Limn: The Root of Lakes and Water Sciences
Byline: Explore the fascinating root "Limn," derived from the Greek word for "lake." Found in terms like limnology and limnetic, this root connects us to the study and appreciation of freshwater ecosystems, bridging disciplines like ecology, biology, and geography.
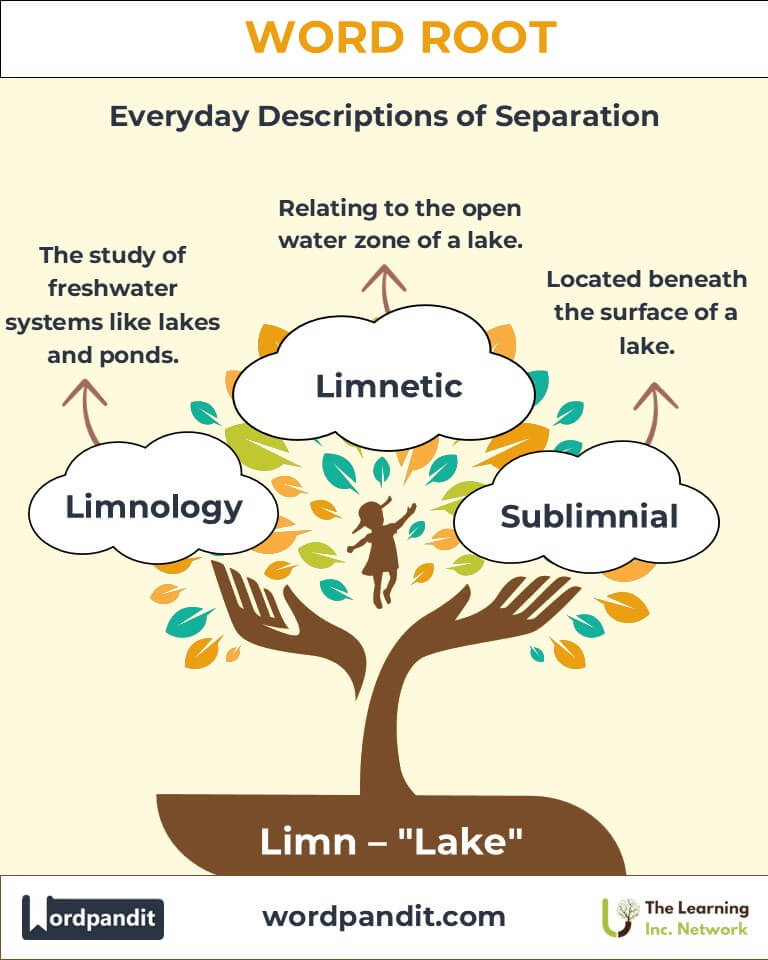
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Limn"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Limn"
- Common Limn-Related Terms
- "Limn" Through Time
- "Limn" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Limn" in Action
- Cultural Significance of the "Limn" Root
- The "Limn" Family Tree
- FAQs About the Limn Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: limn Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Kerat
Introduction: The Essence of "Limn"
The word root "Limn" (pronounced lim) draws its meaning from the Greek word limne, meaning "lake." It forms the basis of words like limnology (the study of lakes and freshwater systems) and limnetic (relating to the open waters of a lake). This root symbolizes a deep connection to aquatic ecosystems, shedding light on the biological, chemical, and ecological intricacies of freshwater environments.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root limn originated in Ancient Greece, where limne referred specifically to lakes or marshy areas. Over time, the term expanded its scope as it entered scientific discourse. In the 19th century, when limnology emerged as a distinct field, the root gained prominence in describing lake ecosystems and their unique characteristics. This evolution underscores humanity's growing interest in understanding freshwater habitats.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Limn"
Picture a serene lake surrounded by lush greenery, with scientists observing the water’s surface and depths. The calm waters represent the root "Limn" as the foundation of freshwater studies.
Mnemonic Device: "Limn links lakes to life—exploring their depths and dynamics."
Common Limn-Related Terms
- Limnology (lim-NOL-uh-jee):
- Definition: The scientific study of freshwater systems, such as lakes and ponds.
- Example: "Her research in limnology focused on the effects of climate change on lake ecosystems."
- Limnetic (lim-NET-ik):
- Definition: Pertaining to the open water zone of a lake, away from the shore.
- Example: "The limnetic zone teems with plankton and small fish essential to the lake's food web."
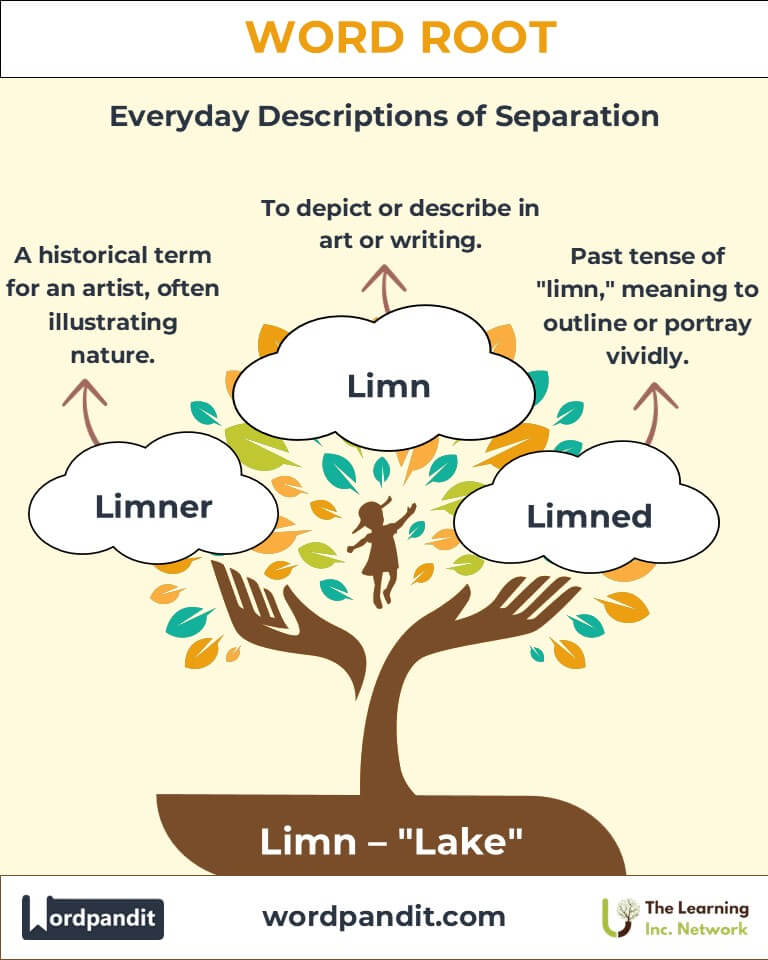
- Limner (LIM-ner):
- Definition: Historically, a person who illustrated or painted, often evoking scenes of nature or water.
