Scler: The Root of Hardness in Language and Science
Byline: Discover the resilience and complexity of the root "scler," originating from Greek, meaning "hard." This versatile root finds its presence in medical terminology, biological sciences, and beyond, signifying strength and rigidity in both physical and metaphorical senses.
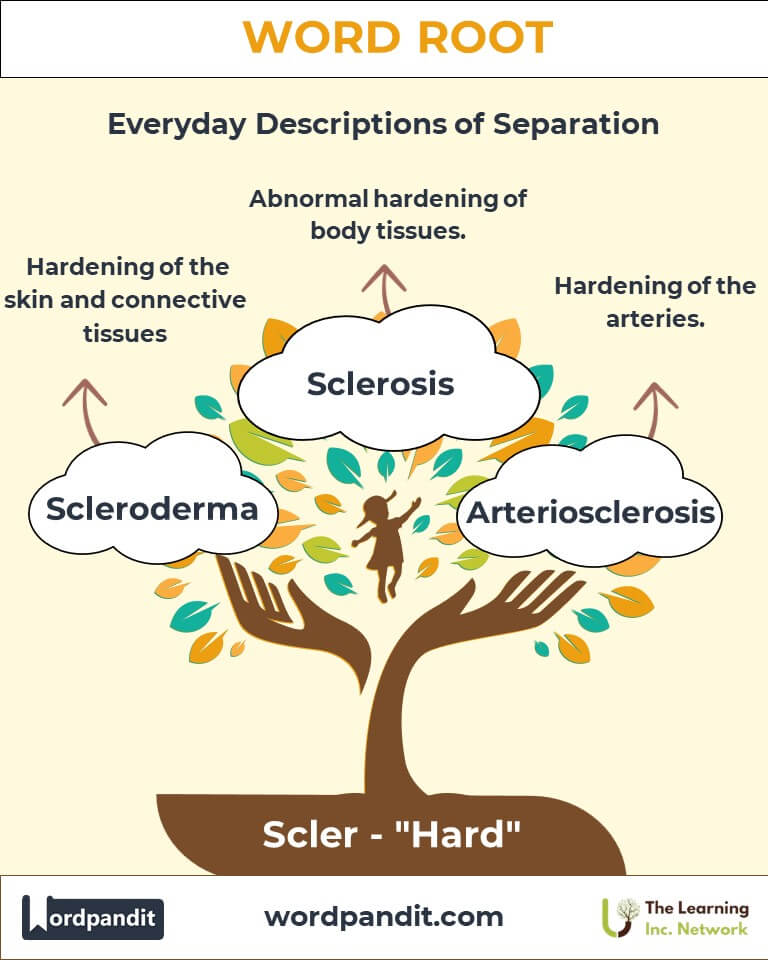
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Scler"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Scler"
- Common "Scler"-Related Terms
- "Scler" Through Time
- "Scler" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Scler" in Action
- Cultural Significance of "Scler"
- The "Scler" Family Tree
- FAQs about the "Scler" Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Scler" Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Scler"
1. Introduction: The Essence of "Scler"
When you hear the term "sclerosis," what comes to mind? Likely, you think of medical conditions involving rigidity or hardening. The root "scler" (pronounced skleer) comes from the Greek word skleros, meaning "hard." This root is a cornerstone in understanding conditions and concepts related to stiffness or inflexibility. Found primarily in medicine and biology, "scler" helps articulate phenomena where hardness or resistance is key.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The journey of "scler" begins in ancient Greek, where skleros was used to describe physical hardness. In early medical texts, it was adopted to explain pathologies characterized by hardening, such as arteriosclerosis (hardening of arteries). Over time, "scler" extended into biology and related sciences to describe both structural rigidity and pathological states.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Scler"
Imagine a rigid shield with the word "SCLER" engraved on it. This shield is unyielding, much like the conditions and concepts the root represents.
Mnemonic Device: “SCLER shields are hard as stone—they don’t bend or break!”
4. Common "Scler"-Related Terms
- Sclerosis (skleh-roh-sis): A condition of abnormal hardening in body tissues.
Example: "Multiple sclerosis affects the nervous system, causing hardened lesions in the brain and spinal cord." - Scleroderma (skleh-roh-dur-muh): A disease marked by the hardening of the skin and connective tissues.
