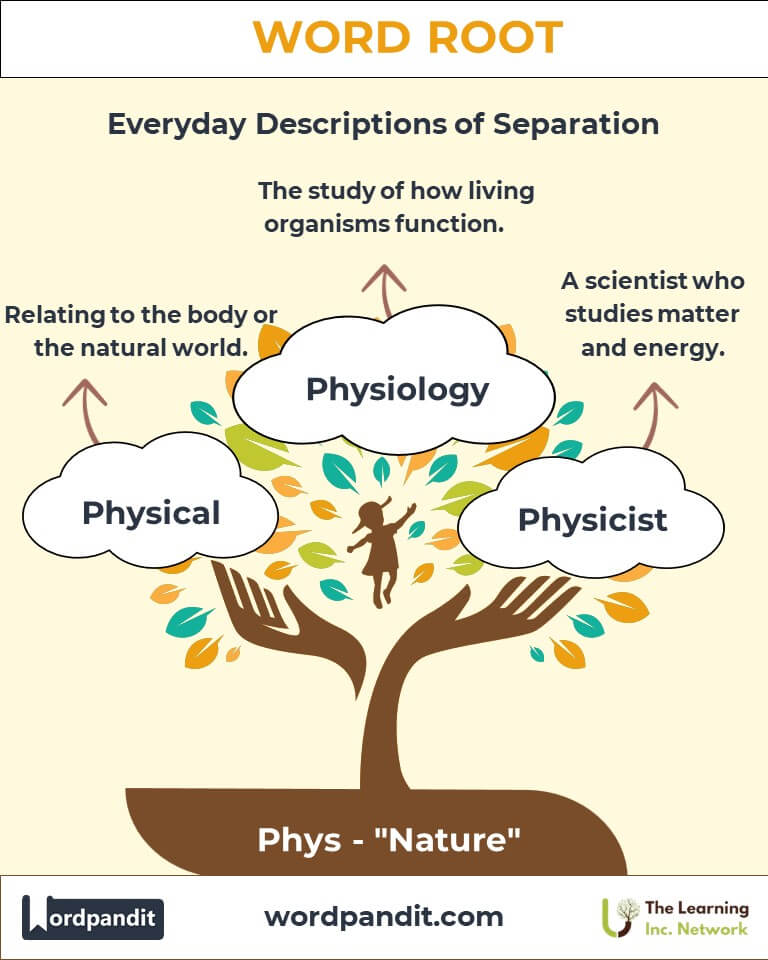
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Phys"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Phys"
- Common "Phys"-Related Terms
- "Phys" Through Time
- "Phys" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Phys" in Action
- Cultural Significance of the "Phys" Root
- The "Phys" Family Tree
- FAQs about the "Phys" Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Phys" Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Phys"
Introduction: The Essence of "Phys"
When we think about the word "nature," we often imagine the physical world around us. The root "phys" (pronounced fizz) embodies this very idea. Originating from Greek, "physis" represents the essence of growth, life, and the natural order. Today, its influence spans disciplines, including science, medicine, and even philosophy, reflecting humanity’s quest to understand the physical world.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "phys" traces its origins to the Greek "physis," which translates to "nature" or "natural order." In ancient Greece, philosophers like Aristotle used "physis" to discuss the inherent characteristics of living beings and the natural world. As Greek thought influenced Roman culture and later the development of modern European languages, "phys" became embedded in terms related to the body, life sciences, and physical phenomena.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Phys"
Picture a lush forest teeming with life. A bright sign reads "PHYS," symbolizing the harmony of natural elements—trees, rivers, and animals.
Mnemonic:
“PHYS connects the physical world with the essence of life and nature.”
Common "Phys"-Related Terms
- Physical: Relating to the body or natural world.
Example: "Regular physical activity improves overall health." - Physiology: The study of how living organisms function.
