Strept: Twists in Language, Medicine, and Science
Byline: Explore the fascinating world of the word root "strept," derived from the Greek word streptos, meaning "twisted" or "curved." From its vital role in medical terminology to its surprising applications in biology, the root "strept" highlights twists and turns in both language and life.
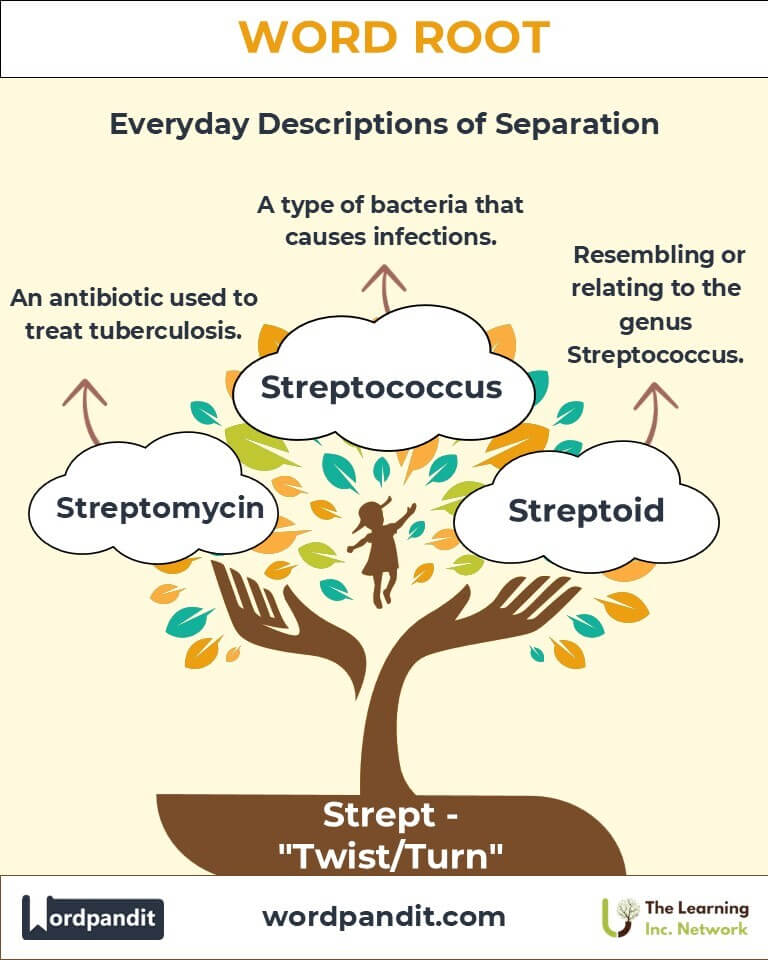
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Strept
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Strept
- Common Strept-Related Terms
- Strept Through Time
- Strept in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Strept in Action
- Cultural Significance of Strept
- The Strept Family Tree
- FAQs about the Strept Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Strept Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Strept
1. Introduction: The Essence of Strept
What do spiral bacteria, antibiotics, and the shape of a twisted ribbon have in common? The answer lies in the word root "strept." Derived from the Greek word streptos, meaning "twisted" or "curved," this root has shaped the vocabulary of medicine and biology. From terms like streptococcus (twisted-chain bacteria) to streptomycin (a groundbreaking antibiotic), "strept" connects the twists of language with life-saving science.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "strept" originates from the Greek streptos, denoting "twisted" or "curved." Ancient Greek scientists used the term to describe objects with curved or spiraled shapes. The adoption of this root in scientific vocabulary flourished during the 19th century, as microbiologists observed the twisted chain-like formations of certain bacteria. Terms like streptococcus (1890s) emerged, laying the groundwork for modern microbiology and medicine.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Strept
To remember "strept," picture a twisted spiral staircase leading to a lab filled with microscopes and antibiotics.
Mnemonic Device: "Strept spirals into science—curving chains and groundbreaking discoveries!"
4. Common Strept-Related Terms
- Streptococcus (strep-toh-KAH-kus):
- Definition: A genus of bacteria characterized by chain-like formations.
- Example: "Strep throat is caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, a type of twisted-chain bacteria."
- Streptomycin (strep-toh-MY-sin):
- Definition: An antibiotic derived from Streptomyces bacteria, effective against tuberculosis.
- Example: "The discovery of streptomycin revolutionized the treatment of infectious diseases."
- Streptodermatitis (strep-toh-derm-ah-TIE-tis):
- Definition: Inflammation of the skin caused by streptococcal bacteria.
- Example: "The patient’s rash was diagnosed as streptodermatitis, requiring antibiotic therapy."
- Streptokinase (strep-toh-KAI-nase):
- Definition: An enzyme produced by streptococcal bacteria, used to dissolve blood clots.
- Example: "Doctors administered streptokinase to treat the patient’s heart attack."
