Thermo: The Root of Heat in Science and Life
Explore the power and versatility of the root "thermo," derived from the Greek word "thermē," meaning heat. From everyday devices like thermometers to advanced technologies such as thermostats, this root embodies humanity's ingenuity in harnessing and measuring heat.
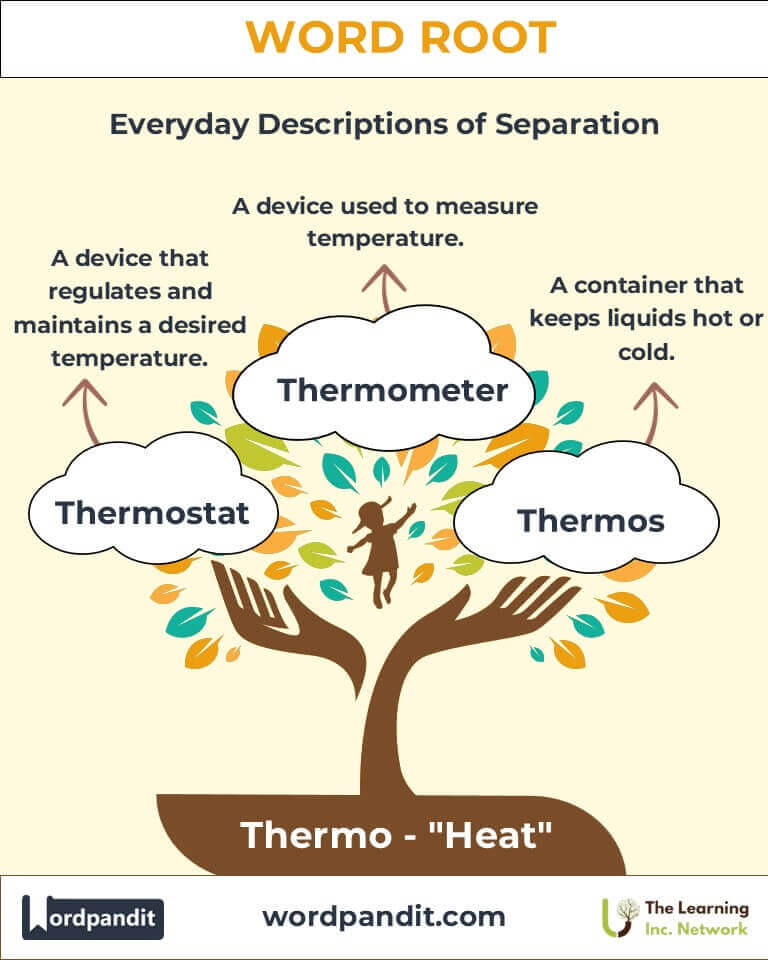
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Thermo"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Thermo"
- Common "Thermo"-Related Terms
- "Thermo" Through Time
- "Thermo" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Thermo" in Action
- Cultural Significance of the "Thermo" Root
- The "Thermo" Family Tree
- FAQs about the "Thermo" Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Thermo" Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Thermo"
Introduction: The Essence of "Thermo"
What makes a thermometer indispensable in medicine or a thermostat crucial for comfort? The root "thermo" links them all. Pronounced "thur-mo," this Greek root signifies "heat," forming the foundation of countless terms across science, technology, and daily life. Its relevance spans from understanding Earth's climate to revolutionizing modern industry.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "thermo" traces back to the Greek word "thermē," meaning heat or warmth. Ancient Greeks recognized heat's fundamental role in sustaining life and its transformative power, as in cooking or metallurgy. With the advent of modern science, the root "thermo" entered the lexicon of physics and technology, shaping terms like "thermodynamics" and "thermometer."
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Thermo"
Imagine holding a glowing thermometer in your hand, its rising red line symbolizing heat and energy. This vivid image connects "thermo" with heat in all forms.
Mnemonic Device: "Thermo is the heat we measure, manage, and marvel at."
Common "Thermo"-Related Terms
- Thermometer (thur-mom-uh-ter): An instrument for measuring temperature.
- Example: "The nurse used a thermometer to check the patient's fever."
- Thermostat (thur-mo-stat): A device that regulates temperature.
- Example: "The thermostat adjusted the room to a cozy 72 degrees."
- Thermal (thur-muhl): Relating to heat or temperature.
- Example: "He wore a thermal jacket to stay warm in the snow."
- Thermodynamics (thur-mo-dy-nam-iks): The science of heat, energy, and work.
- Example: "Thermodynamics explains how engines convert heat into motion."
- Thermoplastic (thur-moh-plas-tik): A type of plastic that becomes moldable when heated.
- Example: "Thermoplastics are widely used in 3D printing."
- Thermos (thur-mohs): A container designed to keep liquids hot or cold.
- Example: "She carried tea in her thermos during the hike."
"Thermo" Through Time
- Thermopylae (Ancient): The name of the famous Greek battlefield means "hot gates," referencing the area's natural hot springs.
