Urb: The Root of Urban Life and Development
Discover the fascinating roots of "urb," derived from the Latin word for "city," and how it shapes our understanding of urban landscapes, suburban sprawl, and the cultural dynamism of metropolitan life. From the bustling centers of commerce to quiet suburban neighborhoods, the "urb" root is a linguistic cornerstone of human settlement and development.
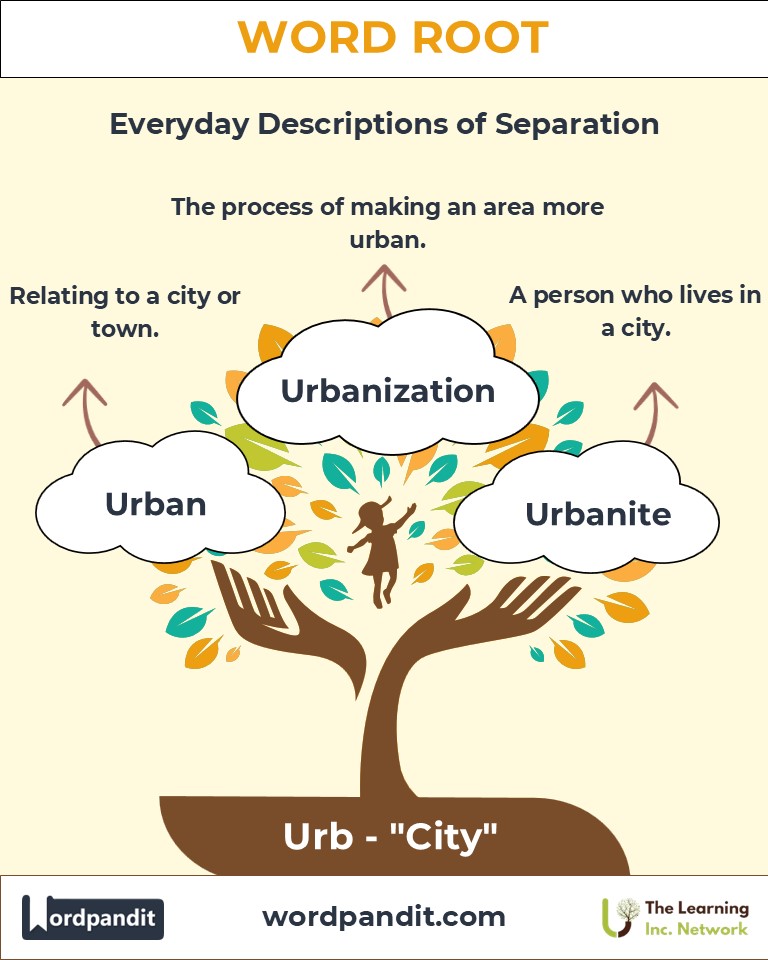
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Urb"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Urb
- Common Urb-Related Terms
- Urb Through Time
- Urb in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Urb in Action
- Cultural Significance of Urb
- The Urb Family Tree
- FAQs About the Urb Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Urb Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Legacy of Urb
Introduction: The Essence of "Urb"
What defines a city? Its skyline, bustling streets, or vibrant cultural life? At the heart of these concepts lies the root "urb," pronounced urb, from Latin, meaning "city." This root connects the essence of urbanization to language, describing everything from city planning to suburban lifestyles. The "urb" root invites us to explore the evolution and impact of cities on civilization.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "urb" originates from the Latin word urbs, meaning "city." Ancient Rome, known as the Urbs Aeterna (the Eternal City), was a focal point of this term. Over time, "urb" became the foundation for words describing cities, their outskirts, and the urbanization process. As cities expanded, terms like "urban" and "suburban" emerged to encapsulate the complexity of human settlements.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Urb
To remember "urb," visualize a vibrant cityscape with towering skyscrapers, bustling streets, and green parks.
Mnemonic: "Urb builds the urban world—from downtown to the suburbs."
Common Urb-Related Terms
- Urban (ur-buhn): Relating to a city or town.
Example: "The urban lifestyle often includes fast-paced living and cultural diversity." - Suburban (suh-bur-buhn): Pertaining to areas on the outskirts of a city.
Example: "Suburban neighborhoods offer a quieter alternative to city life." - Urbanite (ur-buh-nahyt): A person who lives in a city.
Example: "As an urbanite, she thrived on the energy of metropolitan life." - Urbanization (ur-buh-nuh-zay-shun): The process of making an area more urban.
