Telos: The Root of Purpose and End in Philosophy and Beyond
Discover the profound significance of "telos," the Greek root meaning "end" or "purpose." From philosophical explorations like teleology to practical applications in modern technology, this root encapsulates the pursuit of ultimate goals and destinations.
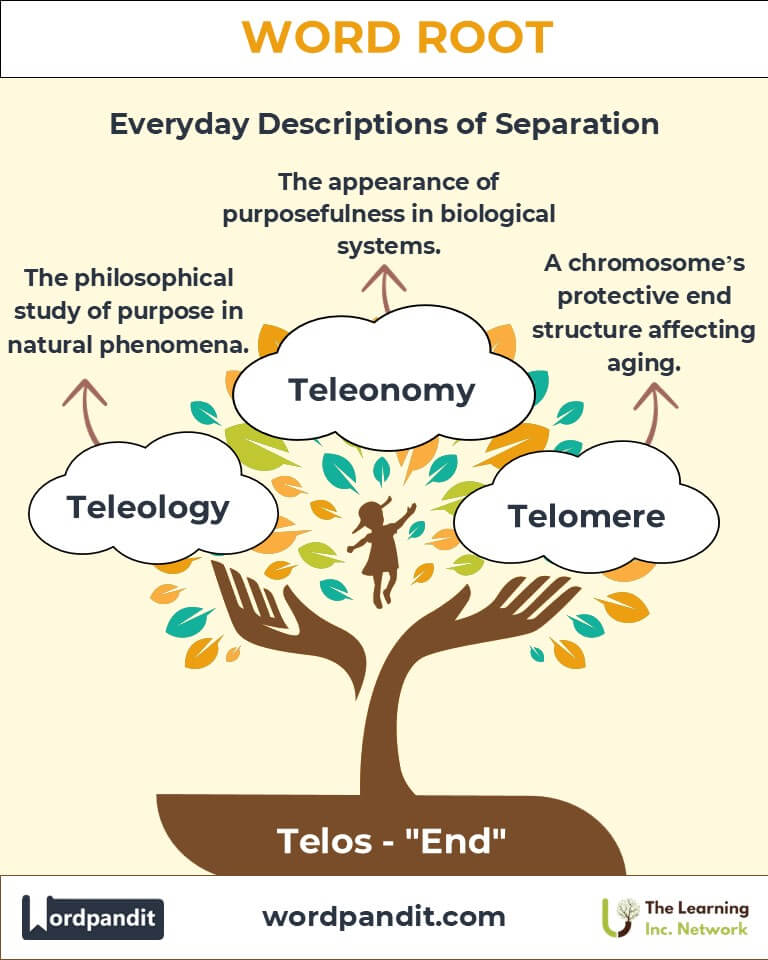
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Telos
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Telos
- Common Telos-Related Terms
- Telos Through Time
- Telos in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Telos in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Telos Root
- The Telos Family Tree
- FAQs about the Telos Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Telos Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Telos
Introduction: The Essence of Telos
At the heart of human endeavor lies the search for purpose and meaning—a concept deeply rooted in "telos" (pronounced TEE-lohs or TEH-lohs). Originating from Greek, telos signifies "end" or "ultimate purpose." It forms the backbone of teleology, the philosophical study of purpose, and appears in diverse contexts, from ethics to engineering. Understanding telos enriches our appreciation of life's goals and the systems we create to achieve them.

Etymology and Historical Journey
"Telos" traces back to ancient Greek, where it referred to the ultimate end or goal of an action or object. Philosophers like Aristotle emphasized telos in explaining natural processes and ethical behavior, suggesting that everything in nature has a purpose. The concept migrated into Latin and later English through philosophical and theological texts, maintaining its association with purpose and finality.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Telos
To remember "telos," imagine an archer aiming at a target, symbolizing the purposeful pursuit of a goal. The archer’s intent to hit the bullseye mirrors the essence of telos as the ultimate aim.
Mnemonic Device: "Telos is the target we strive for, the purpose that drives us forward."
Common Telos-Related Terms
- Teleology (TEE-lee-OL-uh-jee): The philosophical study of purpose or design in natural phenomena.