- Thermodynamics (Modern): Emerging during the Industrial Revolution, thermodynamics shaped innovations in engines and energy systems.
- Thermistor (Contemporary): A modern invention, the thermistor is a temperature-sensitive resistor essential in electronic devices.
"Thermo" in Specialized Fields
- Medicine:
- Thermography: Imaging technique that uses heat to detect abnormalities, such as inflammation or tumors.
- Engineering:
- Thermal Insulation: Materials designed to reduce heat transfer, used in buildings and spacecraft.
- Environmental Science:
- Thermohaline Circulation: Describes the large-scale ocean currents driven by heat and salinity differences.
- Material Science:
- Thermoelectric Devices: Convert heat directly into electricity, advancing sustainable energy solutions.
Illustrative Story: "Thermo" in Action
During a freezing winter, engineer Maria used her expertise in thermodynamics to design a self-regulating thermostat for her elderly grandmother. The thermostat adjusted the room's temperature automatically, ensuring warmth and energy efficiency. Maria’s innovation, inspired by the "thermo" root, demonstrated the profound impact of understanding and applying heat.
Cultural Significance of the "Thermo" Root
Heat, symbolized by the root "thermo," represents life, transformation, and energy in cultures worldwide. Ancient myths, such as the Greek tale of Prometheus stealing fire, highlight humanity's relationship with heat. Today, "thermo" remains central to discussions on climate change, energy sustainability, and technological advancement.

The "Thermo" Family Tree
- Pyro- (Fire):
- Pyrometer: Instrument for measuring high temperatures.
- Pyrotechnics: The art of creating fireworks.
- Cryo- (Cold):
- Cryotherapy: Treatment using extreme cold.
- Cryogenics: The science of very low temperatures.
- Calor- (Heat in Latin):
- Calorie: A unit of energy measurement.
- Calorimeter: A device used to measure heat in chemical reactions.

FAQs About " Thermo "
Q: What does "thermo" mean, and where does it originate?
A: The root "thermo" means "heat" and comes from the Greek word thermē, which translates to "heat" or "warmth." It is foundational in words related to heat, temperature, and thermal processes. The significance of "thermo" is evident in fields like physics, medicine, and environmental science, where understanding heat plays a crucial role.
Q: How does a thermometer differ from a thermostat?
A: A thermometer measures temperature, giving precise readings of how hot or cold something is. Examples include clinical thermometers for body temperature and outdoor thermometers for weather. A thermostat, on the other hand, is a device used to regulate and maintain a desired temperature. For example, thermostats in homes automatically adjust heating or cooling systems to maintain comfort levels.
Q: What is thermal energy, and how does it relate to the "thermo" root?
A: Thermal energy refers to the total kinetic energy of particles in a substance, which we perceive as heat. It is a fundamental concept in thermodynamics, a field of study dedicated to understanding how heat, energy, and work interact. The "thermo" root highlights the importance of heat in energy transfer and conversion processes, from powering engines to driving natural phenomena like ocean currents.
Q: What role does "thermo" play in medicine?
A: In medicine, "thermo" is central to diagnostic and therapeutic tools. For instance, thermography uses infrared imaging to detect heat patterns in the body, helping identify inflammation or abnormal tissue growth. Devices like thermometers monitor body temperature, an essential indicator of health. Innovations like thermal ablation use heat to treat conditions like tumors.
Q: What is thermodynamics, and why is it significant?
A: Thermodynamics is the branch of science that studies heat, energy, and their transformations. It underpins much of modern technology, from engines and power plants to refrigeration and climate models. The laws of thermodynamics explain how energy moves and changes form, guiding innovations in sustainable energy and understanding natural systems like weather patterns.
Q: Are "thermal" and "thermoplastic" related?
A: Yes, both terms derive from the root "thermo." Thermal relates to heat or temperature, such as in thermal clothing, which traps heat. Thermoplastics are materials that become soft and moldable when heated but harden upon cooling. They are widely used in manufacturing, including in 3D printing and packaging.
Q: What does "thermohaline circulation" mean?
A: Thermohaline circulation describes the global movement of ocean currents driven by differences in temperature ("thermo") and salinity ("haline"). These currents regulate Earth's climate by distributing heat across the globe, such as the Gulf Stream warming parts of Europe.
Q: How does "thermo" connect to renewable energy?
A: The "thermo" root plays a vital role in renewable energy technologies. Geothermal energy harnesses heat from the Earth's interior to produce electricity. Thermoelectric devices convert temperature differences into electricity, offering potential for sustainable energy innovations.
Test Your Knowledge: " Thermo " Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "thermo" mean?
2. Which device measures temperature?
3. What is thermodynamics?
4. Which term describes heat transfer reduction?
5. What is a thermistor used for?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Thermo"
The root "thermo" reflects humanity's quest to understand and harness heat. From ancient myths to groundbreaking technologies, its influence permeates science, culture, and daily life. As we face global challenges like climate change, the legacy of "thermo" reminds us of the transformative power of heat in shaping a sustainable future.














