Uro: The Tail-End Connection Across Fields
Discover: The fascinating journey of the root "uro," meaning "tail," and its influence on scientific, linguistic, and cultural expressions. From its role in zoology to its symbolic significance, explore how this root shapes our understanding of anatomy, language, and beyond.
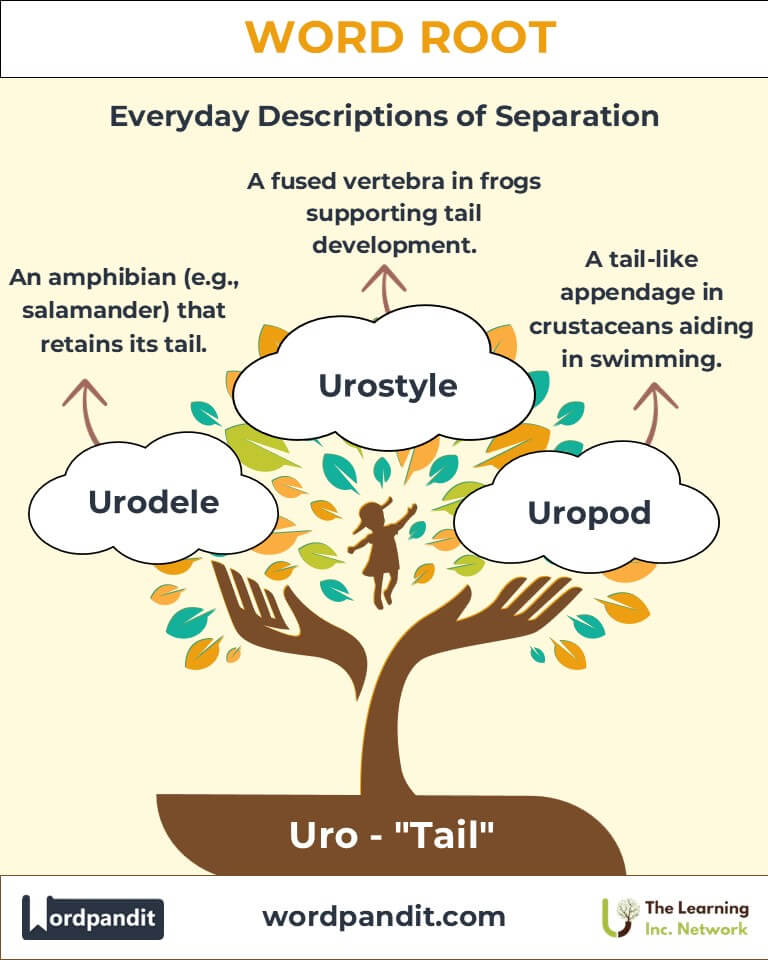
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Significance of Uro
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Uro
- Common Uro-Related Terms
- Uro Through Time
- Uro in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Uro in Action
- Cultural Significance of Uro
- The Uro Family Tree
- FAQs about the Uro Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Uro Word Root Quiz
- The Enduring Legacy of Uro
1. Introduction: The Significance of Uro
What ties a salamander to medical studies? The answer lies in the root "uro," derived from Greek and Latin origins, meaning "tail." Pronounced "yoo-roh," this root underpins terms across disciplines, particularly zoology and medicine. From urodele amphibians, known for their tails, to urology, a branch of medicine focusing on the urinary tract, "uro" highlights the interconnectedness of form and function.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "uro" originates from the Greek oura and Latin cauda, both meaning "tail." Ancient naturalists used the term to describe tailed creatures, especially amphibians and reptiles. Over time, its meaning expanded metaphorically to include "trailing ends" in anatomy and even symbolic representations of continuity or lineage.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Uro
To remember "uro," imagine a lizard proudly flicking its tail, the hallmark of its identity.
Mnemonic Device: "Uro – where tails tell tales, from animals to anatomy."
