Hist: The Root of Tissue in Science and Beyond
Byline: Delve into the fascinating world of the root "hist," derived from the Greek word "histos," meaning "tissue" or "web." From the intricate study of histology to the visual representation of histograms, this root weaves through the realms of biology, medicine, and data visualization, highlighting its multifaceted significance.
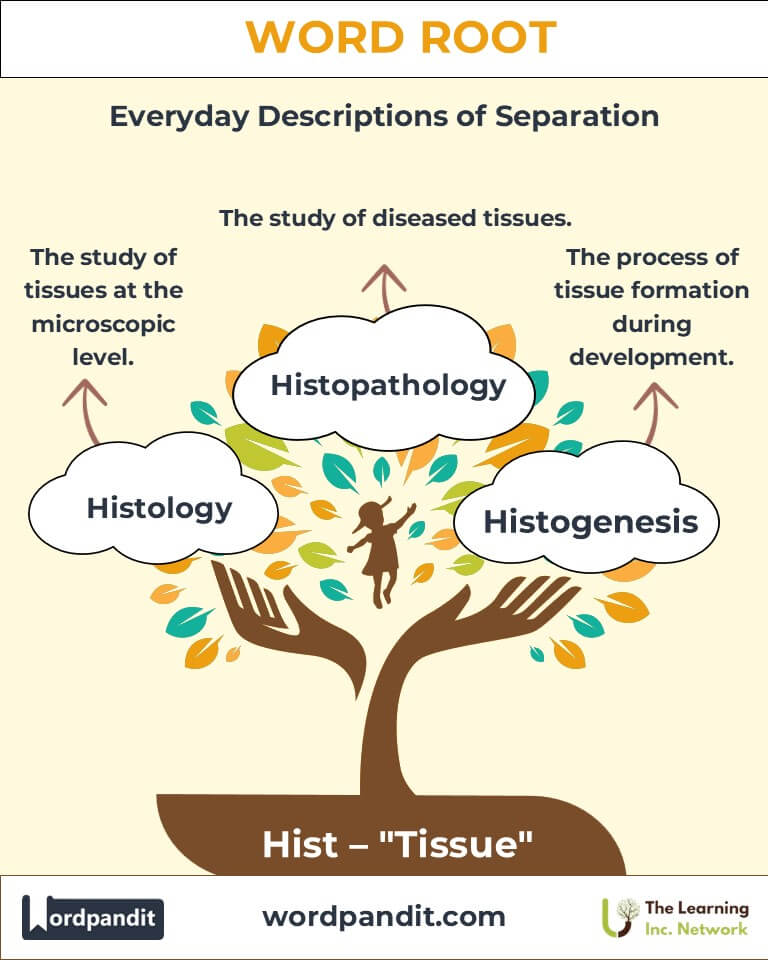
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Fabric of Hist
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Hist
- Common Hist-Related Terms
- Hist Through Time
- Hist in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Hist in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Hist Root
- The Hist Family Tree
- FAQs About the Hist Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Hist Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Everlasting Influence of Hist
Introduction: The Fabric of Hist
When you hear the word "tissue," your mind might immediately wander to the soft paper used to dab away tears. In biology, however, "tissue" represents the very essence of life’s structure. The root "hist", pronounced "hist" (rhyming with "list"), is derived from the Greek word histos, meaning "tissue" or "web." This foundational term forms the bedrock of anatomical and cellular studies, seamlessly connecting science, technology, and art.

Etymology and Historical Journey
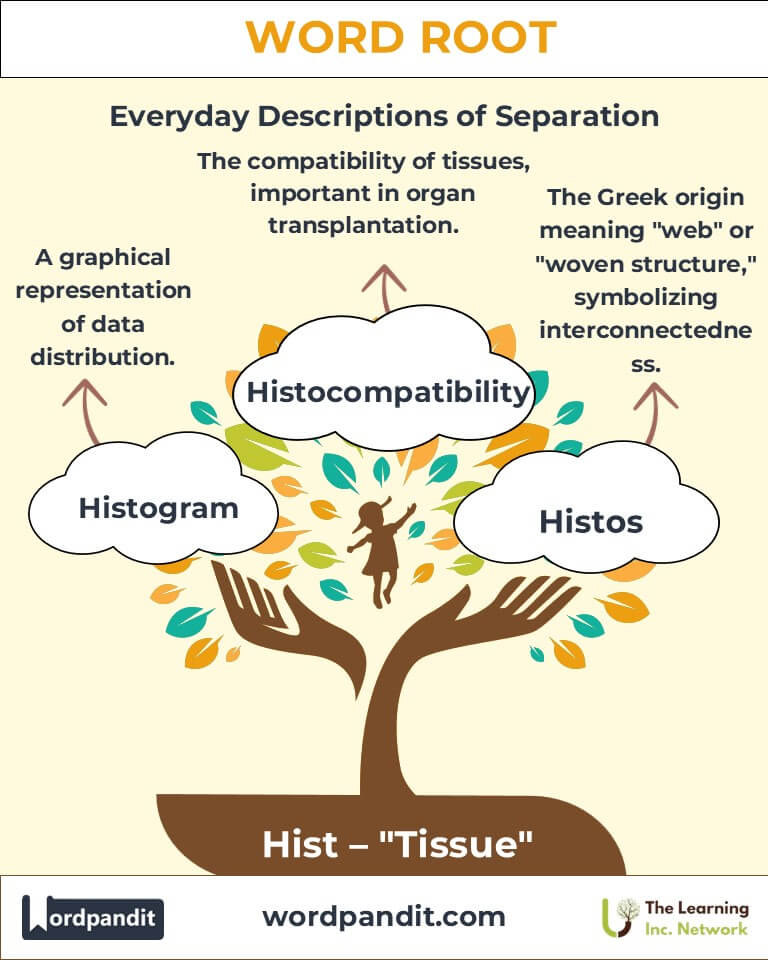
The origin of "hist" lies in the Greek histos, which translates to "tissue" or "web," and was used metaphorically to describe woven structures. Over centuries, the term evolved in the fields of biology and medicine, where tissues—collections of cells working together—became pivotal to understanding organisms. The invention of the microscope in the 17th century revolutionized histology, leading to groundbreaking discoveries about cellular structures.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Hist
To remember "hist", picture a spider weaving a delicate web, symbolizing the interconnectedness of tissues within the body.