- Example: "Darwin challenged traditional teleology by explaining adaptation through natural selection."
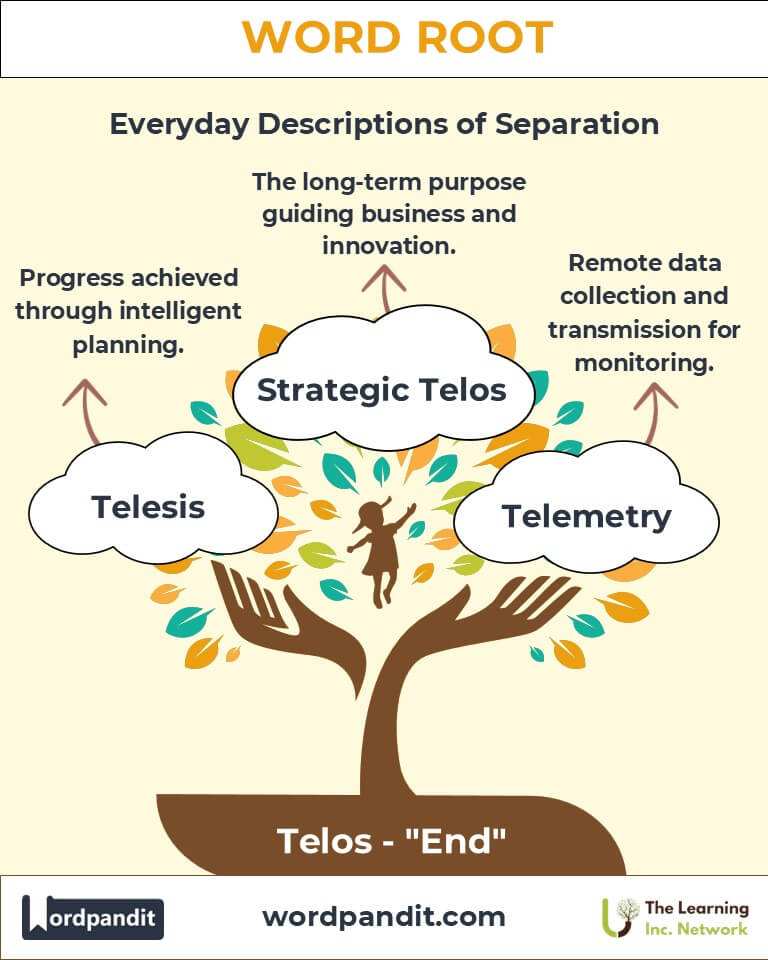
- Telemetry (tuh-LEM-uh-tree): The automated collection and transmission of data over distances.
- Example: "Satellites use telemetry to monitor environmental changes."
- Teleonomy (TEL-ee-AH-nuh-mee): The apparent purposefulness in biological systems.
- Example: "Biologists study teleonomy to understand adaptive traits."
- Telomere (TEL-oh-meer): The end structure of a chromosome that protects genetic information.
- Example: "Telomeres shorten with age, influencing cellular lifespan."
- Telesis (TEL-uh-sis): Progress achieved through intelligent planning.
- Example: "Urban development often requires careful telesis."
Telos Through Time
- Teleology in Ancient Greece: Aristotle proposed that everything has a telos, or ultimate purpose, such as a seed’s telos to become a tree.
- Modern Evolutionary Biology: While rejecting innate purposes, Darwin’s theory of natural selection is sometimes described as replacing teleology with teleonomy.
- Technological Evolution: Telemetry, derived from telos, now powers innovations like remote patient monitoring and space exploration.
Telos in Specialized Fields
- Philosophy:
- Ethics: Telos underpins virtue ethics, where moral actions align with an individual's ultimate purpose.
- Metaphysics: Explores telos in the context of existential questions about life's purpose.
- Biology:
- Telomeres: Studied for their role in aging and disease prevention.
- Technology:
- Telemetry: Crucial for real-time data collection in fields like aerospace and healthcare.
- Business:
- Strategic Planning: Employs telos-like concepts to define mission statements and long-term objectives.
