Rhiz: The Root of Roots in Science and Language
Discover the intricate world of the word root "Rhiz," derived from the Greek word "rhiza," meaning "root." From rhizomes in botany to rhizoids in fungi, this root provides a foundational understanding of structures and systems that anchor growth and connectivity across biological and linguistic domains.
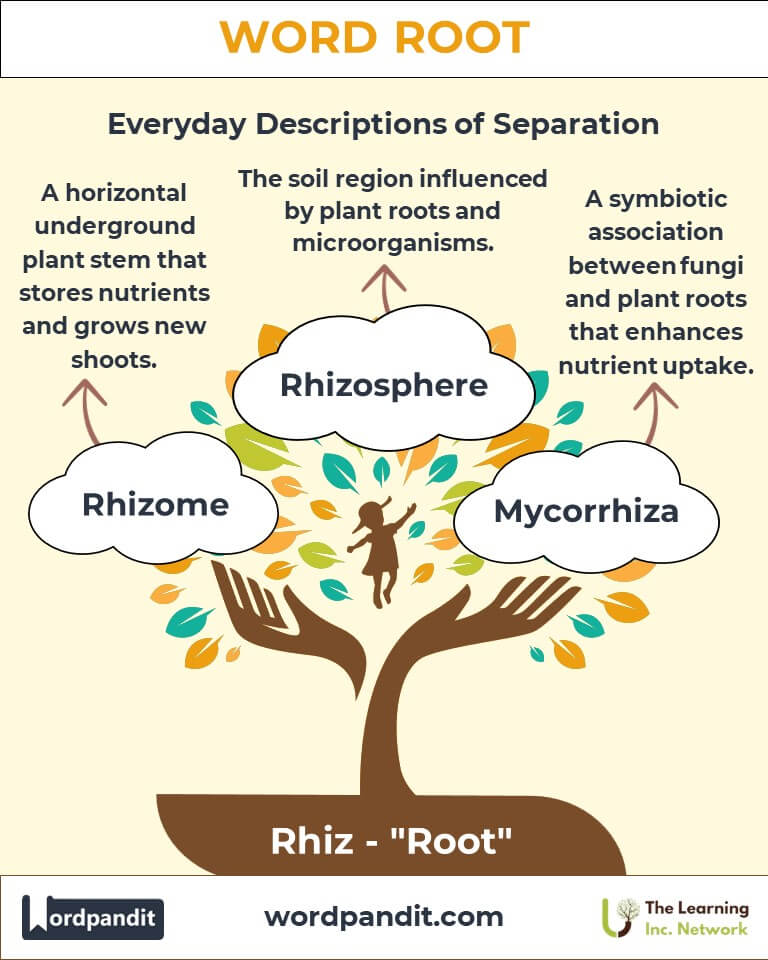
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Rhiz
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Rhiz
- Common Rhiz-Related Terms
- Rhiz Through Time
- Rhiz in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Rhiz in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Rhiz Root
- The Rhiz Family Tree
- FAQs About the Rhiz Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Rhiz Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Rhiz
1. Introduction: The Essence of Rhiz
The word root "Rhiz" (pronounced rīz) takes us deep into the concept of anchoring and growth. Meaning "root" in Greek, "Rhiz" is the basis for many scientific terms related to plants, fungi, and ecosystems. Whether describing rhizomes—the underground stems of plants—or rhizoids, tiny root-like structures in fungi and algae, this root emphasizes connectivity and foundation. In language, "Rhiz" also represents metaphoric growth, branching into diverse disciplines.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "Rhiz" originates from the Greek word rhiza, meaning "root." Ancient Greek botanists used it to describe the subterranean parts of plants that anchored them to the earth. As botanical sciences evolved, "Rhiz" found its way into Latin and subsequently English, enriching technical terminology in botany, ecology, and mycology.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Rhiz
To remember "Rhiz," imagine a sprawling network of roots beneath the soil, connecting and nourishing plants.
"Rhiz runs deep, anchoring growth in the ground and knowledge in words."
4. Common Rhiz-Related Terms
- Rhizome: A horizontal underground plant stem that often sends out roots and shoots. Example: "Ginger grows from a rhizome, a structure that stores nutrients."