Mnemonic Device: "Hist is the web of life, linking cells to create tissues."
Common Hist-Related Terms
- Histology (his-TOL-uh-jee): The study of tissues at the microscopic level.
Example: "Histology revealed abnormalities in the patient’s liver tissue." - Histopathology (his-toh-puh-THOL-uh-jee): The study of diseased tissues.
Example: "The histopathology report confirmed a diagnosis of cancer." - Histogenesis (his-toh-JEN-uh-sis): The process of tissue formation during development.
Example: "The embryologist studied histogenesis in vertebrates." - Histogram (HIS-toh-gram): A graphical representation of data distribution.
Example: "The histogram displayed the frequency of different test scores." - Histocompatibility (his-toh-kuhm-PAT-uh-bil-i-tee): The compatibility of tissues, important in organ transplantation.
Example: "The donor’s histocompatibility matched the recipient’s."
Hist Through Time
- Ancient Understanding: The Greeks conceptualized "histos" as woven structures, akin to fabric, symbolizing interconnection.
- Modern Application: The term "histology" emerged in the 19th century as microscopy advanced, allowing scientists to explore tissues in unprecedented detail.
Hist in Specialized Fields
- Medicine:
Histopathology: Essential in diagnosing diseases by examining tissue samples.
Histocompatibility: Critical for ensuring successful organ transplants. - Biology:
Histogenesis: Explores how tissues form during embryonic development. - Data Science:
Histograms: Widely used for visualizing data distributions in statistics and machine learning.
Illustrative Story: Hist in Action
Dr. Maria, a histologist, received a mysterious tissue sample from a patient experiencing unexplained symptoms. Using her expertise in histology, she examined the sample under a microscope, identifying an unusual pattern of cell growth. Her findings led to an early cancer diagnosis, saving the patient’s life. Meanwhile, a statistician used histograms to map the spread of the disease, contributing to public health interventions.
Cultural Significance of the Hist Root
The concept of histos as a web resonates deeply across cultures, symbolizing connection and interdependence. Whether in medical breakthroughs or data visualization, "hist" highlights the importance of understanding structures, both biological and metaphorical.

The Hist Family Tree
- Cyto- (Cell):
Example: Cytology—The study of cells. - Patho- (Disease):
Example: Pathology—The study of diseases. - Graph- (Writing/Representation):
Example: Graphic—Pertaining to visual representations.
FAQs About the Hist Word Root
Q: What does "hist" mean, and where does it originate?
A: The root "hist" means "tissue" or "web," derived from the Greek word "histos." In its original sense, it referred to woven or structured materials, symbolizing interconnectedness. Over time, it evolved to describe biological tissues, forming the foundation of terms in anatomy and cellular biology.
Q: What is histology, and why is it important?
A: Histology is the microscopic study of tissues. It is vital in medicine and biology because it helps scientists and doctors understand the structure and function of tissues, aiding in diagnosing diseases, studying developmental biology, and advancing medical treatments.
Q: What is a histogram, and how is it used?
A: A histogram is a graphical representation of data distribution, often used in statistics and data analysis. By displaying the frequency of data points in defined intervals, histograms help identify trends, patterns, or anomalies, making them a crucial tool in fields like research, machine learning, and business analytics.
Q: What does histocompatibility mean, and how does it affect medical procedures?
A: Histocompatibility refers to the compatibility of tissues between a donor and a recipient, particularly in organ transplants. Successful histocompatibility ensures that the recipient's immune system does not reject the transplanted organ or tissue, making it a cornerstone of transplant medicine.
Q: How does histogenesis relate to human development?
A: Histogenesis is the process by which tissues form and develop during embryogenesis. It involves cell differentiation and organization, leading to the creation of various tissue types (e.g., muscle, nerve, connective tissue) essential for proper organ and system function in the body.
Q: How does histopathology differ from histology?
A: While histology focuses on the general structure and function of tissues, histopathology specifically studies tissues that are diseased or damaged. This branch of pathology helps identify abnormalities at the cellular level, aiding in diagnosing conditions like cancer or infections.
Q: Why is the root "hist" relevant beyond biology?
A: While its primary use is in biology and medicine, "hist" extends into other fields like data science through terms like "histogram," where it symbolizes organized structures or distributions. This shows the adaptability of the root in conveying structured relationships.
Test Your Knowledge: Hist Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "hist" signify?
2. Which term involves studying diseased tissues?
3. What is a histogram?
4. What is histogenesis?
5. What does histocompatibility impact?
Conclusion: The Everlasting Influence of Hist
The root "hist" intertwines biology, medicine, and technology, illustrating the beauty and complexity of structures both seen and unseen. As science and technology advance, this root will continue to weave through disciplines, reminding us of the interconnected nature of knowledge and life itself.












