Fovea: The Pit of Precision in Vision and Beyond
Explore the depth of the word root "Fovea," its origins, and its impact on language, anatomy, and technology. From its role in the sharpest point of human vision to its metaphorical and practical implications, discover how this root illuminates our understanding of precision.
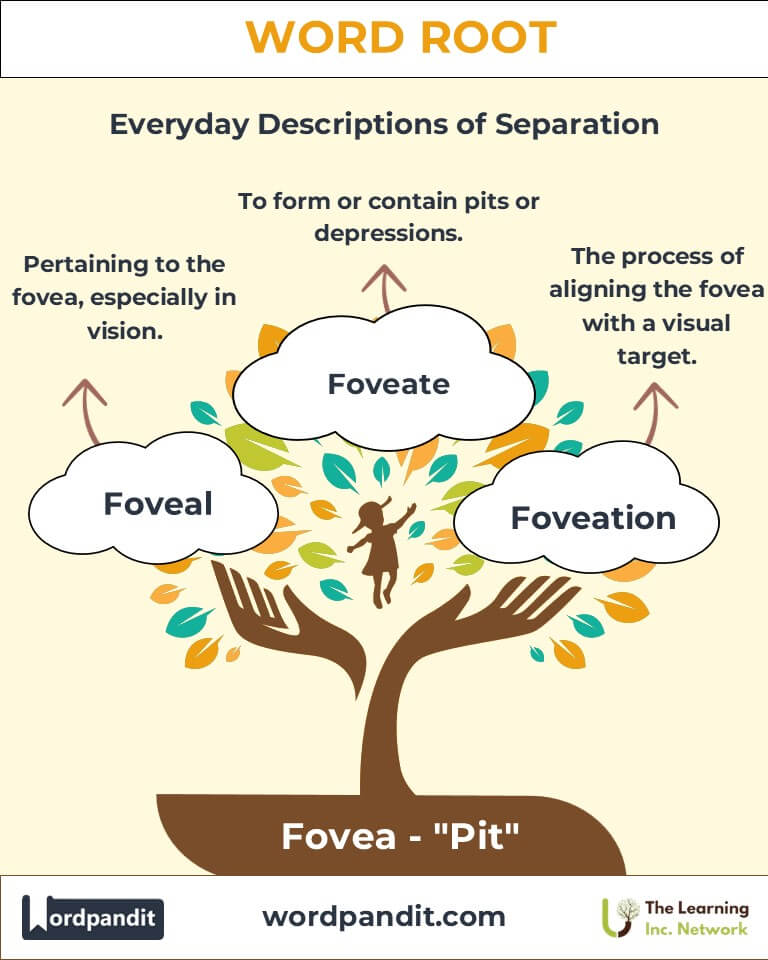
Table of Contents
- Introduction: Discovering the Depth of "Fovea"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Fovea
- Common Fovea-Related Terms
- Fovea Through Time
- Fovea in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Fovea in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Fovea
- The Fovea Family Tree
- FAQs About the Fovea Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Fovea Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Fovea
Introduction: Discovering the Depth of "Fovea"
Did you know that the sharpest part of your vision is named after a tiny pit? The word root fovea, pronounced “foh-vee-uh,” originates from Latin, meaning “pit” or “depression.” It plays a crucial role in anatomy, particularly in the eye, where it denotes the region responsible for the most acute visual focus. Beyond anatomy, this root finds applications in diverse fields, symbolizing precision, centrality, and attention to detail.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The term fovea traces its origin to classical Latin, where it was used to describe pits or hollows in landscapes or objects. Its adoption into scientific terminology began in the 17th century, particularly in anatomy, when early anatomists began to map the intricate structures of the eye.
In this context, the fovea centralis—a depression in the retina—became central to understanding how humans perceive detail and color. Over time, the root evolved to represent more abstract concepts of focus and centrality in various disciplines.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Fovea
To remember fovea, picture a small pit in the ground with a gem sparkling at its center, symbolizing the concentrated focus it represents in the human eye.
Mnemonic Device: “Fovea—The tiny pit in your eye where vision shines brightest.”
This imagery highlights the role of the fovea as the central point of clarity in our visual field.
Common Fovea-Related Terms
- Foveal (foh-vee-uhl):
- Meaning: Pertaining to the fovea, especially in the context of the eye.
