Trich: The Root of Hair in Science and Beyond
Discover the fascinating world of "trich," a root word derived from the Greek thrix, meaning "hair." Found in fields as diverse as botany and dermatology, "trich" gives rise to terms like "trichome" and "trichology," highlighting its significance across scientific and practical domains.
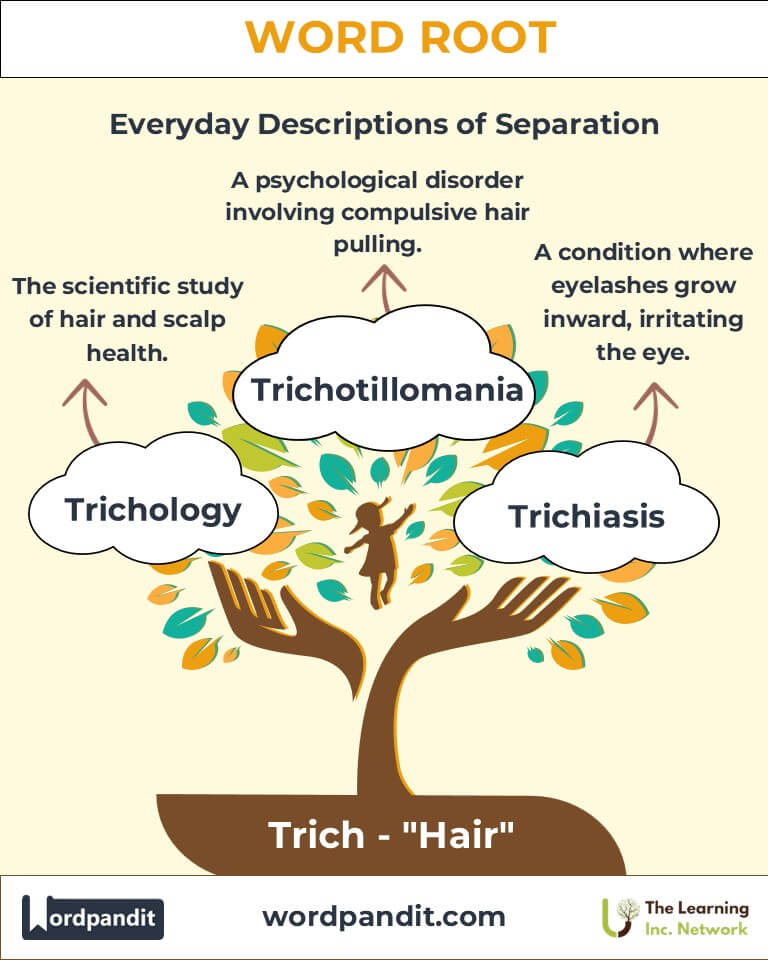
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Trich
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Trich
- Common Trich-Related Terms
- Trich Through Time
- Trich in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Trich in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Trich Root
- The Trich Family Tree
- FAQs about the Trich Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Trich Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Trich
Introduction: The Essence of Trich
When you hear the word "trich," what comes to mind? For botanists, it's the tiny hairs on plants known as trichomes. For dermatologists, it’s the study of hair, or trichology. Pronounced "trik," this Greek-derived root captures the intricate roles that hair plays in nature, science, and daily life.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The word root trich originates from the Greek thrix, meaning "hair." Ancient Greek scholars used the term to describe hair-related phenomena, both human and botanical. As science expanded, trich became the foundation for specialized terms in biology, medicine, and cosmetology.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Trich
Visualize a tree with branches covered in tiny, hair-like projections. This image links "trich" to its Greek meaning and reminds us of its role in both human and plant contexts.
Mnemonic Device: "Trich is the trick to studying hair—from human strands to botanical bristles!"
Common Trich-Related Terms
- Trichome (TRIK-ohm): Tiny hair-like structures on plants, aiding in protection and water retention.
Example: "The plant’s trichomes deterred pests with their sticky texture." - Trichology (trik-OL-oh-jee): The scientific study of hair and scalp health.
Example: "A trichology expert diagnosed the patient’s hair loss." - Trichiasis (trik-EYE-uh-sis): A medical condition where eyelashes grow inward, irritating the eye.
