Tachy: The Root of Speed in Language and Science
Uncover the significance of the root "Tachy," derived from the Greek word "tachys," meaning "swift" or "fast." This dynamic root forms the foundation of terms in medicine, technology, and everyday life, encapsulating the essence of rapid motion and quick responses.
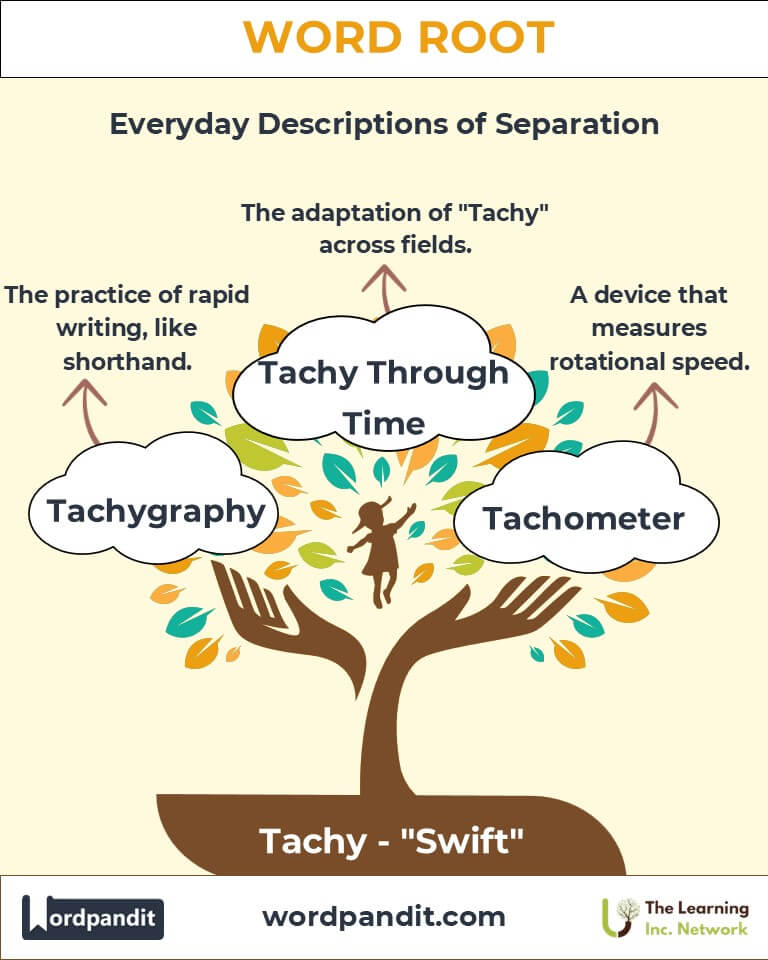
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Tachy
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Tachy
- Common Tachy-Related Terms
- Tachy Through Time
- Tachy in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Tachy in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Tachy Root
- The Tachy Family Tree
- FAQs about the Tachy Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Tachy Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Swift Legacy of Tachy
Introduction: The Essence of Tachy
Speed defines much of modern life, from the swift heartbeat of excitement to the fast-paced mechanics of machines. The root "Tachy" (pronounced TAK-ee) captures this essence of swiftness and rapidity. Derived from the Greek "tachys," meaning "swift," this root appears in terms that measure, diagnose, or describe speed across disciplines like medicine and technology.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "Tachy" originates from the ancient Greek "tachys," symbolizing swiftness or quickness. The concept of speed has always intrigued humans, from ancient philosophers observing motion to modern engineers designing high-speed machinery. Over time, "tachy" became integral to medical and technological terminology, reflecting our growing fascination with acceleration and rapid processes.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Tachy
To remember "Tachy," think of a racecar speeding on a track or a heart racing during a thrilling moment.
Mnemonic Device: “Tachy takes life into high gear—swift and fast!”
