Rota: The Root of Motion and Cycles in Language
Discover the dynamic essence of the root "rota," derived from the Latin word for "wheel." From everyday terms like "rotate" to complex systems in engineering and philosophy, this versatile root highlights the perpetual motion and cycles that define both nature and human innovation.
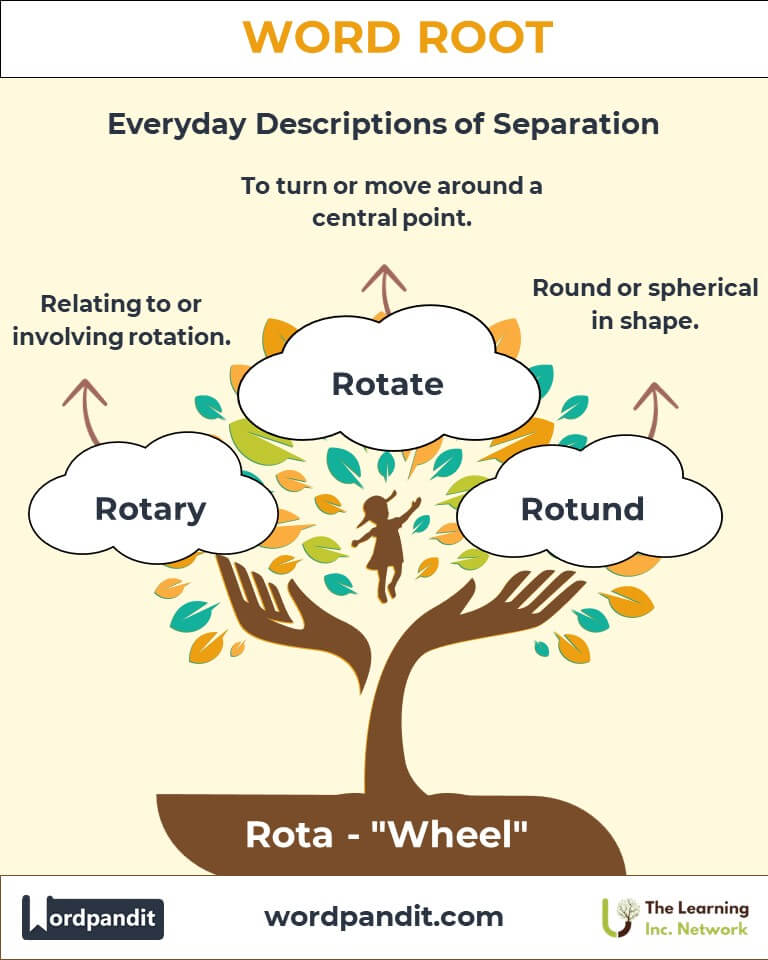
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Rota
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Rota
- Common Rota-Related Terms
- Rota Through Time
- Rota in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Rota in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Rota Root
- The Rota Family Tree
- FAQs about the Rota Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Rota Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Rota
Introduction: The Essence of Rota
Picture a spinning wheel, propelling vehicles forward or marking the passage of time. The root "rota," pronounced row-tuh, signifies "wheel" in Latin and represents motion, rotation, and cyclical patterns. This root has influenced various languages and fields, from mechanics to philosophy, symbolizing innovation, continuity, and transformation.
Etymology and Historical Journey
The word root "rota" originates from the Latin term for "wheel." In ancient Rome, "rota" referred to literal wheels used in chariots and machinery, symbolizing progress and motion. Over time, this concept transcended physical wheels to embody abstract ideas like cycles, rotations, and roles. As languages evolved, "rota" infused words related to movement, repetition, and systematic change.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Rota
To remember "rota," visualize a giant ferris wheel, constantly turning and offering new perspectives.
Mnemonic Device:
"Rota spins the wheel of progress, from cycles of life to revolutions of time."
Common Rota-Related Terms
- Rotate (row-tayt): To turn or move around a central point.
Example: "The Earth rotates on its axis, creating day and night." - Rotary (row-tuh-ree): Relating to or involving rotation.
Example: "Rotary engines operate through circular motion rather than pistons." - Rotund (row-tund): Round or spherical in shape.