Example: "Surgery corrected her trichiasis, relieving chronic discomfort." - Trichotillomania (trik-oh-til-oh-MAY-nee-uh): A psychological disorder involving compulsive hair pulling.
Example: "Therapy helped manage her trichotillomania." - Trichopathology (trik-oh-puh-THOL-uh-jee): The study of diseases affecting hair.
Example: "The trichopathologist analyzed the sample for signs of alopecia."
Trich Through Time
- Trichology: Originating in the late 19th century, trichology emerged as a distinct field of study focusing on hair care and scalp health.
- Trichomes in Botany: First documented by early botanists, trichomes were initially identified as mere plant hairs. Modern research now highlights their roles in defense and environmental adaptation.
Trich in Specialized Fields
- Botany:
Trichomes provide plants with protection against herbivores and help retain moisture in arid environments.
Example: Trichomes on tomato plants deter pests with their sticky secretions. - Dermatology:
Trichology addresses hair loss, scalp conditions, and cosmetic concerns.
Example: Advances in trichology have revolutionized hair transplant techniques. - Psychology:
Disorders like trichotillomania offer insights into compulsive behaviors and their treatments.
Example: Cognitive-behavioral therapy helps patients manage this condition.
Illustrative Story: Trich in Action
Dr. Lina, a botanist, discovered a species of desert plant whose trichomes helped it survive extreme heat. Inspired, she collaborated with engineers to design moisture-retaining materials for sustainable agriculture. Meanwhile, her colleague, a trichologist, applied similar principles to develop scalp treatments that mimic natural hydration processes. Together, their work demonstrated how "trich" connects ecosystems and human innovation.
Cultural Significance of the Trich Root
Hair has been a symbol of beauty, identity, and power across cultures. From ancient Egyptian wigs to modern hair restoration techniques, the study of "trich" reflects humanity’s evolving relationship with hair as both a cultural and biological feature.

The Trich Family Tree
- Pilo- (Latin, hair):
- Pilose: Covered in soft hairs.
- Piloerection: The technical term for "goosebumps."
- Cili- (Latin, small hair-like structure):
- Cilia: Microscopic hair-like structures in cells.
- Supercilious: Derived metaphorically, meaning "haughty," from raised eyebrows.
- Capill- (Latin, hair):
- Capillary: Thin, hair-like blood vessels.
- Capillature: The arrangement of hair.

FAQs About " Trich "
Q: What does the root "Trich" mean?
A: "Trich" originates from the Greek word thrix, meaning "hair." It is commonly used in medical, biological, and anatomical terms related to hair or hair-like structures.
Q: What is trichology?
A: Trichology is the branch of dermatology that deals with the scientific study of hair and scalp health. It involves diagnosing and treating hair loss, dandruff, and other hair-related disorders.
Q: How does the term "trichome" relate to plants?
A: In plants, a "trichome" refers to tiny, hair-like outgrowths on the epidermis of leaves and stems. These structures can serve various purposes, such as reducing water loss, deterring herbivores, or trapping insects in carnivorous plants.
Q: What is trichotillomania?
A: Trichotillomania is a psychological condition characterized by an irresistible urge to pull out one’s hair, often leading to noticeable hair loss. It is considered an impulse control disorder and may require therapy or medical treatment.
Q: How does the term "trichiasis" apply to eyelash conditions?
A: Trichiasis is a condition where eyelashes grow inward toward the eye, causing irritation or damage to the cornea. Treatment options include plucking, electrolysis, or minor surgical procedures to correct the growth direction.
Q: What is the purpose of trichomes on cannabis plants?
A: Trichomes on cannabis plants produce resin containing cannabinoids and terpenes, which contribute to the plant’s aroma, flavor, and effects. They also serve as a natural defense mechanism against pests and UV radiation.
Test Your Knowledge: " Trich " Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "Trich" mean?
2. What does trichology study?
3. What are trichomes in plants?
4. What is trichotillomania?
5. How do trichomes benefit cannabis plants?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Trich
From the microscopic trichomes of plants to the complex world of trichology, the root "trich" underscores the significance of hair in science and daily life. As research advances, the applications of "trich" continue to grow, reminding us of the interconnectedness of all living things. Embrace the intricate beauty of "trich" in nature and nurture!