Common Tachy-Related Terms
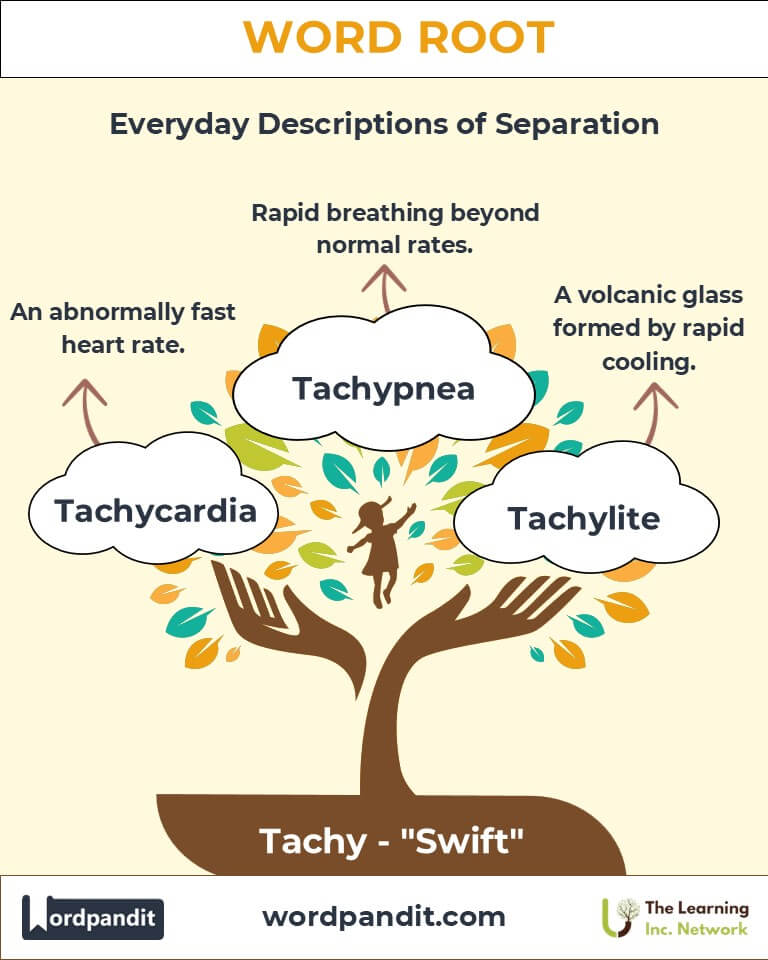
- Tachycardia (tak-ee-KAR-dee-uh): A medical condition characterized by an abnormally fast heart rate.
- Example: "The patient was diagnosed with tachycardia after their pulse exceeded 100 beats per minute at rest."
- Tachometer (tuh-KOM-i-ter): An instrument used to measure the speed of a rotating object, such as an engine.
- Example: "The tachometer showed the car’s engine revving at 7,000 RPM."
- Tachypnea (tak-IP-nee-uh): Abnormally rapid breathing.
- Example: "After the intense workout, his tachypnea gradually returned to a normal breathing rate."
- Tachylite (TAK-i-light): A type of volcanic glass formed rapidly from cooling lava.
- Example: "The geologist collected a sample of tachylite from the volcanic site."
- Tachygraphy (tak-IG-ruh-fee): The art or technique of rapid writing, such as shorthand.
- Example: "Tachygraphy was widely used by clerks in ancient times to record speeches quickly."
Tachy Through Time
- Tachycardia: Used since the early days of cardiology to describe abnormally fast heart rhythms, this term remains central to diagnosing heart conditions.
- Tachometer: Emerging in the industrial age, this tool became vital in measuring engine performance, symbolizing technological progress.
- Tachygraphy: From ancient scribes recording court proceedings to modern shorthand techniques, the concept of rapid writing has stood the test of time.
Tachy in Specialized Fields
- Medicine:
- Terms like tachycardia and tachypnea are critical in diagnosing and managing conditions involving rapid heartbeats or breathing.
- Example: "Emergency doctors monitor tachycardia to assess cardiovascular distress."
- Technology:
- The tachometer is a key instrument in automotive and mechanical engineering, ensuring optimal engine performance.
- Example: "Modern cars display tachometer readings on digital dashboards for real-time monitoring."
- Geology:
- Tachylite, a rapidly cooled volcanic glass, provides insights into the speed of lava solidification.
- Example: "The discovery of tachylite indicated a sudden cooling event during the eruption."
