Spher: Exploring the Sphere of Influence Across Languages and Fields
Delve into the origins and applications of the root "spher," meaning "ball." From everyday words like "sphere" to scientific concepts like "atmosphere," this root illustrates the profound interconnectedness of forms, ideas, and environments.
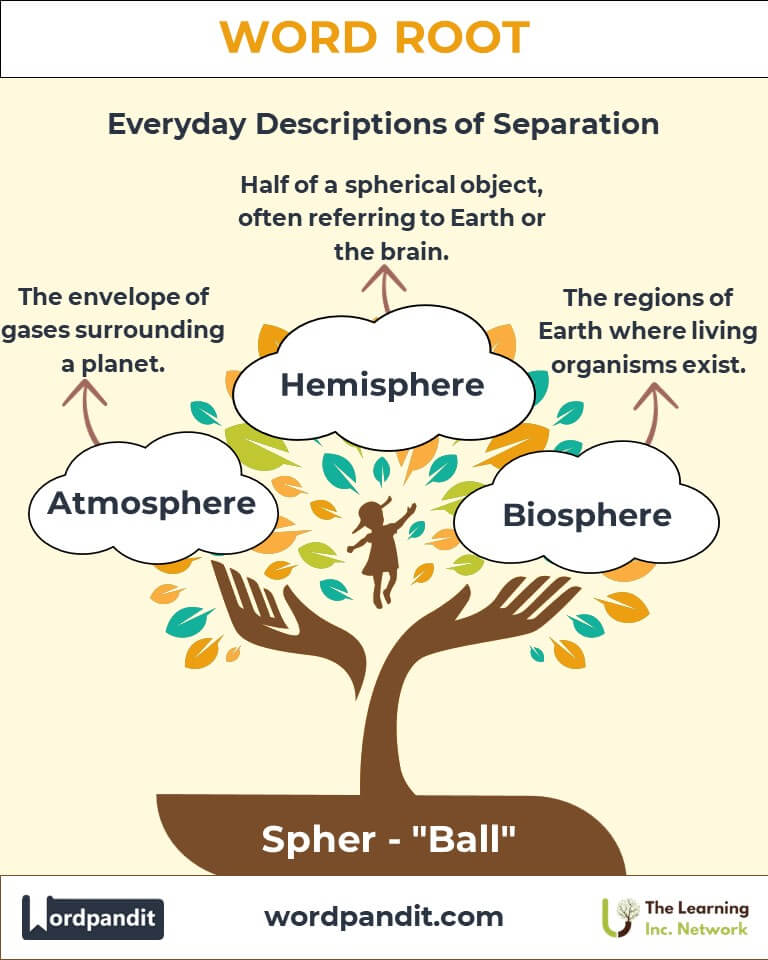
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Spher"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Spher"
- Common "Spher"-Related Terms
- "Spher" Through Time
- "Spher" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Spher" in Action
- Cultural Significance of "Spher"
- The "Spher" Family Tree
- FAQs About the "Spher" Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Spher" Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Spher"
Introduction: The Essence of "Spher"
What connects the Earth, the atmosphere, and an elegant mathematical concept? The word root "spher" ties them together, symbolizing the idea of a ball or a sphere. Derived from the Greek word sphaira (ball), this root has rolled through time into languages and fields as diverse as geometry, astronomy, and environmental science. Its versatile applications showcase humanity's fascination with symmetry, balance, and the encompassing nature of spheres.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "spher" originates from the Greek sphaira, meaning "ball" or "globe." It first entered scientific and philosophical discussions in ancient Greece, where spheres symbolized perfection and unity. By the Middle Ages, the term had extended into Latin as sphaera, influencing the vocabulary of astronomy and geometry. Over centuries, "spher" became a linguistic staple for describing roundness and wholeness across disciplines.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Spher"
Imagine a glowing crystal ball floating in the air, reflecting the entire world within it. This vivid image helps cement "spher" as a symbol of completeness and connection.
Mnemonic Device:
“Spher spins like a globe, linking ideas, shapes, and realms.”
Common "Spher"-Related Terms
- Sphere (sfeer): A perfectly round, three-dimensional shape.
Example: "The artist sculpted a flawless marble sphere for the exhibit." - Atmosphere (at-muh-sfeer): The envelope of gases surrounding a planet.
Example: "The atmosphere of Earth is essential for life." - Hemisphere (hem-uh-sfeer): Half of a spherical object, especially referring to Earth or the brain.
Example: "The Northern Hemisphere experiences winter while the Southern Hemisphere enjoys summer." - Stratosphere (strat-uh-sfeer): A layer of Earth's atmosphere located above the troposphere.
Example: "Airplanes typically fly in the lower stratosphere." - Biosphere (bye-oh-sfeer): The regions of Earth where living organisms exist.
Example: "The biosphere supports a diverse range of ecosystems."