- Streptophyta (strep-TOH-fy-tuh):
- Definition: A group of green algae and plants with twisted or spiraled structures.
- Example: "The evolutionary traits of Streptophyta link algae to land plants."
5. Strept Through Time
- Streptococcus (19th Century):
- Observed under early microscopes, its twisted chains inspired the name.
- Impact: Led to breakthroughs in diagnosing bacterial infections.
- Streptomycin (1940s):
- Discovered by Selman Waksman and his team, this antibiotic became a cornerstone of modern medicine.
- Evolution: Continues to be pivotal in treating antibiotic-resistant infections.
6. Strept in Specialized Fields
- Medicine:
- Streptococcus bacteria: Known for causing illnesses such as strep throat, scarlet fever, and rheumatic fever.
- Streptomycin: Essential for combating tuberculosis and bacterial infections.
- Biochemistry:
- Streptokinase: Enzyme used in thrombolytic therapy to dissolve dangerous blood clots.
- Botany:
- Streptophyta: A major group linking algae to land plants, shedding light on plant evolution.
7. Illustrative Story: Strept in Action
Dr. Clara Lee, a microbiologist, was investigating an outbreak of a mysterious throat infection in her community. Using her lab’s resources, she identified Streptococcus pyogenes as the culprit. Collaborating with local doctors, she ensured patients received prompt treatment with streptomycin. Clara’s work highlighted the critical role of "strept" in diagnosing and treating infections, proving that even microscopic twists can have a massive impact.
8. Cultural Significance of Strept
The root "strept" finds its echoes in culture through its association with health and discovery. Terms like "strep throat" are universally recognized, and the development of streptomycin is celebrated as a landmark achievement in medical history. The root also symbolizes the interconnectedness of science and humanity, as it reminds us of the twists and turns in the journey of innovation.

9. The Strept Family Tree
- Spiro- (spiral): Refers to coiled or twisted structures.
- Example: Spirochete (spiral-shaped bacteria).
- Tors- (twist): Denotes twisting or turning.
- Example: Torsion (act of twisting).
- Helico- (spiral): Used for helical shapes.
- Example: Helicobacter (spiral-shaped bacteria linked to ulcers).
10. FAQs About " Strept "
Q: What does "strept" mean, and where does it come from?
A: "Strept" means "twisted" or "curved," derived from the Greek word streptos. The root is commonly used in scientific and medical terminology to describe objects or organisms with twisted or chain-like structures, such as the twisted chains of streptococcal bacteria.
Q: What is streptococcus, and why is it significant?
A: Streptococcus is a genus of bacteria characterized by its chain-like, twisted structure. It is significant because it includes many species responsible for human diseases, such as strep throat (Streptococcus pyogenes), scarlet fever, and pneumonia. These bacteria are a focus of research in microbiology and medicine due to their widespread impact on health.
Q: How did streptomycin revolutionize medicine?
A: Streptomycin, discovered by Selman Waksman in the 1940s, was the first antibiotic effective against tuberculosis (TB). Its ability to combat TB and other bacterial infections marked a breakthrough in medical history. Streptomycin remains vital in treating antibiotic-resistant bacterial strains.
Q: What is the role of streptokinase in medicine?
A: Streptokinase is an enzyme derived from streptococcal bacteria, used in thrombolytic therapy to dissolve blood clots in conditions such as heart attacks and strokes. By breaking down clots, streptokinase can restore blood flow to critical areas, reducing the risk of severe complications.
Q: Are streptococcal infections always severe?
A: No, streptococcal infections can range from mild to severe. Common conditions like strep throat are easily treatable with antibiotics, while more severe infections, such as necrotizing fasciitis (flesh-eating disease), require immediate and intensive medical care.
Q: What are Streptophyta, and why are they important in botany?
A: Streptophyta is a group of green algae and land plants that share certain twisted or spiraled cellular features. They are important in botany because they represent a critical evolutionary link between aquatic algae and terrestrial plants, offering insights into how plants adapted to land environments.
Q: How do scientists use the term "strept" in modern research?
A: The term "strept" is used in naming and describing various organisms and substances with twisted or chain-like characteristics. For example, in microbiology, it describes bacterial shapes, and in biochemistry, it appears in enzymes like streptokinase. Its applications help classify and understand biological structures and functions.
11. Test Your Knowledge: " Strept " Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "strept" mean?
2. Which bacteria causes strep throat?
3. What does streptomycin treat?
4. What enzyme dissolves blood clots?
5. Which group links algae to plants?
12. Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Strept
The root "strept" embodies the twists of discovery in science and language. From ancient Greek observations to lifesaving medical innovations, it has enriched our understanding of the microscopic and macroscopic world. As science advances, "strept" will continue to spiral into new realms of knowledge, connecting us to the beauty of life's complexity.














