Bi: The Duality Root in Language and Life
Discover how the root "Bi," meaning "two," creates a linguistic framework for duality, symmetry, and pairing in language, science, and everyday life. Explore how words like "bicycle" and "bilateral" reflect the essence of balance and twofold structures.
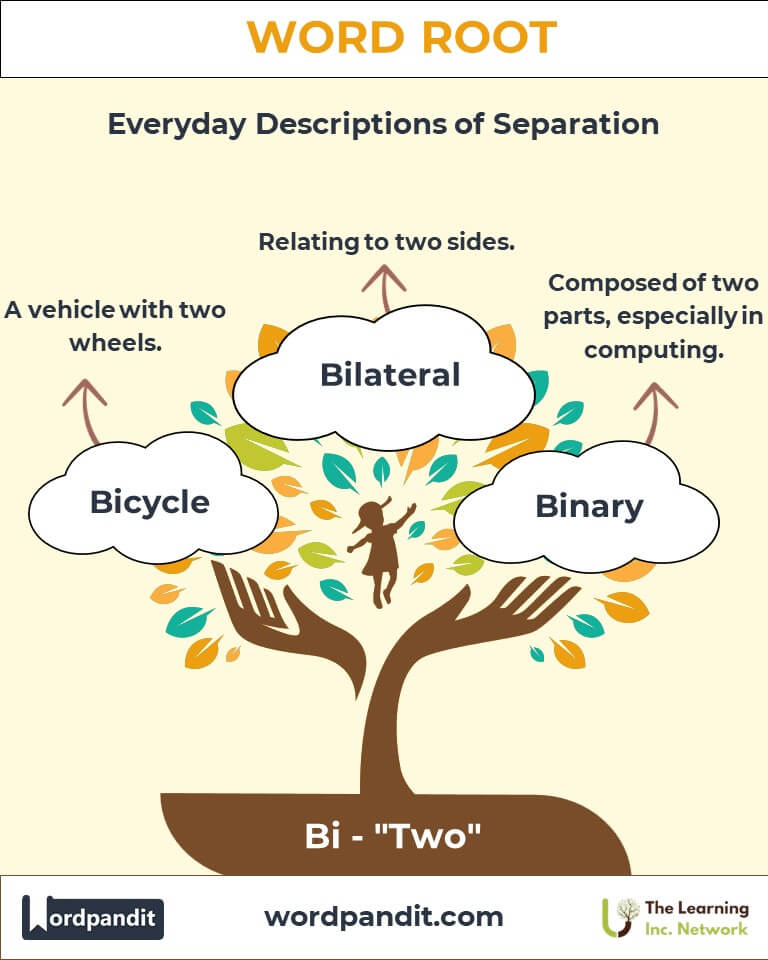
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Power of Bi
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Bi
- Common Bi-Related Terms
- Bi Through Time
- Bi in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Bi in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Bi Root
- The Bi Family Tree
- FAQs about the Bi Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Bi Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Bi
Introduction: The Power of Bi
Think of a bicycle speeding down the street or a bilateral agreement forging cooperation between two nations. The root "Bi," meaning "two," forms the basis of these ideas, symbolizing duality, symmetry, and balance. Originating from the Latin word "bis," meaning "twice," this versatile root influences fields ranging from geometry to diplomacy, encapsulating the concept of twoness in both concrete and abstract forms.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "Bi" derives from the Latin bis, meaning "twice." It was absorbed into English during the Middle Ages, influencing mathematical, biological, and everyday vocabulary. Over time, "Bi" became a linguistic cornerstone for describing pairs, symmetry, and binary oppositions, adapting to modern contexts like technology and relationships.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Bi
Visualize a bicycle with two wheels rolling smoothly along a road, perfectly balanced. This image represents the essence of "Bi"—a connection between two entities working harmoniously.
Mnemonic Device: "Bi is the balancing act of two—two wheels, two sides, two parts in motion."