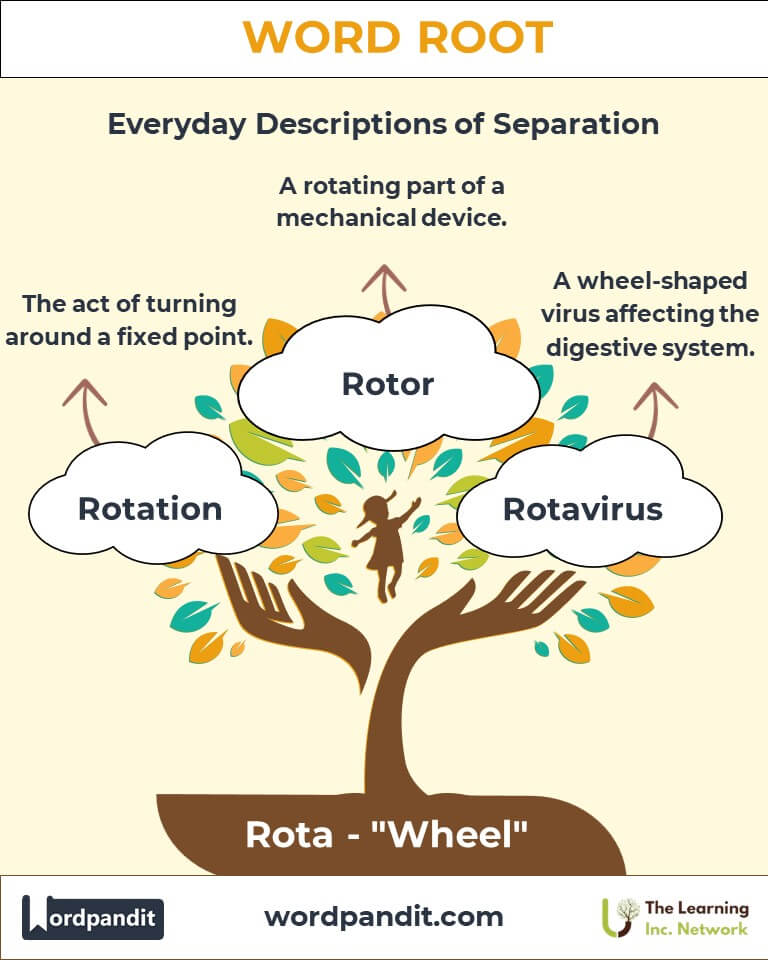
Example: "The rotund sculpture resembled a perfect globe." - Rotation (row-tay-shun): The act of turning around a fixed point.
Example: "Crop rotation improves soil fertility by alternating planted crops." - Rotor (row-tur): A rotating part of a mechanical device.
Example: "Helicopter rotors enable vertical flight by spinning rapidly."
Rota Through Time
- Rota Fortunae (Wheel of Fortune): In medieval philosophy, this concept represented the unpredictable nature of fate, with fortunes rising and falling like a wheel in motion.
- Rotograph: An early term for a rotary printing press, illustrating how the root adapted to describe technological advancements.
Rota in Specialized Fields
- Engineering: Rotary motion drives gears and engines, converting energy into mechanical work.
- Agriculture: Crop rotation minimizes pests and improves soil quality through systematic planting.
- Medicine: Rotavirus refers to a wheel-shaped virus affecting the digestive system.
- Astronomy: Planetary rotation explains day-night cycles and seasonal variations.
Illustrative Story: Rota in Action
Sophia, a young engineer, was tasked with designing a more efficient rotary wind turbine. Inspired by the smooth rotation of a bicycle wheel, she created a prototype that converted wind into energy with 30% more efficiency. Her breakthrough, celebrated by her peers, demonstrated the timeless power of "rota" to drive innovation and sustainability.
Cultural Significance of the Rota Root
The concept of the wheel, symbolized by "rota," appears in various cultures as a metaphor for life’s cycles and progress. In Buddhism, the "Dharmachakra" or Wheel of Dharma represents the path to enlightenment, while in modern contexts, rotary clubs embody the spirit of service and cooperation.
The Rota Family Tree
- Cycl (Greek: "circle, wheel"):
- Bicycle: A vehicle with two wheels.
- Cyclone: A weather system with a circular wind pattern.
- Orb (Latin: "circle, sphere"):
- Orbit: A curved path around a celestial body.
- Orbicular: Having a rounded shape.
- Gyro (Greek: "turn, spin"):
- Gyroscope: A device maintaining orientation through rotation.
- Gyrate: To spin or whirl.
FAQs About the Rota Word Root
Q: What does "rota" mean?
A: "Rota" is the Latin word for "wheel," symbolizing motion, cycles, and transformation. Its significance lies in representing physical and abstract concepts, from spinning objects to the passage of time and systemic rotations in nature and human endeavors.
Q: How does the root "rota" appear in modern vocabulary?
A: The root "rota" is present in terms like "rotate" (to turn around a central point), "rotary" (relating to circular motion), and "rotor" (a rotating mechanical part). These words span fields like engineering, medicine, and astronomy, emphasizing the universal applicability of this root.
Q: What is the cultural or philosophical importance of "rota"?
A: Culturally, "rota" resonates with the idea of cycles and change. For example, the "Rota Fortunae" (Wheel of Fortune) in medieval philosophy illustrates the unpredictability of fate, while in Buddhism, the Wheel of Dharma symbolizes spiritual progress.
Q: How does "rota" relate to time and cycles?
A: The root "rota" represents the cyclical nature of time and patterns, such as Earth's rotation creating day and night. It also applies to agricultural cycles like crop rotation, which maintains soil health and ensures sustainable farming practices.
Q: What is a rotary engine, and how is it different from traditional engines?
A: A rotary engine uses a rotating motion, instead of linear pistons, to generate mechanical energy. This design is compact and efficient, making it ideal for applications like aircraft and some automobiles.
Test Your Knowledge: Rota Word Root Quiz
1. What does "rota" mean?
2. Which term describes turning around a fixed point?
3. What is a "rotor"?
4. Which system involves crop rotation?
5. What does "Rota Fortunae" represent?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Rota
The root "rota" exemplifies perpetual motion, cycles, and progress, resonating across languages and disciplines. From ancient wheels to modern engines, its influence reflects humanity's ingenuity and resilience. Let "rota" inspire you to embrace the cycles of life and propel forward with purpose.