Illustrative Story: Telos in Action
In a small coastal village, Sofia, a marine biologist, worked tirelessly to protect endangered sea turtles. Each day, she tracked their migratory patterns using telemetry. For Sofia, the turtles symbolized telos—the drive to return home despite immense challenges. Her work not only safeguarded the turtles but also inspired the community to embrace their own purposes, proving that pursuing telos brings meaning to life.
Cultural Significance of the Telos Root
The idea of telos resonates in art, religion, and philosophy, reflecting humanity’s quest for meaning. From Aristotle’s ethics to modern goal-setting methodologies, telos inspires individuals and societies to strive for excellence, fostering progress and innovation.

The Telos Family Tree
- Tele- (distant):
- Telephone: A device for distant communication.
- Telescope: An instrument for observing distant objects.
- Endo- (within):
- Endgame: The final phase of a game.
- Endurance: The ability to sustain effort until the end.
- Final- (last):
- Finale: The concluding part of a performance.
- Finite: Having limits or an end.
FAQs About " Telos "
Q: What does "telos" mean?
A: Telos means "end" or "ultimate purpose" in Greek. It represents the final goal or outcome toward which something is directed, whether in nature, philosophy, or human actions.
Q: How is telos significant in philosophy?
A: In philosophy, telos is central to Aristotle’s concept of teleology. Aristotle believed that all natural entities and actions are directed toward an ultimate purpose, whether it's a seed growing into a tree or humans seeking happiness (eudaimonia). This idea shaped ancient and medieval thought on causation and purpose.
Q: What is teleology?
A: Teleology is the study of design or purpose in natural phenomena. It examines how objects, organisms, or processes are oriented toward specific ends. For example, a teleological explanation of the heart would focus on its purpose to pump blood, not just its physical structure.
Q: How is telos connected to telemetry?
A: Telemetry, derived from the root telos (end) and metron (measure), refers to the remote collection and transmission of data to achieve specific goals, like monitoring satellites or managing patient health in medicine. It involves using data as a means to guide actions toward defined purposes.
Q: What are telomeres, and why are they important?
A: Telomeres are protective caps at the ends of chromosomes that prevent genetic material from deteriorating or fusing with other chromosomes. They are critical for maintaining cellular health, and their gradual shortening is associated with aging and certain diseases.
Q: Is telos relevant in business?
A: Absolutely. Telos informs the creation of mission statements, long-term goals, and strategic plans. Businesses often define their "telos" as their ultimate purpose or vision, guiding their operations and decision-making processes.
Q: What is the difference between telos and teleology?
A: While telos refers to the concept of purpose or end, teleology is the study or explanation of phenomena in terms of their purposes or goals. For instance, telos is the goal itself, while teleology explains how and why an action or process aims toward that goal.
Q: Can telos have spiritual or metaphysical connotations?
A: Yes. In many spiritual or philosophical traditions, telos represents the ultimate purpose of life or existence. For example, in Christianity, the telos of human life might be union with God, while in existentialism, it might involve creating personal meaning.
Q: How does telos relate to biology?
A: In biology, telos is implicit in the study of evolutionary adaptations, where traits and behaviors are often analyzed in terms of their function or purpose. For example, the telos of wings in birds is flight, and the telos of photosynthesis is energy production.
Q: What is the role of telos in ethics?
A: Telos plays a key role in virtue ethics, especially in Aristotle’s framework. He argued that moral virtues align human behavior with their ultimate purpose or telos—living a life of reason and achieving eudaimonia (human flourishing).
Test Your Knowledge: " Telos " Mastery Quiz
1. What does "telos" mean?
2. What is telemetry?
3. Who emphasized telos in philosophy?
4. What are telomeres?
5. Which field uses telemetry extensively?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Telos
Telos embodies the essence of purpose and finality, guiding actions across disciplines and generations. From Aristotle’s teachings to modern technology, it shapes how we understand the world and ourselves. As we continue to innovate and explore, telos remains a timeless reminder of our shared quest for meaning and progress.