Common Bi-Related Terms
- Bicycle (bye-si-kul): A vehicle with two wheels powered by pedaling.
- Example: "She rode her bicycle to the park every morning."
- Bilateral (bye-lat-er-uhl): Relating to two sides, often in agreements or anatomy.
- Example: "The countries signed a bilateral trade agreement to benefit both parties."
- Binary (bye-nuh-ree): Composed of two parts; in computing, refers to the base-2 number system.
- Example: "Binary code forms the backbone of computer programming."
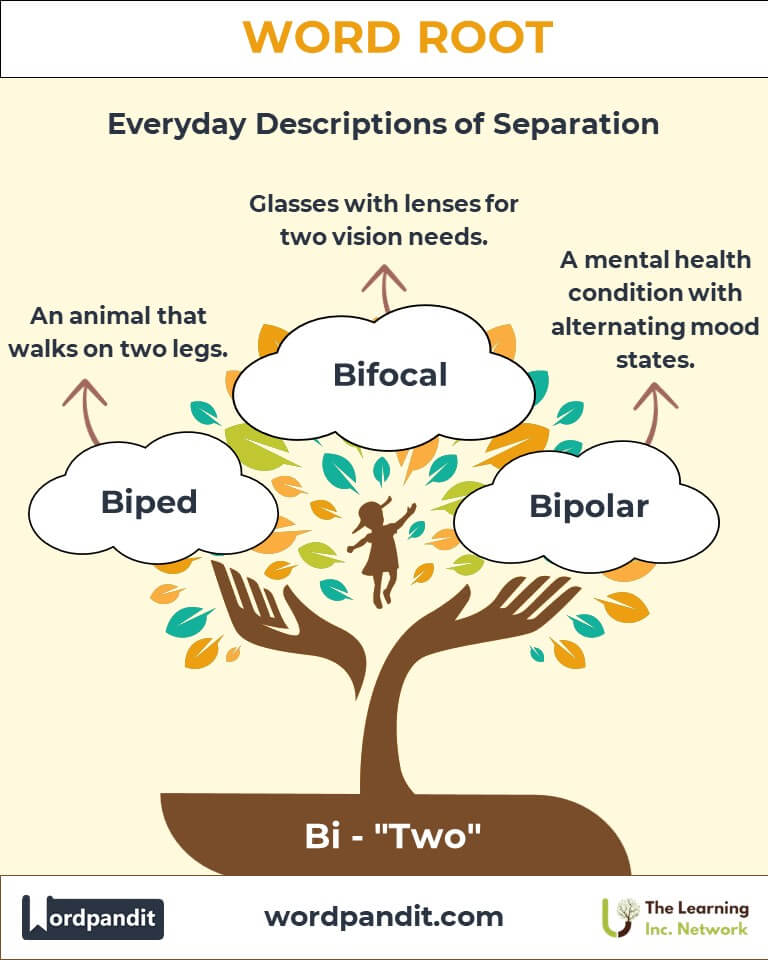
- Biped (bye-ped): An animal that walks on two legs.
- Example: "Humans are classified as bipeds due to their upright posture."
- Bimonthly (bye-munth-lee): Occurring twice a month or every two months.
- Example: "The magazine is published bimonthly, with issues in January and July."
- Bifocal (bye-foh-kuhl): Glasses with lenses for two different vision needs.
- Example: "He used bifocals to read and see distant objects clearly."
Bi Through Time
- Bicornuate (Historical): Referring to a structure with two horns, such as a bicornuate uterus in anatomy.
- Bipartite (Medieval Law): Describing a division into two parts, commonly used in contracts and charters.
Bi in Specialized Fields
- Biology:
- Bilateral Symmetry: Describes organisms with symmetrical body halves, like humans and butterflies.
- Significance: A key evolutionary trait for mobility and functionality.
- Technology:
- Binary System: The foundation of computing, representing data using two states (0 and 1).
