Sulf: The Root of Chemistry and Transformation in Language
Explore the essence of the root "sulf," derived from Latin, meaning "sulfur." Sulfur, one of nature's most dynamic elements, shapes words in chemistry, industry, and environmental science. From sulfates to sulfides, this root embodies transformation, bonding, and reactivity.
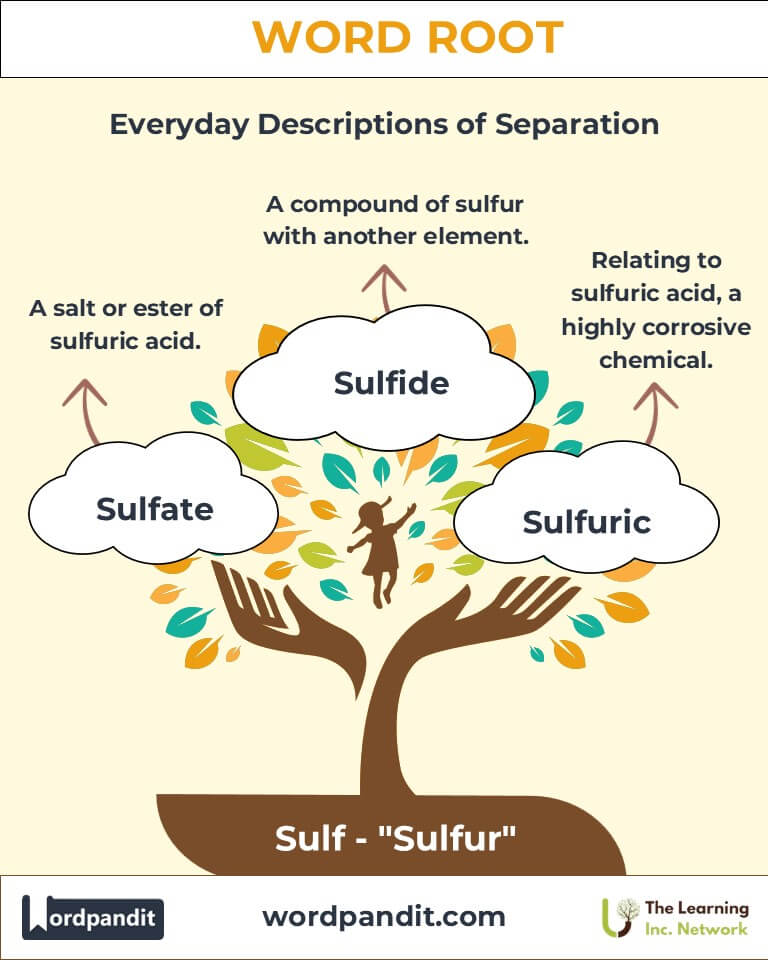
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Power of Sulf
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Sulf
- Common Sulf-Related Terms
- Sulf Through Time
- Sulf in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Sulf in Action
- Cultural Significance of Sulf
- The Sulf Family Tree
- FAQs about the Sulf Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Sulf Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Sulf
Introduction: The Power of Sulf
What do sulfates in detergents and sulfides in minerals have in common? Both stem from the root "sulf," which signifies sulfur. Pronounced “suhlf,” this root traces back to Latin origins and has become integral in understanding compounds pivotal to chemistry, medicine, and environmental science. Sulfur’s transformative properties and its role in life-sustaining processes underscore the versatility and importance of this root.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "sulf" originates from the Latin word sulfur, meaning "brimstone." Sulfur's association with fire and alchemy dates back to ancient civilizations, where it was used in rituals and early medicines. During the Industrial Revolution, sulfur compounds became central to chemical manufacturing, cementing "sulf" as a foundational term in science.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Sulf
Picture a glowing yellow sulfur crystal sparking a chain reaction in a lab. To remember "sulf," think:
Mnemonic Device: “Sulf sparks life and industry, from sulfates to sulfides.”
Common Sulf-Related Terms
- Sulfate (suhl-fate): A salt or ester of sulfuric acid.
- Example: "Sulfates are used in shampoos for their cleansing properties."
- Sulfide (suhl-fahyd): A compound of sulfur with another element.
- Example: "Pyrite, or 'fool's gold,' is a common sulfide mineral."