- Example: "Foveal vision allows us to see fine details, like reading small print."
- Foveate (foh-vee-ate):
- Meaning: To form or contain pits or depressions.
- Example: "The foveated surface of the artifact suggested it was ancient and weathered."
- Foveation (foh-vee-ay-shun):
- Meaning: The process of aligning the fovea with a visual target.
- Example: "During eye tracking, foveation is used to measure where the subject focuses their gaze."
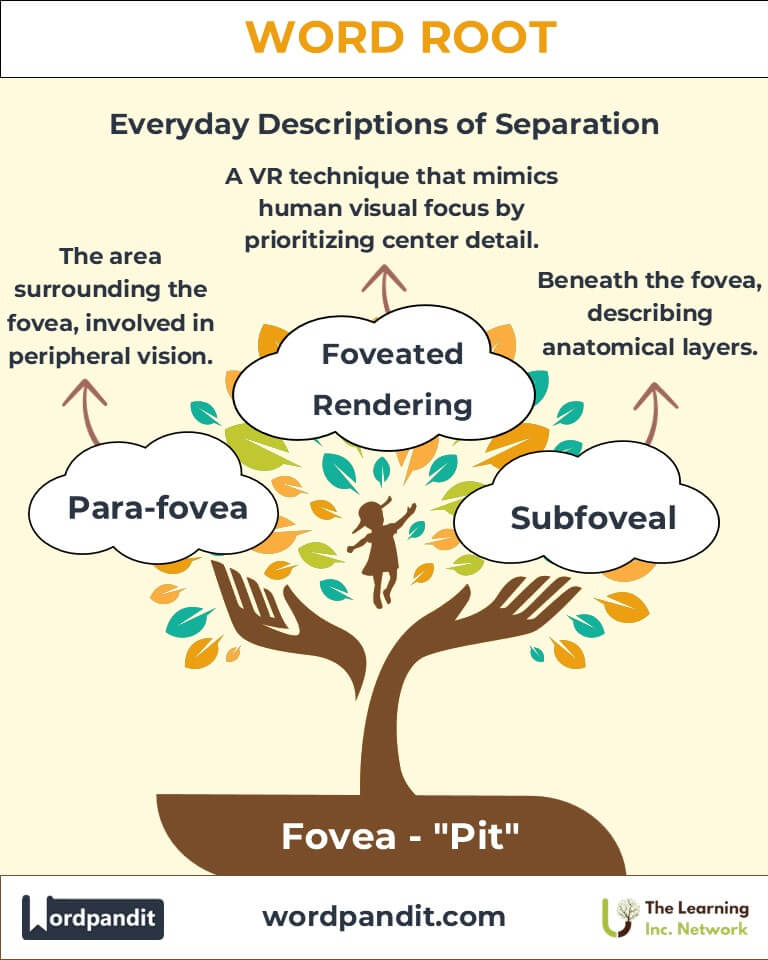
- Para-fovea (par-uh-foh-vee-uh):
- Meaning: The area surrounding the fovea, involved in peripheral vision.
- Example: "The para-fovea aids in detecting motion outside our central focus."
- Subfoveal (sub-foh-vee-uhl):
- Meaning: Beneath the fovea, often describing anatomical layers.
- Example: "Subfoveal conditions can affect central vision significantly."
Fovea Through Time
- The Anatomical Fovea: Originally identified for its role in human vision, the fovea centralis remains a cornerstone of ophthalmology and neuroscience. Advances in imaging have deepened our understanding of its contribution to focus and clarity.
- Technological Foveation: The concept of foveation has expanded into technology, particularly in virtual reality (VR), where foveated rendering mimics human vision by focusing computational power on the center of the display.
Fovea in Specialized Fields
Medicine and Ophthalmology: Understanding diseases like macular degeneration hinges on studying the fovea, as damage here leads to vision loss.
Neuroscience: Research on the fovea sheds light on how the brain processes visual input, with implications for treating conditions like amblyopia.
Virtual Reality and Gaming: Foveated rendering reduces computational demand by mimicking human focus, enhancing VR performance and realism.
Biology: Many birds have highly specialized foveae, enabling exceptional vision for hunting or navigation.