Illustrative Story: Tachy in Action
During a Formula 1 race, the pit crew relied on a tachometer to monitor the car’s engine speed. Meanwhile, in the stands, a paramedic assisted a fan experiencing tachycardia brought on by the excitement of the event. Across the globe, a volcanologist examined tachylite samples to understand a recent eruption’s rapid cooling process. These instances showcase the versatility of "Tachy" in capturing life’s swift moments.
Cultural Significance of the Tachy Root
"Tachy" symbolizes humanity’s fascination with speed and efficiency. From ancient tachygraphy to modern tachometers, this root reflects our drive to measure, analyze, and harness rapid motion. Its presence in language underscores the universal importance of swiftness in science, industry, and everyday life.

The Tachy Family Tree
- Brady (slow):
- Example: Bradycardia (slow heart rate).
- Chron (time):
- Example: Chronograph (a device for measuring time).
- Meter (measure):
- Example: Speedometer (measures vehicle speed).
- Card (heart):
- Example: Cardiogram (a recording of heart activity).
FAQs About " Tachy "
Q: What does "Tachy" mean?
A: The root "Tachy" comes from the Greek word tachys, meaning "swift" or "fast." It is used in terms across various fields to denote speed or rapidity. Examples include "tachycardia," which refers to a rapid heartbeat, and "tachometer," a device for measuring the rotational speed of an engine or similar mechanisms.
Q: What is tachycardia?
A: Tachycardia is a medical condition characterized by an abnormally fast heart rate, typically exceeding 100 beats per minute at rest. It can be caused by stress, fever, heart disease, or other conditions. Depending on the type and cause, it may be harmless or require medical treatment to prevent complications like heart failure or stroke.
Q: How does a tachometer function?
A: A tachometer measures the rotational speed of an engine or mechanical component, usually in revolutions per minute (RPM). It works by detecting the motion of parts like a crankshaft, converting this data into a numerical reading. Tachometers are critical for maintaining performance and preventing mechanical damage in vehicles, machinery, and industrial equipment.
Q: What is tachypnea?
A: Tachypnea is a condition involving abnormally rapid breathing. It often occurs as a response to physical exertion, anxiety, or medical conditions such as respiratory infections, asthma, or heart failure. Tachypnea is a sign that the body requires more oxygen or is attempting to expel excess carbon dioxide.
Q: What is tachygraphy?
A: Tachygraphy refers to the art of rapid writing, often in shorthand. Historically, it was used by scribes and clerks to record speeches, court proceedings, and other events in real-time. The practice highlights the need for speed and efficiency in communication, particularly in administrative and legal contexts.
Q: Is tachycardia always harmful?
A: Not necessarily. Tachycardia can be a normal response to exercise, excitement, or stress (physiological tachycardia). However, if it occurs without an obvious cause or persists for a long time, it may indicate an underlying condition requiring medical evaluation, such as arrhythmias or heart disorders.
Q: What is the connection between "Tachy" and technology?
A: The root "Tachy" appears in technological terms like "tachometer," a device crucial for monitoring speed in mechanical systems. Its usage in technology underscores humanity’s drive to measure, control, and optimize speed and performance in machines and processes.
Q: How does tachy relate to medicine and diagnostics?
A: In medicine, "Tachy" is central to terms like tachycardia (fast heartbeat) and tachypnea (rapid breathing). These conditions are critical diagnostic markers for cardiovascular and respiratory health, guiding treatment decisions and monitoring the body’s response to stress or illness.
Test Your Knowledge: " Tachy " Mastery Quiz
1. What does "Tachy" mean?
2. Which medical condition involves a fast heartbeat?
3. What does a tachometer measure?
4. What does tachypnea describe?
5. What field uses tachygraphy?
Conclusion: The Swift Legacy of Tachy
The root "Tachy" embodies the spirit of swiftness, finding relevance in medicine, technology, and communication. From the rapid heartbeat of tachycardia to the speed-measuring tachometer, it symbolizes humanity’s enduring fascination with motion and efficiency. Exploring "Tachy" enriches our understanding of the dynamic processes that define life and innovation.