- Example: "The limner’s artwork captured the tranquil beauty of the lakeside."
- Sublimnial (sub-LIM-nee-uhl):
- Definition: Situated beneath the surface of a lake or waterbody.
- Example: "The sublimnial zone hosts diverse aquatic plant species."
"Limn" Through Time
- Ancient Usage:
Limne in Greek culture often referred to sacred or mythological lakes. These bodies of water were considered mystical and revered.
- Scientific Application:
With the advent of limnology in the 19th century, the term took on a precise scientific meaning, focusing on freshwater ecosystems’ ecological and biological dynamics.
- Modern Adaptation:
Contemporary studies utilize "limn" to address urgent issues like pollution, habitat degradation, and climate change impacts on lakes.
"Limn" in Specialized Fields
- Ecology:
Limnology focuses on freshwater systems’ biodiversity and their ecological roles.
- Environmental Science:
Analyzing human-induced changes in limnetic zones provides insights into ecosystem health and sustainability.
- Art and Literature:
Historical limners used their craft to depict nature’s beauty, often inspired by lakes and rivers.
Illustrative Story: "Limn" in Action
Dr. Elena Sorenson, a renowned limnologist, worked tirelessly to uncover the secrets of a disappearing alpine lake. As her team studied the limnetic zone, they discovered a unique species of phytoplankton, which was crucial for maintaining the lake’s ecological balance. Her work highlighted the urgent need for conservation efforts to protect these vital freshwater ecosystems.
Cultural Significance of the "Limn" Root
Lakes have held symbolic and practical importance throughout history. From ancient myths about sacred lakes to the modern use of lakes for recreation and sustenance, the root "Limn" reflects humanity’s enduring fascination with freshwater. Artistic traditions, too, have been inspired by lakes, as seen in the works of poets and limners alike.

The "Limn" Family Tree
- Hydr- (Greek: "water"):
- Hydrology: Study of water.
- Hydration: The process of providing water.
- Aqua- (Latin: "water"):
- Aquarium: A tank for aquatic life.
- Aquatic: Pertaining to water.
- Pelag- (Greek: "sea or open water"):
- Pelagic: Relating to the open sea.
- Pelagology: Study of oceanic environments.
FAQs About the Limn Word Root
Q: What does "Limn" mean?
A: Limn is derived from the Greek word limne, meaning "lake." It refers to freshwater systems such as lakes, ponds, and marshes. This root is foundational in words related to the study and exploration of these aquatic environments.
Q: What is limnology?
A: Limnology is the scientific study of inland freshwater systems like lakes, rivers, and ponds. It examines their biological, chemical, and physical characteristics, as well as their ecological roles. Limnology is essential for understanding freshwater ecosystems' health and sustainability.
Q: What does limnetic refer to?
A: The term "limnetic" describes the open water zone of a lake that is well-lit and supports photosynthetic organisms like algae and plankton. This zone is vital for aquatic ecosystems, as it forms the primary source of energy for many food webs.
Q: Is "limn" only used in science?
A: No, "limn" also appears in art and literature. Historically, a limner was an artist who painted or illustrated, often depicting lakes or aquatic scenes. This highlights the word's versatility beyond scientific contexts.
Q: What is the sublimnial zone?
A: The sublimnial zone refers to the areas beneath the surface of a lake, often rich in biodiversity. This region hosts aquatic plants, invertebrates, and fish that play critical roles in nutrient cycling and ecosystem stability.
Q: Why is limnology important?
A: Limnology helps us understand and address critical issues such as water pollution, habitat degradation, and the effects of climate change on freshwater ecosystems. Insights from limnology guide the sustainable management of water resources.
Q: How does limnology relate to environmental conservation?
A: By studying freshwater systems, limnology identifies factors that threaten these ecosystems, such as invasive species, pollution, and over-extraction of water. It provides the knowledge needed for conservation efforts, including habitat restoration and sustainable water usage.
Test Your Knowledge: Limn Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "Limn" signify?
2. What is the focus of limnology?
3. Which zone does "limnetic" describe?
4. What is a limner?
5. Which term relates to below a lake’s surface?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Limn"
The root "Limn" illuminates our connection to lakes and their ecosystems, highlighting the scientific and cultural significance of these vital freshwater bodies. As environmental challenges grow, the study of "Limn" offers hope and solutions for preserving these natural treasures. Whether in science, art, or daily life, the legacy of "Limn" inspires us to value and protect our water resources.