Illustrative Story: Fovea in Action
Dr. Lina, a neuroscientist, was on the brink of a breakthrough in understanding human focus. Her experiments on eye-tracking systems revealed a unique pattern in how people’s foveae responded to color changes. This insight helped develop a revolutionary VR headset that adapted real-time visuals to users' gaze, making virtual worlds appear sharper and more lifelike. Dr. Lina’s dedication to exploring the “tiny pit” led to a monumental leap in immersive technology.
Cultural Significance of the Fovea
The idea of a central pit or focal point resonates in various cultures and philosophies. Metaphorically, the fovea can represent precision, focus, or introspection. It parallels ideas like the “third eye” in spiritual practices, symbolizing clarity and vision beyond the physical realm.

The Fovea Family Tree
- Foramen (Latin: opening):
- Foraminal: Relating to openings, as in bones.
- Foraminate: Perforated with holes.
- Cavus (Latin: hollow):
- Cavity: A hollow space, often used in dentistry.
- Cavern: A large cave or hollow.
- Lacus (Latin: lake or hollow):
- Lacuna: A gap or empty space, especially in texts or anatomy.
FAQs About the "Fovea" Word Root
1. What does "fovea" mean, and where does it originate from?
"Fovea" means "pit" or "depression" and originates from the Latin word fovea. In its most well-known usage, it refers to the small, central depression in the retina responsible for sharp and detailed vision. The term symbolizes focus and precision in various disciplines beyond anatomy.
2. What is the role of the fovea in human vision?
The fovea is the retina's central pit that contains a high concentration of cone cells, the photoreceptors responsible for color and fine detail perception. It enables tasks like reading, driving, and recognizing faces by providing the clearest and sharpest visual focus.
3. What is foveated rendering, and how is it used in technology?
Foveated rendering is a technique in virtual reality (VR) and gaming that mimics the human eye's focus. By concentrating computational resources on rendering the central field of view (where the fovea focuses) and reducing detail in peripheral areas, it enhances performance while maintaining visual realism.
4. Can animals have foveae in their eyes?
Yes, many animals, especially birds of prey like hawks and eagles, have highly specialized foveae. These allow them to see fine details at great distances, aiding in hunting and navigation. Some animals even have multiple foveae to adapt to different visual tasks.
5. What happens if the fovea is damaged?
Damage to the fovea, such as from macular degeneration, can severely affect central vision, making it difficult to perform detailed tasks like reading or recognizing faces. Peripheral vision often remains intact, but the clarity and detail provided by the fovea are lost.
6. What is the para-fovea, and how does it assist vision?
The para-fovea is the region surrounding the fovea. While it does not provide the same sharpness as the fovea, it plays a critical role in peripheral vision and motion detection, helping guide the eye to shift focus toward new objects of interest.
7. Is the fovea present in all species?
No, not all species have a fovea. While it is present in many vertebrates with a need for high-acuity vision (like primates and birds), animals that rely more on peripheral or low-light vision, such as nocturnal animals, may lack a distinct fovea.
8. How does the fovea relate to neuroscience?
The fovea is central to neuroscience research as it provides insights into how the brain processes visual information. Studies on eye movements, focus, and disorders like amblyopia (lazy eye) often involve understanding the fovea's interaction with the visual cortex.
9. What is foveation in biological contexts?
Foveation in biology refers to aligning the fovea with a visual target. This process is crucial for maintaining sharp focus and is a key area of study in understanding visual behavior and eye-tracking technologies.
10. Can the fovea adapt or heal after injury?
While some conditions, like minor injuries or inflammations, may allow partial recovery of foveal function, severe damage such as scarring or degeneration often leads to permanent central vision loss. Treatments like retinal implants and therapies are being developed to mitigate such effects.
Test Your Knowledge: Fovea Word Root Quiz
1. What does "fovea" mean?
2. Where is the fovea located?
3. What is foveated rendering?
4. What does para-fovea refer to?
5. Can the fovea heal itself?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Fovea
From its humble Latin origins as a “pit,” fovea has evolved into a cornerstone of scientific, technological, and cultural understanding. Its applications span from understanding human vision to powering cutting-edge VR systems. As we continue to explore the depths of precision in biology and technology, the legacy of fovea will remain central, sharpening our focus on the intricate details that shape our world.