- Impact: Powers digital technology, from smartphones to artificial intelligence.
- Medicine:
- Bipolar Disorder: A mental health condition characterized by alternating periods of mania and depression.
- Importance: Understanding "Bi" in this context aids in diagnosing and treating the disorder.
- Politics:
- Bipartisan Agreements: Collaboration between two political parties.
- Example: Promotes unity in policymaking.
Illustrative Story: Bi in Action
Lila, a tech-savvy teenager, discovered the power of "Bi" while coding her first app using binary logic. At the same time, her grandfather, a retired diplomat, shared tales of crafting bilateral treaties during his career. Together, they created an interactive game illustrating the harmony of dualities in logic and human relationships, showcasing the versatile power of "Bi."
Cultural Significance of the Bi Root
The root "Bi" transcends linguistic boundaries, symbolizing balance, unity, and cooperation. In Eastern philosophy, duality appears as yin and yang. In Western culture, "Bi" underpins binary oppositions, such as good vs. evil. Its presence in art, architecture, and philosophy highlights humanity's enduring fascination with pairs and symmetry.

The Bi Family Tree
- Di- (Greek: Two):
- Example: Dipole - A molecule with two opposite charges.
- Duo- (Latin: Two):
- Example: Duologue - A conversation between two characters.
- Ambi- (Latin: Both):
- Example: Ambidextrous - Able to use both hands equally well.
FAQs About the "Bi" Word Root
Q: What does "Bi" mean, and where does it come from?
A: "Bi" means "two" and originates from the Latin word bis, meaning "twice." This root is commonly used to signify duality, symmetry, or something composed of two parts.
Q: What is the significance of "Bi" in mathematics and science?
A: In mathematics, "Bi" appears in terms like binary, which refers to the base-2 number system used in computing (0s and 1s). In science, it is found in concepts like bilateral symmetry, which describes organisms with two identical sides, such as humans and butterflies.
Q: How does "Bi" differ from "Di"?
A: Both "Bi" and "Di" mean "two," but "Bi" is derived from Latin, while "Di" comes from Greek. For example, bicycle (two wheels) uses "Bi," whereas dioxide (two oxygen atoms) uses "Di."
Q: What does "Bilateral" mean, and where is it used?
A: "Bilateral" means "involving two sides." It is used in various contexts, such as:
- Politics: A bilateral agreement is a treaty between two countries.
- Anatomy: Humans have bilateral symmetry, with left and right sides mirroring each other.
Q: Why does "Bimonthly" have two meanings?
A: The term "bimonthly" can mean "once every two months" or "twice a month," creating ambiguity. To clarify, some prefer using "semi-monthly" for "twice a month" and "bimonthly" strictly for "every two months."
Q: What role does "Bi" play in biology?
A: "Bi" is essential in biology to describe paired or dual structures, such as:
- Biped: Animals that walk on two legs.
- Bilateral symmetry: Organisms with identical left and right sides.
Q: What is the practical application of the binary system?
A: The binary system, based on two digits (0 and 1), is foundational to modern computing. It encodes data, powers algorithms, and enables everything from simple calculations to advanced AI systems.
Q: What does "Bifocal" mean, and who uses it?
A: "Bifocal" refers to glasses with lenses designed for two vision needs, such as correcting both nearsightedness and farsightedness. These are commonly used by individuals with presbyopia, a condition that affects close-up vision with age.
Test Your Knowledge: Bi Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "Bi" mean?
2. Which term describes an animal that walks on two legs?
3. What is bilateral symmetry?
4. What is the binary system used in?
5. What does "Bifocal" refer to?
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Bi
The root "Bi" continues to shape language, science, and culture, symbolizing duality, balance, and connection. From the technological marvel of binary code to the biological elegance of bilateral symmetry, its influence spans disciplines. As we uncover new dualities in our evolving world, "Bi" remains a testament to the power of two.












