- This is an assessment test.
- These tests focus on geometry and mensuration and are meant to indicate your preparation level for the subject.
- Kindly take the tests in this series with a pre-defined schedule.
Geometry and Mensuration: Test 28
Congratulations - you have completed Geometry and Mensuration: Test 28.You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.You correct answer percentage: %%PERCENTAGE%% .Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Your answers are highlighted below.
Question 1 |
ABCD is a rhombus. AB is produced to F and BA is produced to E such that AB= AE= BF. Also ED and CF are produced to meet at G. Then:
ED > CF | |
EG⊥GF | |
ED2 +CF2= EF2 | |
ED||CF |
Question 1 Explanation:
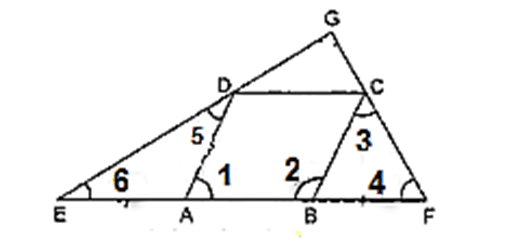 height="246"/>
height="246"/>Here AB= AE= BF.......(1)Given ABCD is a rhombus.
Therefore, AB = BC = CD = AD ... (2)
On equating (1) and (2), we get
BC = BF
⇒∠4 = ∠3 [Angles opposite to equal sides are equal]
Again, ∠B is the exterior angle of triangle BFC.
Therefore, ∠2 = ∠3 + ∠4 = 2∠4 ... (3)
Similarly, AE = AD ⇒∠5 = ∠6
Also, ∠A is the exterior angle of triangle ADE
⇒∠1 = 2∠6 ... (4)
Also, ∠1 +∠2 = 180° [consecutive interior angles]
∴ 2∠6 + 2∠4 = 180°
⇒∠6 + ∠4 = 90° ... (5)
Now, in triangle EGF, by angle sum property of triangle
⇒ 90°+ ∠G = 180° [using (5)]
Thus, EG ⊥ FG.
Question 2 |
Two equal circles of radius 4 cm intersect each other such that each passes through the centre of the other. The length of the common chord is:
$ \displaystyle 2\sqrt{3}$ | |
$ \displaystyle 4\sqrt{3}$ | |
$ \displaystyle 2\sqrt{2}$ | |
$ \displaystyle 8$ |
Question 2 Explanation:
$ \begin{array}{l}The\text{ }length\text{ }of\text{ }the\text{ }common\text{ }chord\text{ }=\text{ }\\2\text{ }\times \text{ }length\text{ }of\text{ }the\text{ }altitude\text{ }of\text{ }the\text{ }equilateral\text{ }triangle\text{ }of\text{ }side\text{ }4\text{ }cm.\\Thus\text{ }the\text{ }length\text{ }of\text{ }common\text{ }chord\text{ }is\\2\times \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\times 4\\=4\sqrt{3}\end{array}$
Question 3 |
The length of two chords AB and AC of a circle are 8 cm and 6 cm and ∠BAC= 90o, then the radius of circle is
25 cm | |
20 cm | |
4 cm | |
5 cm |
Question 4 |
The tangents are drawn at the extremities of a diameter AB of a circle with centre P. If a tangent to the circle at the point C intersects the other two tangents at Q and R, then the measure of the ∠QPR is
45o | |
60o | |
90o | |
180o |
Question 5 |
The circumcentre of a triangle ΔABC is O. If ∠BAC= 85o and BCA= 75o, then the value of ∠OAC is
40o | |
60o | |
70o | |
90o |
Once you are finished, click the button below. Any items you have not completed will be marked incorrect.
There are 5 questions to complete.
List |
















