Sol: Illuminating the Power of the Sun in Language and Life
Uncover the radiant legacy of the root "Sol," derived from Latin, meaning "sun." This root brightens our language with terms like "solar" and "solstice," connecting us to the cosmos, nature, and even the rhythm of time. Explore how "Sol" shines in scientific disciplines, cultural traditions, and our daily lives.
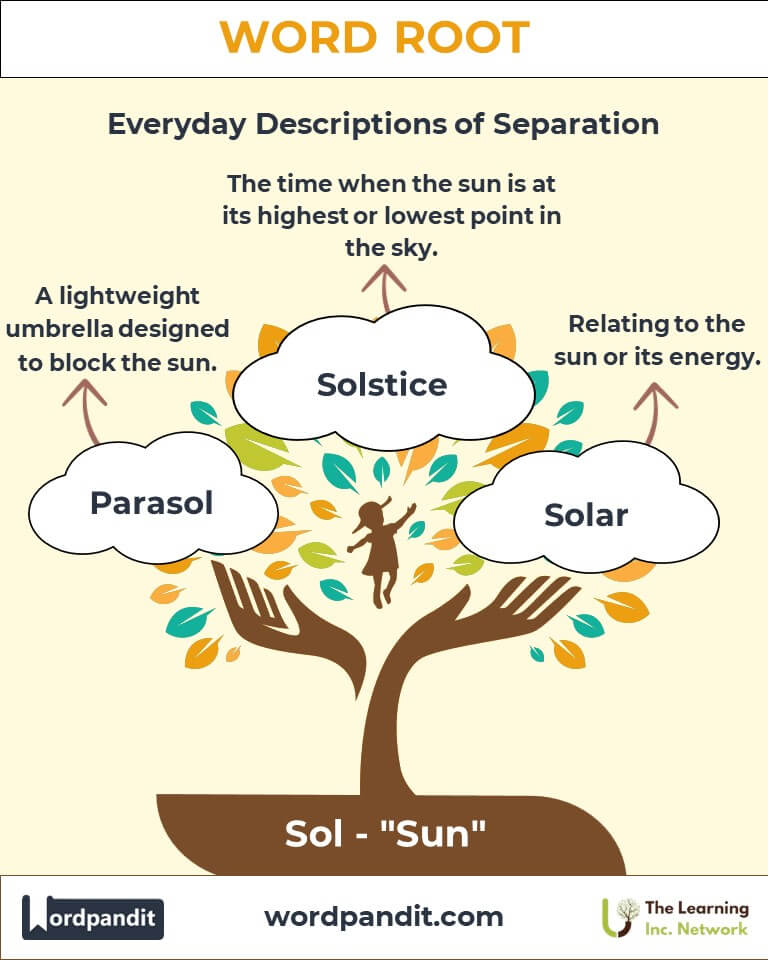
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Sol
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Sol
- Common Sol-Related Terms
- Sol Through Time
- Sol in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Sol in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Sol Root
- The Sol Family Tree
- FAQs About the Sol Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Sol Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of " Sol "
Introduction: The Essence of Sol
What’s brighter than the sun? The linguistic root "Sol," which captures the essence of the sun itself. Derived from the Latin word sol (pronounced "sahl"), meaning "sun," this root has found its way into words that describe everything from solar energy to celestial events. "Sol" connects us to the universe, the seasons, and even our cultural celebrations. Its applications span science, art, and daily language, illuminating its enduring relevance.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "Sol" originates from the Latin sol, directly translating to "sun." Ancient Roman culture revered Sol as the god of the sun, blending mythology with linguistic evolution. The concept of "Sol" crossed into English via scientific and poetic traditions, shaping terms like solar and solstice. These words highlight the celestial body’s influence on Earth’s cycles and our understanding of time.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Sol
To remember "Sol," visualize a glowing solar panel soaking up sunlight, radiating warmth and power.
Mnemonic Device:
“Sol powers the solar system, shining light on words and worlds alike.”
Common Sol-Related Terms
- Solar (SOH-lar): Relating to the sun or its energy.
Example: "Solar panels harness energy directly from sunlight." - Solstice (SOHL-stiss): The times of year when the sun is at its highest or lowest point in the sky.
Example: "The summer solstice marks the longest day of the year." - Parasol (PAR-uh-sahl): A lightweight umbrella designed to block the sun.