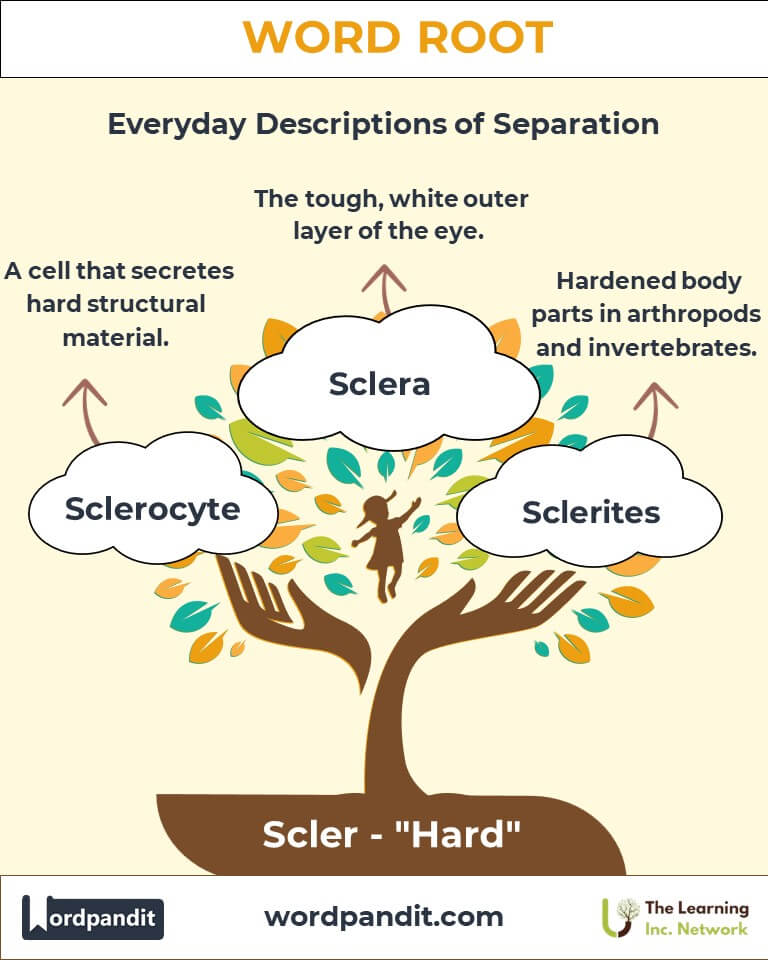
Example: "Scleroderma can result in thick, tight skin, making movement difficult." - Sclera (skleh-ruh): The tough, white outer layer of the eye.
Example: "The sclera protects the eye and maintains its shape." - Arteriosclerosis (ar-teer-ee-oh-skler-oh-sis): Hardening of the arteries.
Example: "Arteriosclerosis increases the risk of heart disease." - Sclerocyte (skleh-roh-site): A type of cell that secretes hard structural material, such as in sponges.
Example: "Sclerocytes contribute to the rigid skeleton of certain marine organisms."
5. "Scler" Through Time
- Sclera (Ancient Usage): Originally described in Greek medical texts as the tough membrane of the eye, symbolizing protection and rigidity.
- Sclerosis (Modern Context): Evolved to encompass various medical conditions, particularly those involving tissue hardening.
- Sclerites (Contemporary Biology): Used to describe hardened body parts in arthropods and other invertebrates.
6. "Scler" in Specialized Fields
- Medicine: Scleroderma highlights autoimmune responses leading to tissue hardening; sclerosis describes conditions ranging from nervous system disorders to arterial diseases.
- Biology: Sclerocytes are pivotal in forming structural components in organisms like sponges.
- Anatomy: Sclera is essential for protecting and structuring the eye.
7. Illustrative Story: "Scler" in Action
Dr. Elena Martinez, a researcher, was studying multiple sclerosis, hoping to identify early warning signs. Inspired by the sclera’s role in protecting the eye, she designed a new imaging technique to detect hardened lesions in nerve tissues. Her breakthrough provided hope for patients, illustrating how understanding "scler" could lead to groundbreaking innovations.
8. Cultural Significance of "Scler"
"Scler" symbolizes resilience and rigidity in a broader cultural context. Its influence can be seen in art and literature, where terms like "sclerosis" metaphorically describe inflexibility in thought or societal structures.

9. The "Scler" Family Tree
Explore related roots and their meanings:
- Dur (Hard): Durable, endure.
- Rig (Stiff): Rigid, rigor.
- Calc (Stone): Calcium, calcify.
10. FAQs About the Scler Word Root
Q: What does the root "scler" mean?
A: The root "scler" means "hard." It comes from the Greek word skleros, which refers to physical hardness or rigidity. This root is commonly used in medical and biological contexts to describe tissues, structures, or conditions that are abnormally hard or resistant.
Q: What is sclerosis, and why is it significant?
A: Sclerosis refers to the abnormal hardening of tissues in the body. It is significant because this process often disrupts the normal function of the affected organs or systems. For example, multiple sclerosis affects the nervous system, while arteriosclerosis hardens arteries, leading to cardiovascular complications.
Q: What is the sclera, and what role does it play in the human body?
A: The sclera is the tough, white outer layer of the eye. It protects the inner components of the eye, helps maintain its shape, and serves as an attachment point for the muscles that move the eyeball. Its rigidity is crucial for ocular health.
Q: What is scleroderma, and how does it affect the body?
A: Scleroderma is an autoimmune disorder that leads to the hardening and tightening of the skin and connective tissues. This condition can vary in severity, from localized skin issues to systemic sclerosis, which affects internal organs like the heart and lungs.
Q: What is arteriosclerosis, and how does it differ from atherosclerosis?
A: Arteriosclerosis refers to the hardening and loss of elasticity in arterial walls. Atherosclerosis is a specific type of arteriosclerosis caused by the buildup of fatty deposits (plaques) in arteries. Both restrict blood flow but have different underlying causes.
11. Test Your Knowledge: Scler Mastery Quiz
1. What does "scler" mean?
2. What does sclerosis describe?
3. What is the sclera?
4. What type of cell is a sclerocyte?
5. Which term means "hardening of the arteries"?
12. Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Scler"
The root "scler" reminds us of the importance of strength and structure, whether in biological tissues or metaphorical applications. Its relevance in medical, biological, and cultural contexts highlights the interplay between hardness and resilience.