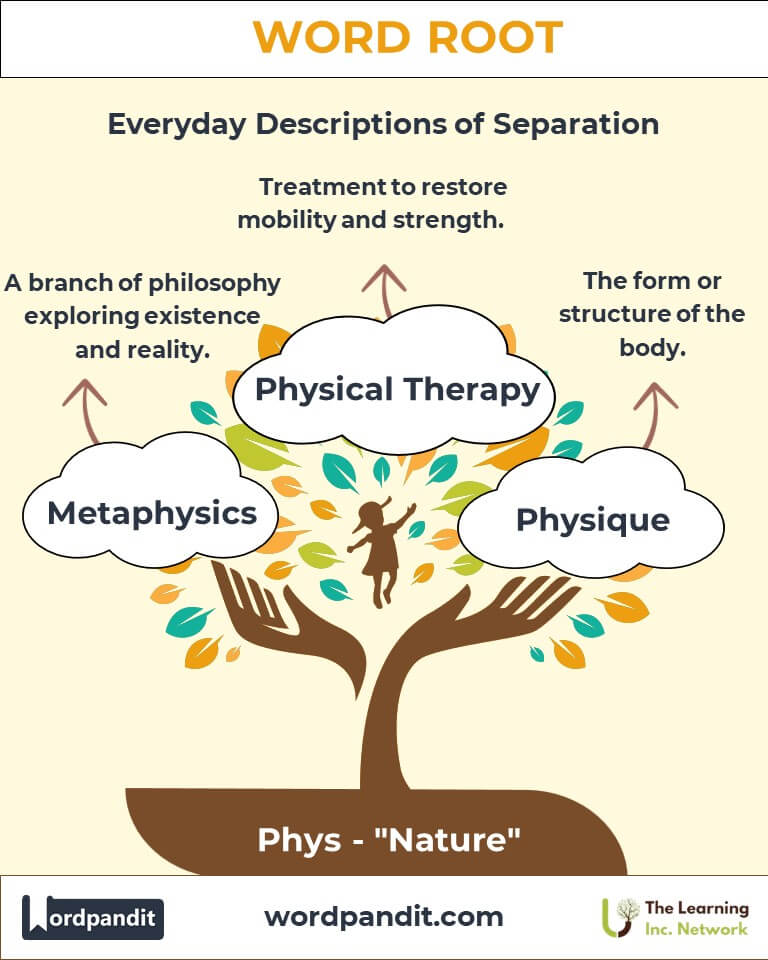
Example: "The physiology of the human heart is a marvel of evolution." - Physique: The form or structure of the body.
Example: "Her athletic physique is the result of years of training." - Physicist: A scientist who studies matter and energy.
Example: "The physicist explained the laws of thermodynamics with enthusiasm." - Metaphysics: A branch of philosophy exploring existence and reality.
Example: "Metaphysics seeks answers to profound questions about life and the universe."
"Phys" Through Time
- Physics: Once a branch of philosophy, it evolved into a science studying matter, energy, and natural laws.
Example: From Aristotle’s teachings to Newton’s laws and quantum mechanics. - Physic (Archaic): An old term for medicine or healing practices.
Historical Use: Physicians in medieval times were often called “physics.”
"Phys" in Specialized Fields
- Medicine: Physiology helps diagnose diseases and understand organ function.
Example: Cardiac physiology underpins life-saving heart treatments. - Sports and Fitness: Physical therapy aids recovery.
Example: Athletes rely on physical therapists to heal from injuries. - Philosophy: Metaphysics examines reality beyond the physical.
Illustrative Story: "Phys" in Action
Dr. Lila, a physiologist, was passionate about helping people understand their bodies. One day, she conducted a workshop on physical wellness for a group of teenagers. Through interactive activities, she demonstrated how the heart pumps blood, explaining physiology in simple terms. By the end of the session, her audience gained a deeper appreciation for the intricate "nature" within themselves.
Cultural Significance of the "Phys" Root
The concept of "phys" resonates across cultures. Ancient Greek philosophers’ exploration of "physis" laid the groundwork for modern science, while physical wellness remains central to global health practices. From yoga’s emphasis on physical harmony to the scientific breakthroughs in physiology, "phys" is a testament to our enduring curiosity about life and nature.

The "Phys" Family Tree
- Bio- (life):
- Biology: The study of living organisms.
- Example: "Biology examines life forms, from bacteria to humans."
- Nat- (birth, nature):
- Natural: Existing in or derived from nature.
- Example: "The natural beauty of the forest left her speechless."
- Therm- (heat):
- Thermodynamics: The study of heat and energy.
- Example: "Thermodynamics is essential in understanding engines."
FAQs About the "Phys" Word Root
Q: What does "phys" mean?
A: The root "phys" comes from the Greek word "physis," meaning "nature" or "natural order." It reflects the essence of life, growth, and the natural world.
Q: Is "phys" used only in scientific contexts?
A: No, "phys" is versatile. For example:
- In science: physics (study of matter and energy) and physiology (study of how organisms function).
- In daily life: physical exercise and appearance.
- In philosophy: metaphysics (exploring reality beyond the physical).
Q: What’s the difference between "physics" and "physiology"?
A: Physics focuses on matter, energy, and natural laws, such as gravity and motion. Physiology examines biological processes like how the heart pumps blood or muscles contract.
Q: What does "metaphysics" explore?
A: Metaphysics goes beyond the physical to examine existence, reality, and the nature of being. The term combines "meta-" (beyond) and "physis" (nature).
Q: How does "physique" differ from "physiology"?
A: Physique refers to physical appearance or body structure. Physiology focuses on the internal processes and functions of the body, such as digestion and respiration.
Test Your Knowledge: "Phys" Word Root Quiz
1. What does the root "phys" mean?
2. Which term describes the study of body functions?
3. What does "physique" refer to?
4. Who studies the laws of the universe?
5. Which field examines existence beyond the physical?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Phys"
The root "phys" serves as a bridge between our understanding of nature and the scientific and philosophical inquiries that shape our world. From physical wellness to the metaphysics of existence, it continues to enrich our vocabulary and deepen our comprehension of life’s mysteries. Embrace the legacy of "phys" by exploring its wonders in science, health, and beyond.