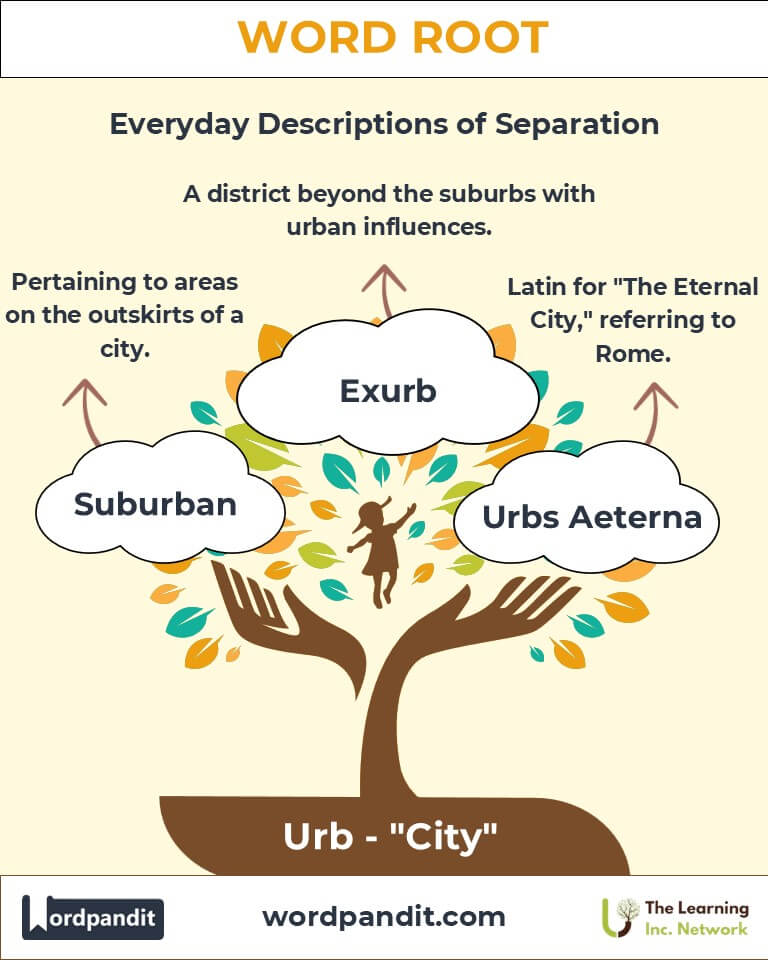
Example: "Rapid urbanization has transformed small towns into bustling cities." - Exurb (ek-sur-b): A district outside the suburbs, typically more rural but with urban influences.
Example: "Exurbs attract those seeking a blend of rural charm and urban convenience."
Urb Through Time
- Urbs Aeterna: Latin for "The Eternal City," referring to Rome's timeless significance.
- Urbanization: In the 19th century, industrial revolutions accelerated urbanization, reshaping landscapes worldwide.
- Suburbia: A mid-20th-century phenomenon tied to post-WWII housing booms and car culture.
Urb in Specialized Fields
- Urban Planning: Designing and organizing city spaces for efficiency and livability.
Example: "Sustainable urban planning prioritizes green spaces and public transport." - Sociology: Studying urban behavior and community dynamics.
Example: "Urban sociology examines how city living influences social interactions." - Economics: Urban economies focus on industries, markets, and resources in cities.
Example: "Urban centers often serve as economic hubs for trade and innovation."
Illustrative Story: Urb in Action
Maria, an urbanite passionate about sustainable living, spearheaded a project to revitalize her city’s downtown. Partnering with urban planners, she transformed vacant lots into green spaces, attracting families and businesses. Meanwhile, her suburban friend, Liam, marveled at how urban renewal breathed new life into their shared community. Their collaboration exemplified the "urb" root's role in fostering dynamic, interconnected lifestyles.
Cultural Significance of Urb
Cities have long been centers of culture, innovation, and progress. The "urb" root encapsulates this significance, appearing in literature, art, and policy discussions. From Rome’s enduring legacy to modern metropolises like Tokyo and New York, "urb" underscores humanity's urban evolution and its impact on civilization.

The Urb Family Tree
- Civ- (Latin: "citizen, city"):
Example: Civil (relating to citizens or public life), Civilization (the stage of human development marked by cities). - Metro- (Greek: "mother city"):
Example: Metropolis (a large, densely populated city), Metropolitan (related to a metropolis). - Polis (Greek: "city-state"):
Example: Acropolis (a fortified part of an ancient city), Politics (activities associated with governance in a city-state).
FAQs About " Urb "
Q: What does "urb" mean?
A: "Urb" means "city" in Latin, and it forms the basis of words related to cities, urban areas, and the process of urbanization.
Q: How does "urban" differ from "suburban"?
A: "Urban" refers to areas within a city characterized by dense population, infrastructure, and cultural activity. "Suburban," on the other hand, pertains to areas on the outskirts of a city, typically more residential and less densely populated.
Q: What is "urbanization"?
A: Urbanization is the process by which rural areas develop into urban centers, often marked by industrialization, population growth, and expansion of infrastructure.
Q: What is an "urbanite"?
A: An urbanite is someone who resides in a city and typically thrives in a fast-paced, culturally rich environment.
Q: What does "exurb" mean?
A: "Exurb" describes a region located beyond the suburbs, often blending rural charm with proximity to urban amenities.
Test Your Knowledge: " Urb " Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "urb" signify?
2. Which term describes city outskirts?
3. What does "urbanization" mean?
4. Who is an urbanite?
5. What does "exurb" describe?
Conclusion: The Legacy of Urb
The "urb" root celebrates the essence of cities as centers of human activity and cultural dynamism. From ancient Rome to modern metropolises, "urb" reflects our evolving relationship with urban spaces and their surrounding regions. As cities continue to grow, so does the relevance of "urb," a linguistic testament to humanity's enduring connection to urban life.