4. Common Uro-Related Terms
- Urology (yoo-rol-uh-jee): The medical field that studies and treats the urinary tract system.
Example: "The urology department specializes in kidney and bladder health." - Urodele (yoo-roh-deel): An order of amphibians that retain their tails, like newts and salamanders.
Example: "The urodele's regenerative abilities are a marvel of nature." - Uropod (yoo-roh-pod): A tail-like appendage in crustaceans aiding in swimming.
Example: "The shrimp's swift movement is powered by its uropod." - Urostyle (yoo-roh-stahyl): A fused vertebra in frogs that supports their tails during development.
Example: "The urostyle plays a crucial role in a frog's skeletal structure." - Urochrome (yoo-roh-krohm): A pigment responsible for the yellow color of urine.
Example: "The presence of urochrome indicates normal kidney function."
5. Uro Through Time
- Ancient Zoology: In early classifications, urodelic creatures were admired for their tails' roles in movement and defense.
- Modern Medicine: The uro root now anchors terms in anatomy and urinary health, emphasizing its metaphorical evolution.
6. Uro in Specialized Fields
- Zoology:
- Urodele: Highlights tail-based features in amphibians.
- Application: Study of regeneration and evolutionary traits.
- Medicine:
- Urology: Focuses on urinary system health.
- Application: Diagnosis and treatment of kidney, bladder, and prostate conditions.
- Marine Biology:
- Uropod: Explores locomotion in crustaceans.
- Application: Understanding aquatic adaptations for survival.
7. Illustrative Story: Uro in Action
In a lush rainforest, a young biologist named Mia studied urodele amphibians. One day, she noticed a salamander regrowing its tail after a predator attack. Inspired, Mia collaborated with a medical team to explore how urodelic regeneration could inform treatments for human injuries. Their research opened doors to breakthroughs in tissue regeneration, uniting nature and medicine.
8. Cultural Significance of Uro
The tail symbolizes persistence and adaptability across cultures. Ancient myths often depicted tailed creatures as guardians of wisdom. In modern contexts, "uro" terms remind us of life's resilience, from amphibian regeneration to the human body's intricate systems.

9. The Uro Family Tree
- Cauda (Latin, "tail"):
Example: "The caudal fin of a fish aids in propulsion." - Rami (Latin, "branch"):
Example: "The nerve fibers ramify across the spinal cord." - Pod (Greek, "foot"):
Example: "Podiatry: Medical care of feet, metaphorically extending 'tail-end' care."
10. FAQs About " Uro "
Q: What does the root "Uro" mean?
A: The root "Uro" comes from the Greek word ouron, meaning "urine." It is commonly used in medical terminology to refer to the urinary system and its related processes.
Q: How is "Uro" used in medical terms?
A: "Uro" appears in many medical terms, such as "urology" (the study of the urinary system) and "urogenital" (pertaining to the urinary and genital systems).
Q: What is a urologist?
A: A urologist is a medical doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating conditions related to the urinary system, including kidneys, bladder, and urethra, as well as the male reproductive system.
Q: Can "Uro" refer to animals?
A: Yes, in zoology, "Uro" can be part of terms describing animals with tails or tail-like structures, derived from the Greek word oura, meaning "tail."
Q: What is urolithiasis?
A: Urolithiasis refers to the formation of stones or calculi in the urinary tract, which can cause discomfort, pain, and urinary issues. It is commonly treated by urologists.
11. Test Your Knowledge: " Uro " Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "Uro" signify?
2. What does a urologist specialize in?
3. How is "Uro" used in zoology?
4. What is the meaning of "urogenital"?
5. What is urolithiasis?
12. The Enduring Legacy of Uro
The root "uro" elegantly bridges biology, medicine, and culture, emphasizing the tail's importance in form, function, and symbolism. Whether in the natural world or the human body, "uro" continues to inspire curiosity and innovation. As science advances, this ancient root remains a vital connection to understanding life's complexity.