"Spher" Through Time
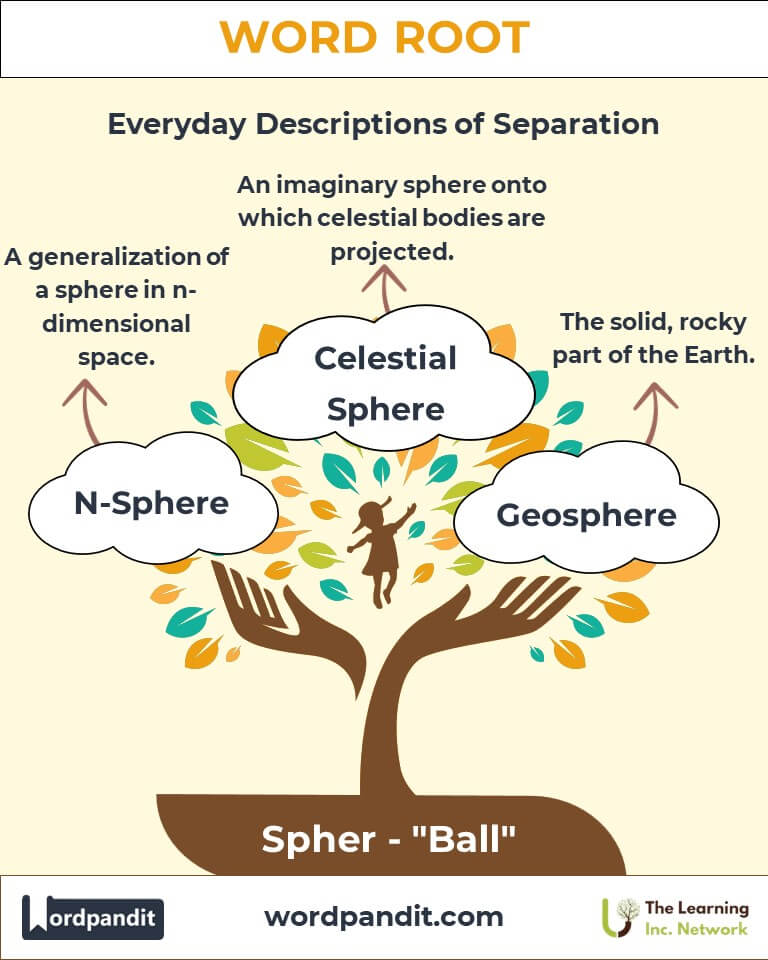
- Geosphere (Ancient Use): Once a term describing the solid, rocky part of the Earth, the "geosphere" emphasized the planet's tangible, spherical nature.
- Sphere of Influence (Modern Use): Evolving from its geometric roots, this metaphorical phrase now represents the extent of a person or organization’s impact.
"Spher" in Specialized Fields
- Astronomy:
Celestial Sphere: An imaginary sphere encompassing the Earth, on which celestial bodies are projected.
Relevance: Central to understanding ancient and modern astronomy. - Environmental Science:
Hydrosphere: Refers to all water found on, under, or over the surface of a planet.
Application: Critical for studying Earth's water cycle. - Mathematics:
N-Sphere: A generalization of a sphere in n-dimensional space.
Importance: Used in complex calculations in physics and geometry. - Medicine:
Ophthalmosphere: A specialized tool resembling a sphere for eye examinations.
Significance: Helps visualize retinal and corneal curvature.
Illustrative Story: "Spher" in Action
One winter evening, Ava looked up at the night sky, fascinated by the celestial sphere dotted with stars. She dreamed of becoming an astronomer. Years later, as a climate scientist, Ava studied the atmosphere, biosphere, and hydrosphere to understand how they interact. Her journey showcased how one concept—the sphere—could inspire both awe and scientific discovery.
Cultural Significance of "Spher"
Spheres have long symbolized unity and perfection in art, religion, and philosophy. In ancient Hindu and Greek cosmology, the universe was often depicted as spherical. Today, the globe remains an emblem of globalization, interconnectedness, and the fragility of Earth's systems.

The "Spher" Family Tree
- Cycl- (Greek: "circle"):
Cyclone: A system of winds rotating inwards.
Cycle: A repeated sequence of events. - Orb- (Latin: "circle or sphere"):
Orbit: The curved path of an object around another.
Orbicular: Circular or spherical in shape. - Circ- (Latin: "around"):
Circle: A round plane figure.
Circumference: The distance around a circular object.
FAQs About " Spher "
Q: What does "spher" mean?
A: "Spher" means "ball" or "sphere" and originates from the Greek word sphaira. It signifies round or circular shapes and has applications in science, geography, and abstract concepts like influence or domains.
Q: Why is the sphere considered a perfect shape in geometry and philosophy?
A: In geometry, the sphere is symmetrical, with all points equidistant from its center, making it a model of balance and uniformity. Philosophically, ancient cultures viewed spheres as representations of perfection, unity, and completeness, symbolizing the cosmos or the divine.
Q: What is the difference between a sphere and a circle?
A: A sphere is three-dimensional (like a ball) and has volume, while a circle is two-dimensional (like a flat ring) and only has area. A sphere is essentially a set of circles stacked together in every direction around a center point.
Q: What is the atmosphere, and why is it important?
A: The atmosphere is the layer of gases surrounding a planet. On Earth, it includes nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other gases. It regulates temperature, protects life from harmful solar radiation, and supports essential processes like respiration and the water cycle.
Q: What is the biosphere?
A: The biosphere encompasses all regions of Earth where life exists, including land, water, and the atmosphere. It is critical because it represents the interconnected web of ecosystems sustaining life on the planet.
Q: What is the celestial sphere?
A: The celestial sphere is an imaginary concept used in astronomy. It represents the sky as a vast, hollow sphere with Earth at its center. Astronomers map stars, planets, and celestial events onto this sphere for observation and navigation.
Test Your Knowledge: " Spher " Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "spher" mean?
2. What is a hemisphere?
3. Which term refers to Earth's gaseous layer?
4. What does the biosphere include?
5. What is the celestial sphere?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Spher"
The root "spher" reminds us of the interconnectedness and unity of the world. From the tangible forms of Earth’s systems to the abstract perfection of a sphere in mathematics, this root has shaped our understanding of balance and wholeness. As we look to the future, let "spher" inspire us to see the world as both fragile and beautifully complete.