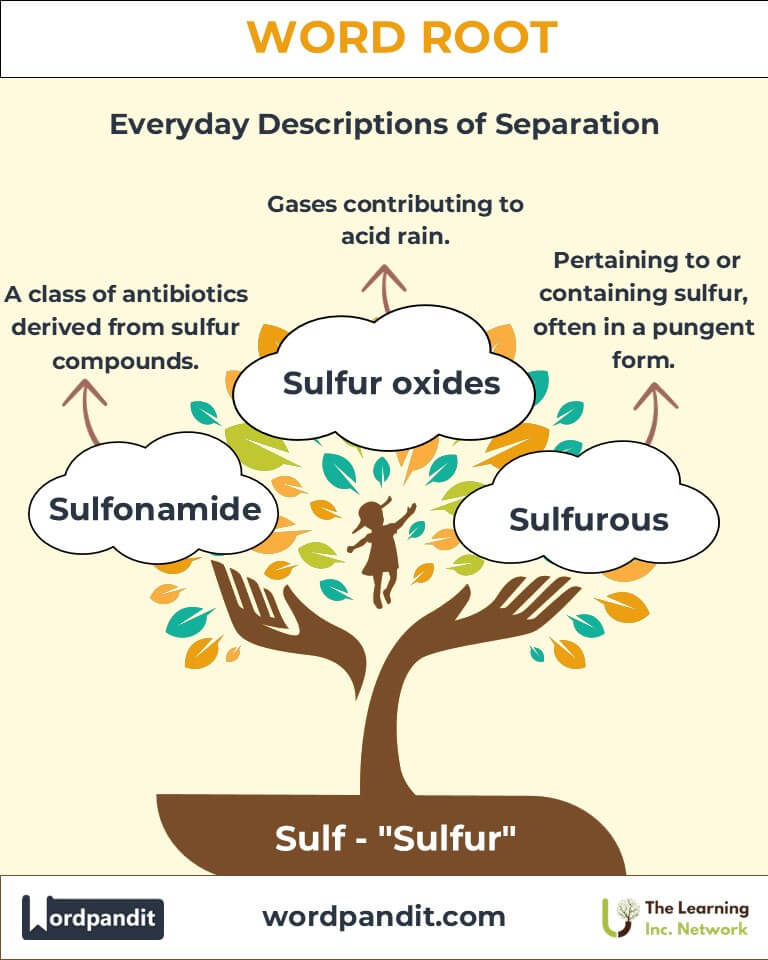
- Sulfurous (suhl-fyur-us): Pertaining to or containing sulfur, often in a pungent or reactive form.
- Example: "The sulfurous odor near the hot springs indicates volcanic activity."
- Sulfonamide (suhl-foh-nuh-mide): A class of antibiotics derived from sulfur compounds.
- Example: "Sulfonamides revolutionized medicine as the first antibacterial drugs."
- Sulfuric (suhl-fyur-ik): Relating to sulfuric acid, a highly corrosive and widely used chemical.
- Example: "Sulfuric acid is essential in fertilizer production."
Sulf Through Time
- Sulfur in Alchemy: Sulfur was one of the three "primordial substances" in medieval alchemy, symbolizing transformation.
- Sulfate Evolution: Sulfates became vital in agriculture and detergents during the 20th century.
Sulf in Specialized Fields
- Chemistry: Sulfides play a key role in metallurgy and ore refinement.
- Medicine: Sulfonamides marked the beginning of antibiotic treatments.
- Environmental Science: Sulfates are both pollutants and nutrients, influencing ecosystems.
Illustrative Story: Sulf in Action
Maria, an environmental chemist, worked tirelessly to reduce sulfate pollution in a local river. By studying natural sulfide cycles, she developed a bioremediation method using bacteria to neutralize harmful compounds. Her groundbreaking work not only restored the river’s health but also highlighted sulfur’s role in both pollution and recovery.
Cultural Significance of Sulf
In many cultures, sulfur’s bright yellow color and association with fire earned it mystical significance. Sulfur was considered both a purifying and destructive force, appearing in myths and early medicines as a tool for transformation.

The Sulf Family Tree
- Thio- (Greek: sulfur):
- Example: Thiosulfate: A sulfur-containing compound used in photography.
- Hydro- (Greek: water):
- Example: Hydrosulfide: A compound of sulfur and hydrogen.
- Ox- (Greek: sharp/acid):
- Example: Sulfur oxides: Gases contributing to acid rain.
FAQs About " Sulf "
Q: What does "sulf" mean?
A: The root "sulf" comes from the Latin word sulfur, which refers to the chemical element sulfur. Sulfur is a non-metal element known for its bright yellow color, strong smell (in compounds like sulfur dioxide), and versatility in forming important chemical compounds such as sulfates and sulfides.
Q: How do sulfates and sulfides differ?
A: Sulfates are salts or esters of sulfuric acid, containing the sulfate ion (SO₄²⁻). They are commonly found in detergents, fertilizers, and natural minerals. Sulfides, on the other hand, are compounds where sulfur bonds directly with metals or nonmetals (e.g., pyrite or hydrogen sulfide). These are often found in ores and can produce a rotten-egg smell when decomposing.
Q: Why is sulfur significant in medicine?
A: Sulfur has antibacterial properties, and sulfur-based drugs, such as sulfonamides, were among the first antibiotics. These drugs, derived from sulfur-containing compounds, helped combat bacterial infections effectively, revolutionizing medicine in the early 20th century.
Q: What are natural sources of sulfur?
A: Sulfur is found naturally in volcanic emissions, hot springs, and minerals like pyrite and gypsum. It is also present in certain amino acids (like cysteine and methionine), which are essential for living organisms.
Q: What is sulfuric acid, and why is it important?
A: Sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) is a highly corrosive liquid used in manufacturing fertilizers, chemicals, and batteries. Its widespread industrial use, especially in creating ammonium sulfate fertilizers, makes it one of the most produced chemicals worldwide.
Test Your Knowledge: " Sulf " Mastery Quiz
1. What does "sulf" signify?
2. Which compound is commonly used in detergents?
3. What was sulfur historically known as in alchemy?
4. Which term describes antibiotics derived from sulfur?
5. What is a common sulfide mineral?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Sulf
The root "sulf" embodies sulfur’s essential role in science and everyday life. From sulfates in personal care products to sulfides in industrial applications, this root connects us to innovations that shape our modern world. As research uncovers new uses for sulfur, the legacy of "sulf" will continue to burn bright, just like the element it represents.