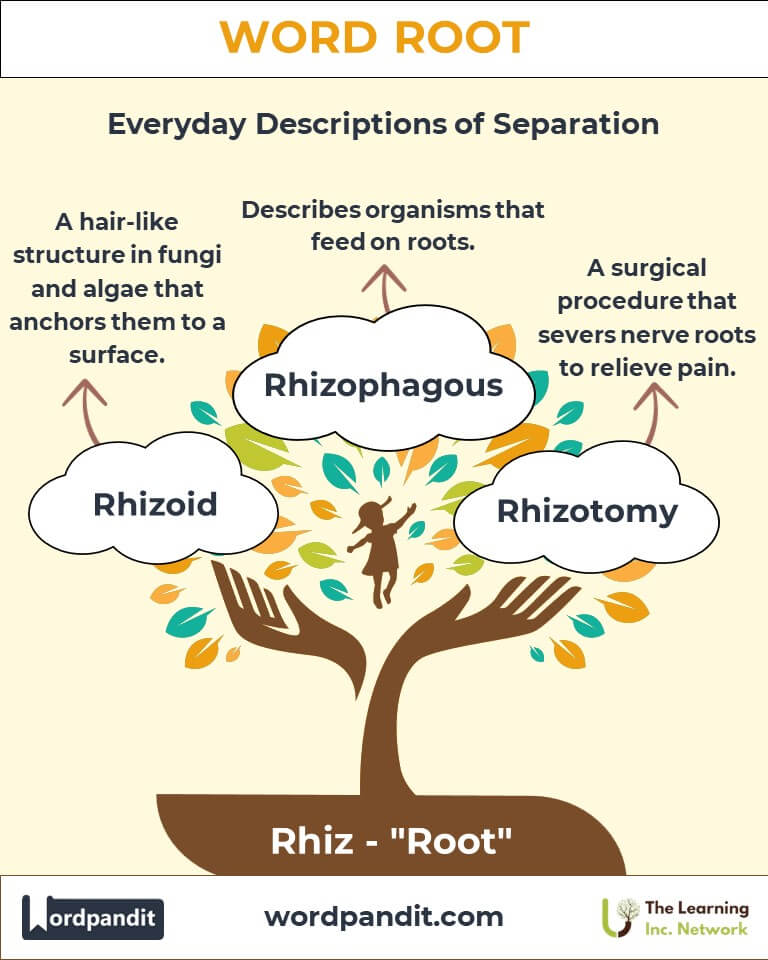
- Rhizoid: A hair-like structure in fungi and algae that anchors them to a substrate. Example: "Rhizoids help mosses attach to rocks and absorb water."
- Rhizosphere: The soil region influenced by plant roots and associated microorganisms. Example: "The rhizosphere is critical for nutrient cycling in ecosystems."
- Mycorrhiza: A symbiotic association between a fungus and plant roots. Example: "Mycorrhizae enhance a plant's nutrient uptake capabilities."
- Rhizotomy: A surgical procedure to sever nerve roots, often to relieve pain. Example: "Doctors performed a rhizotomy to alleviate chronic back pain."
5. Rhiz Through Time
- Ancient Uses: Early Greek and Roman scholars described rhizomes for their role in plant propagation and medicine.
- Modern Discoveries: Advances in microbiology unveiled the rhizosphere's complex interplay between roots and microbes, reshaping agricultural practices.
6. Rhiz in Specialized Fields
- Botany: Rhizomes, like those of bamboo and turmeric, play a vital role in plant reproduction and resilience.
- Ecology: Rhizospheres are studied for their role in nutrient exchange and plant-microbe interactions.
- Medicine: Rhizotomy demonstrates the metaphorical application of "root" in addressing pain at its source.
7. Illustrative Story: Rhiz in Action
In a lush rainforest, a researcher named Elena studied the rhizosphere of towering mahogany trees. She discovered a unique symbiotic fungus that helped trees absorb scarce nutrients. Using her findings, Elena developed a soil treatment that boosted crop yields for struggling farmers. The "roots" of her research literally and figuratively improved lives, showcasing the transformative power of understanding Rhiz.
8. Cultural Significance of the Rhiz Root
The concept of "root" has symbolic resonance in many cultures, representing origin, connection, and stability. From philosophical musings about life's "roots" to ecological metaphors in literature, "Rhiz" is a versatile symbol of growth and interdependence.

9. The Rhiz Family Tree
- Radic- (Latin: "root"):
- Radical: Fundamental or far-reaching.
- Radicle: The embryonic root in a seed.
- Root (English):
- Rooted: Firmly established.
- Uproot: To remove or displace.
- Rhizo- (Greek prefix):
- Rhizogenic: Root-forming.
- Rhizophagous: Feeding on roots.
FAQs About "Rhiz"
Q: What does "Rhiz" mean?
A: "Rhiz" means "root," originating from the Greek word rhiza. It forms the basis of many scientific terms that describe underground or root-like structures in plants, fungi, and other organisms.
Q: What is a rhizome?
A: A rhizome is a horizontal, underground plant stem that can produce roots and shoots from its nodes. Examples include ginger and bamboo. Rhizomes store nutrients and allow plants to survive adverse conditions, making them essential for reproduction and resilience.
Q: What are rhizoids?
A: Rhizoids are hair-like structures found in fungi, mosses, and algae. They serve as anchors, attaching these organisms to surfaces like soil, rocks, or tree bark, and absorb water and nutrients in environments where conventional roots cannot grow.
Q: What is the rhizosphere, and why is it important?
A: The rhizosphere refers to the soil region directly influenced by plant roots and their associated microorganisms. This zone is critical for nutrient exchange, as the roots release organic compounds that attract beneficial microbes, enhancing plant growth and soil health.
Q: How does "Rhiz" relate to medicine?
A: In medicine, "Rhiz" appears in terms like rhizotomy, a surgical procedure where nerve roots are cut to relieve chronic pain. This metaphorical use of "root" highlights the focus on targeting the source of the pain.
Test Your Knowledge: "Rhiz" Mastery Quiz
1. What does "Rhiz" mean?
2. What is a rhizome?
3. Which field studies the rhizosphere?
4. What are rhizoids?
5. What does mycorrhiza describe?
12. Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Rhiz
The root "Rhiz" reminds us of the foundational connections in nature and language. From supporting ecosystems to anchoring complex terms in science, its legacy spans disciplines and centuries. As we continue to uncover the secrets of roots—both literal and figurative—"Rhiz" will remain a vital symbol of growth, interconnection, and discovery.