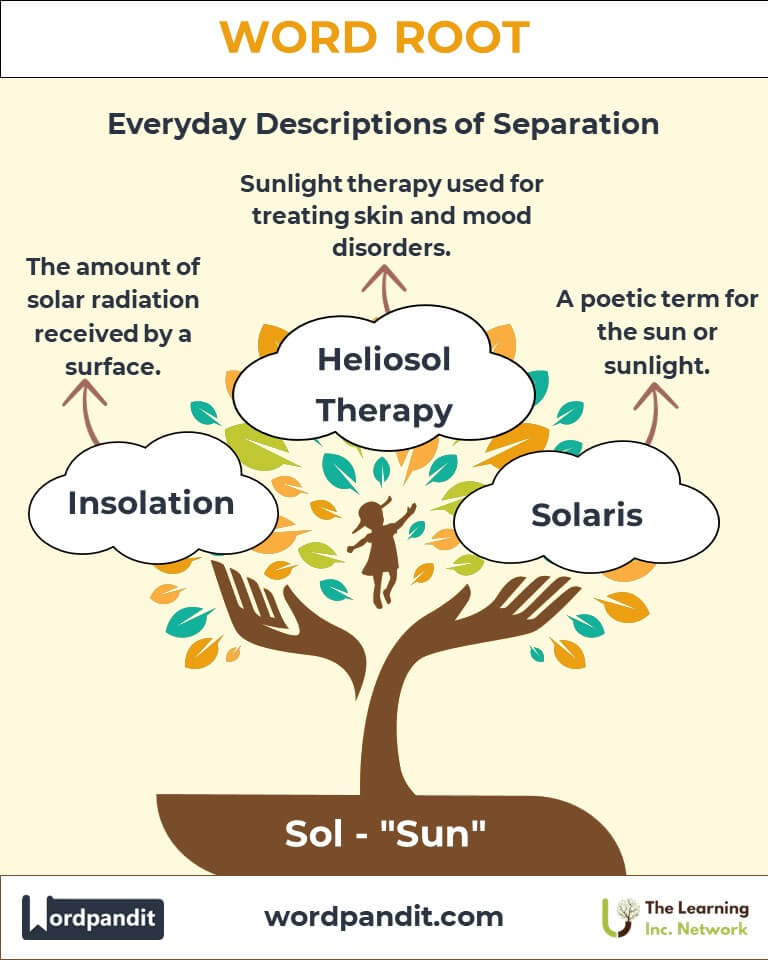
Example: "She carried a parasol to shield herself from the blazing sun." - Insolation (in-suh-LAY-shun): The amount of solar radiation received by a surface.
Example: "The region’s high insolation makes it ideal for solar farms." - Solaris (SOH-lah-ris): A poetic term for the sun or sunlight.
Example: "The Solaris of dawn painted the sky in hues of gold."
Sol Through Time
- Ancient Usage: Roman mythology celebrated Sol Invictus (the Unconquered Sun) as a powerful deity.
- Scientific Revolution: During the 17th century, heliocentric theories redefined the sun’s centrality, reinforcing terms like "solar system."
- Modern Innovation: Words like "solar energy" emerged with advancements in renewable technologies.
Sol in Specialized Fields
- Astronomy:
Solar Flares: Sudden eruptions of energy on the sun's surface, impacting space weather.
Application: Monitoring solar flares helps protect satellites and power grids. - Energy:
Solar Power: Energy harnessed from sunlight, a cornerstone of renewable energy solutions.
Relevance: Solar power drives sustainable initiatives worldwide. - Architecture:
Solar Design: Structures optimized to utilize natural sunlight.
Example: Passive solar homes reduce energy consumption by maximizing natural heating. - Medicine:
Heliosol Therapy: Sunlight therapy used to treat specific skin and mood disorders.
Application: Emphasizes the sun’s role in physical and mental health.
Illustrative Story: Sol in Action
Young inventor Carla dreamed of bringing electricity to her remote village. Inspired by the "Sol" root, she designed solar-powered lanterns using recycled materials. Her invention transformed lives, lighting homes and enabling children to study at night. Carla’s story reflects the transformative power of "Sol" in fostering innovation and hope.
Cultural Significance of the Sol Root
- Festivals:
Inti Raymi: Incan Sun Festival honoring the sun god Inti during the winter solstice.
Makar Sankranti: Hindu festival celebrating the sun’s northward journey. - Art and Literature:
The "Sol" root inspires poetic imagery, symbolizing life, warmth, and enlightenment.

The Sol Family Tree
- Helio- (Greek: "sun"):
Heliograph: A device for signaling using sunlight.
Heliocentric: The model placing the sun at the center of the solar system. - Lumen- (Latin: "light"):
Illuminance: The amount of light per unit area.
Luminous: Emitting or reflecting light.
10. FAQs About " Sol "
Q: What does "Sol" mean?
A: "Sol" means "sun" in Latin, symbolizing light, warmth, and energy. It serves as the foundation for words related to the sun, celestial phenomena, and solar-powered technologies.
Q: What is the origin of the word "Solar"?
A: "Solar" originates from the Latin word solaris, which means "pertaining to the sun." It describes anything related to the sun, such as solar energy or solar systems.
Q: What does "Solstice" signify?
A: "Solstice" comes from the Latin solstitium, combining sol (sun) and stitium (to stand still). It refers to the two times of the year when the sun appears to stand still at its highest or lowest point in the sky, marking the longest or shortest days.
Q: What is "Insolation," and why is it important?
A: Insolation measures the solar radiation received by a specific area. It's crucial in fields like climate science and renewable energy, as it determines the potential for solar power generation in different regions.
Q: Why is the sun called "Sol" in some cultures?
A: The term "Sol" reflects the Roman sun god, Sol Invictus, symbolizing vitality and constancy. Many languages influenced by Latin, such as Spanish and Italian, use "sol" to mean the sun.
Q: What role does "Sol" play in mythology?
A: In Roman mythology, Sol was a deity representing the sun, linked to illumination and life. Similarly, many cultures across the world revere solar deities for their life-giving energy and influence.
11. Test Your Knowledge: " Sol " Mastery Quiz
1. What does "Sol" mean?
2. What marks the longest day of the year?
3. What does "Parasol" protect against?
4. Which field benefits most from "solar energy"?
5. What does "Solaris" symbolize in literature?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Sol
The root "Sol" continues to radiate meaning and utility in our lives, from ancient mythologies to cutting-edge technologies. Its influence spans language, culture, and science, reminding us of the sun’s vital role in our existence. As humanity turns to solar power for a brighter future, the legacy of "Sol" shines ever brighter, guiding innovation and celebrating life.














